Some form of validation is required in every application to help the user insert the correct data. Applications created with Code On Time app generator offer validation in the form of business rules.
Let’s add validation business rules the Employees controller of our sample Northwind app.
Open the Project Designer. In the Solution Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab, right-click on Employees / Business Rules node, and press New Business Rule.
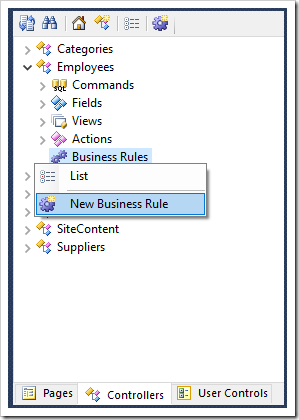
Specify the following:
| Property | Value |
| Type | JavaScript |
| Command Name | Insert |
| Phase | Before |
| Script | if ($row.LastName == 'Smith') {
this.preventDefault();
$row.LastName = null;
}
|
The above script will run when the user presses Save. It will check if the user has specified a Last Name of “Smith” – if so, it will cancel the save operation and clear the field.
Save the new business rule. On the toolbar, press Browse to run the app. Navigate to the Employees page and create a new record.
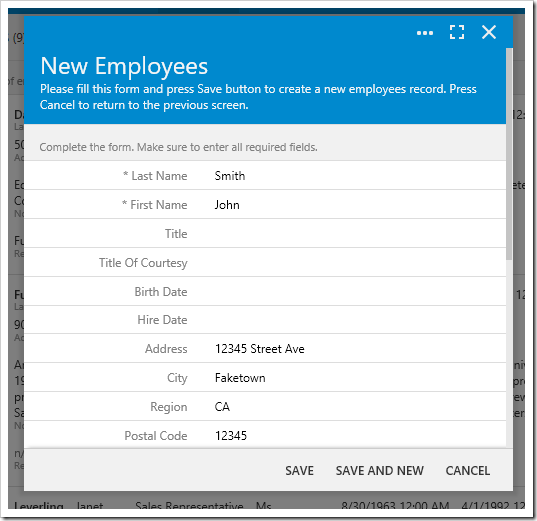
Enter values for the employee and press Save. The save operation will not be executed, and the Last Name field will be cleared.
Our business rule does ensure the user does not enter an incorrect value, but it does not make it clear to the user what is going on. We will want to add some feedback in the form of a message box to help the user understand.
Change the business rule as shown below:
if ($row.LastName == 'Smith') {
this.preventDefault();
// show message box
$app.alert('Last Name "Smith" is not allowed.').done(function () {
// update field value to null
$app.input.execute({
values: [
{ name: 'LastName', value: null }
]
});
// focus on the field
$app.input.focus({ fieldName: 'LastName' });
});
}
Our updated business rule has a few changes. Notice that the $app.alert function is used to display a message to the user. However, this alert will show a different form and change the current context. Attempting to update the field LastName after an alert is displayed will attempt to update a LastName field inside the alert form – which does not exist. Therefore, a done handler will need to be added to the $app.alert method call in order to execute code after the user closes the alert.
One more point to notice is that the $row variable is only in scope during the execution of the business rule. The asynchronous code in the done handler is executed when $row is out of scope. Therefore, it is necessary to use the $app.input.execute API to update the field values when the user returns to the Employees create form. The execute method accepts an object with the property values that contains a list of key value pairs. The $app.input.focus API is called in order to focus on a field called LastName as well.
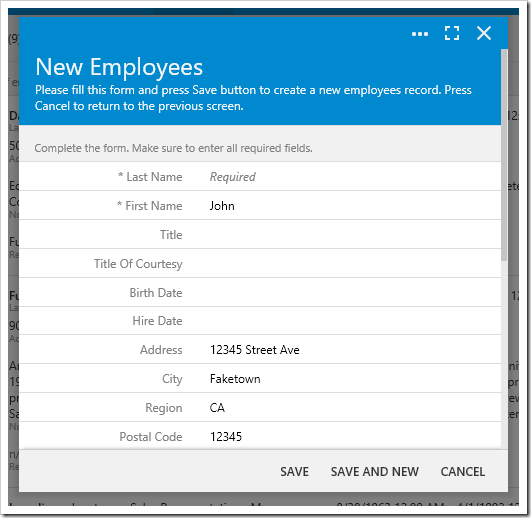
Save the business rule and regenerate the project. Create a new employee with the last name of “Smith” and attempt to save. Notice that a message box now notifies the user that the last name is not allowed.
