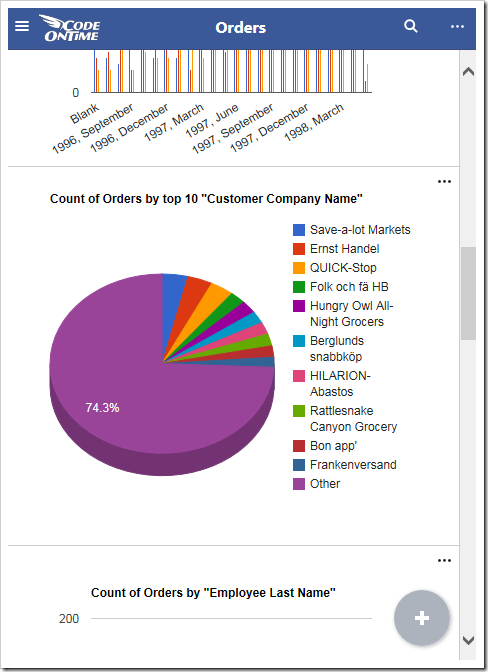
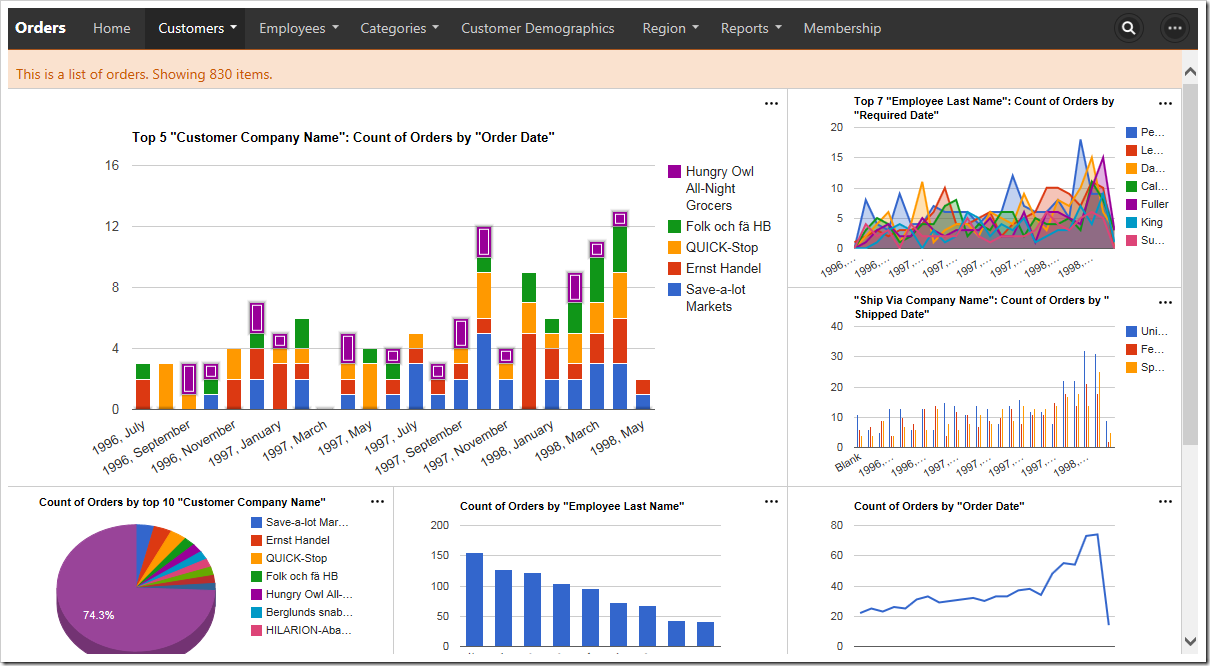
Every Code On Time web app comes with multiple ways of displaying your data. One way to visualize your data is with charts. See an example of charts on the Orders page of Northwind sample below.
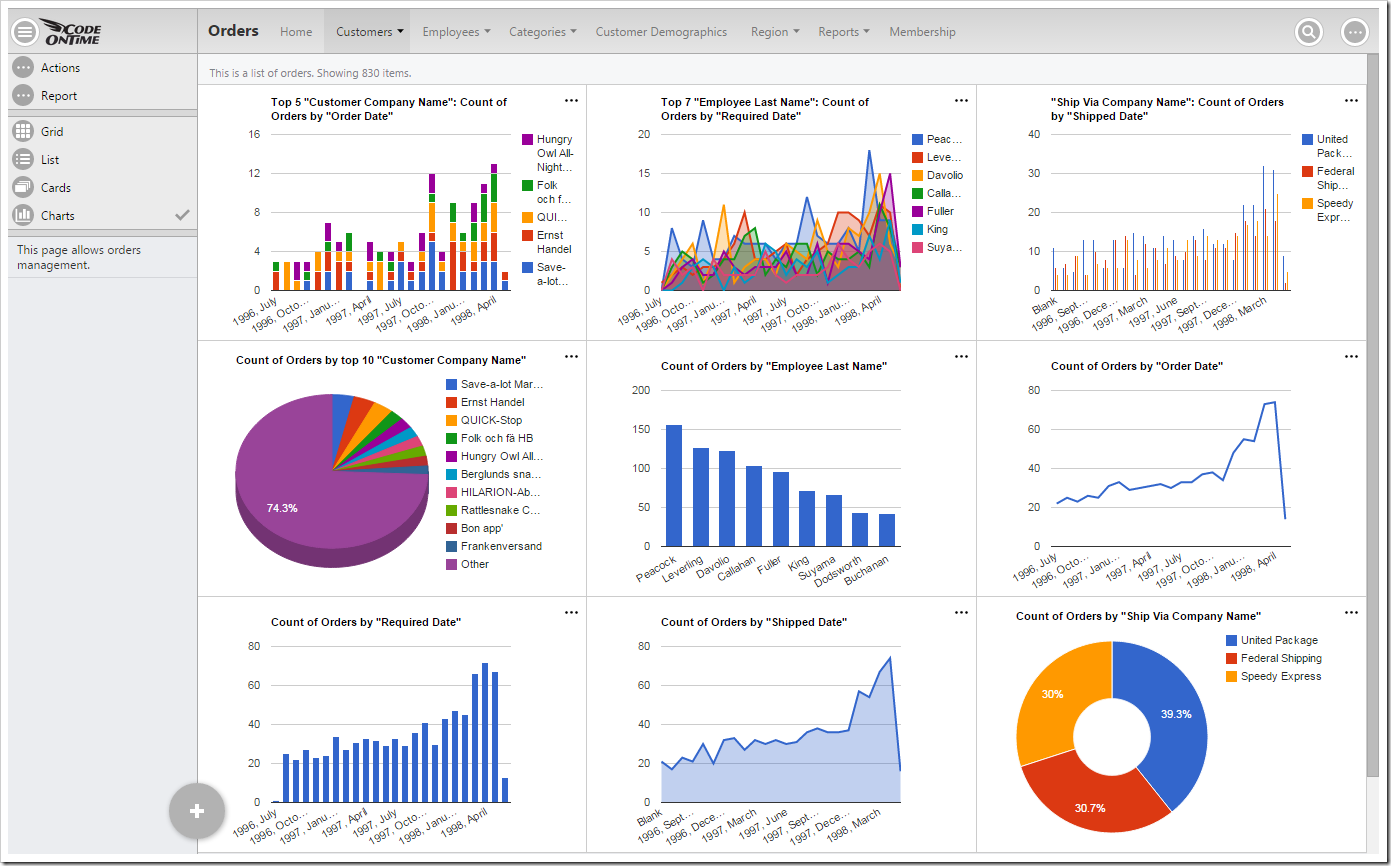
When a user activates the Charts presentation style, any developer-defined charts will be displayed. If none have been defined, then the application will automatically construct charts based on the data fields present in that view.
Activating Charts Presentation
Charts can be activated by clicking on the “Charts” presentation style option in the sidebar on the left hand side of the screen.