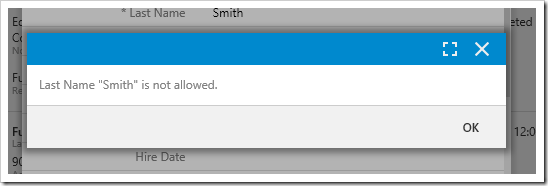
Press OK to close the message box. The Last Name field has been cleared and is currently focused.
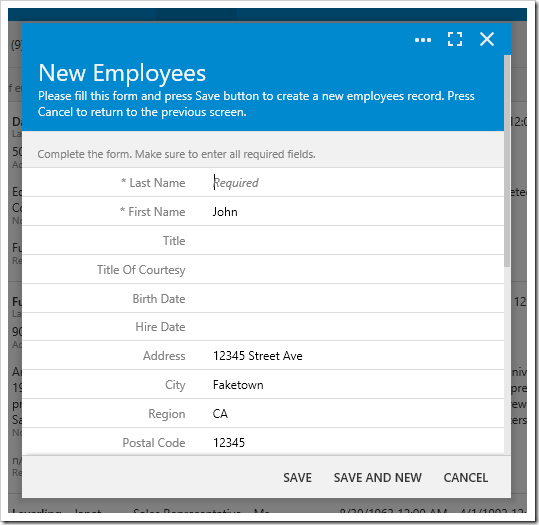
There are other ways of displaying a message to the user without interrupting the workflow. Let’s try the following:
if ($row.LastName == 'Smith') {
this.preventDefault();
$row.LastName = null;
// focus and show message next to field
this.result.focus('LastName', 'Last Name "Smith" is not allowed.');
}
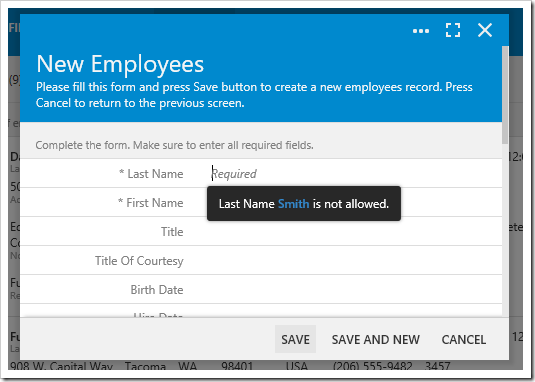
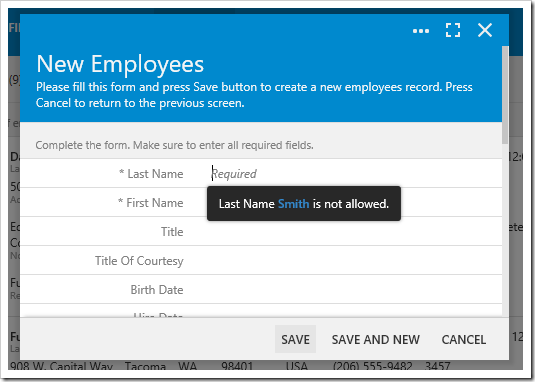
The example above will clear the field, and use the result.focus() method to focus on the field, and display a message next to the input. The result can be seen below.
Another technique is to use the notification API to display a transient message to the user at the bottom of the screen.
if ($row.LastName == 'Smith') {
this.preventDefault();
$row.LastName = null;
this.result.focus('LastName');
$app.touch.notify('Last Name "Smith" is not allowed.');
}
The result can be seen below:
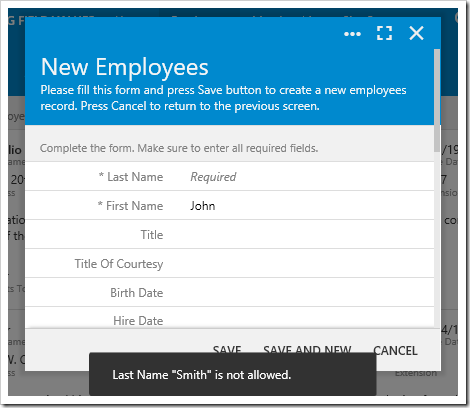
The notification will disappear after a default of 2 seconds.