If the device you are using is narrow or the sidebar has been disabled, you can click on the context menu button “…” in the top right corner of the screen to bring up the context menu.
Then, click on the name of the view to bring up view options.
Select the “Charts” data presentation style, and the view will refresh and display charts to the user.
Responsive Design
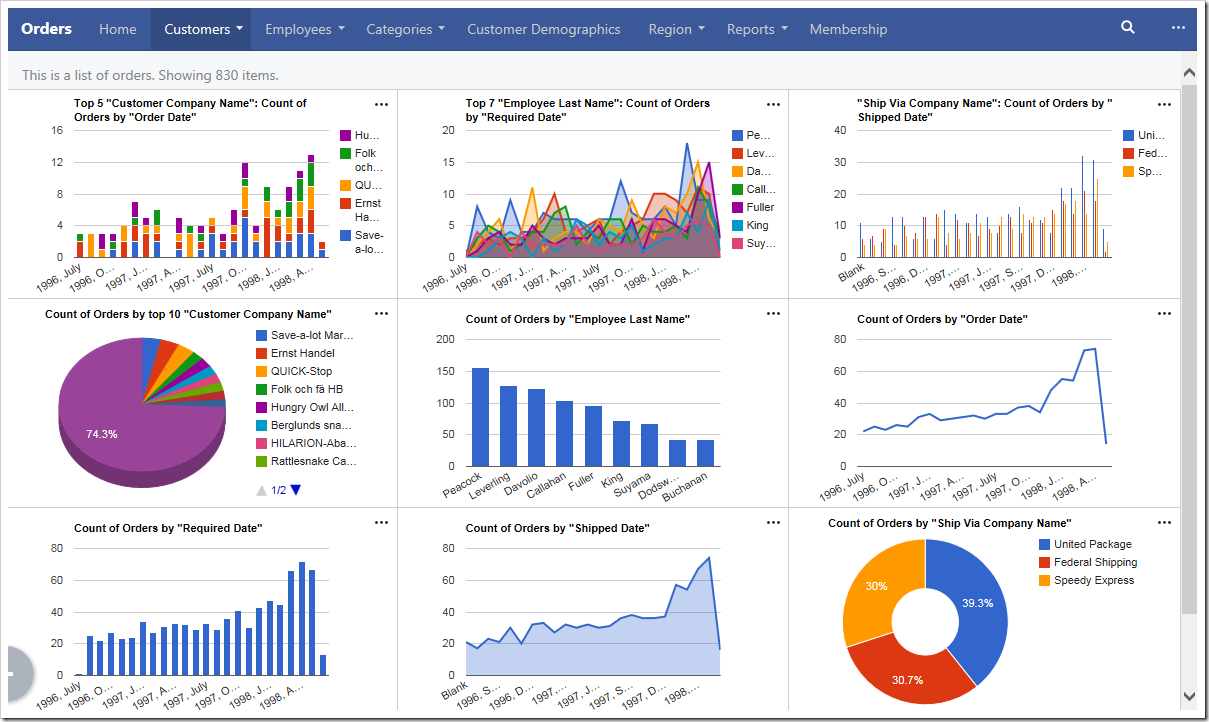
Charts offer a responsive design that will scale to fit any device, regardless of the device’s screen size. You can get a comprehensive snapshot of your data from your phone, tablet, or desktop computer. The largest screen sizes will display three columns of charts.
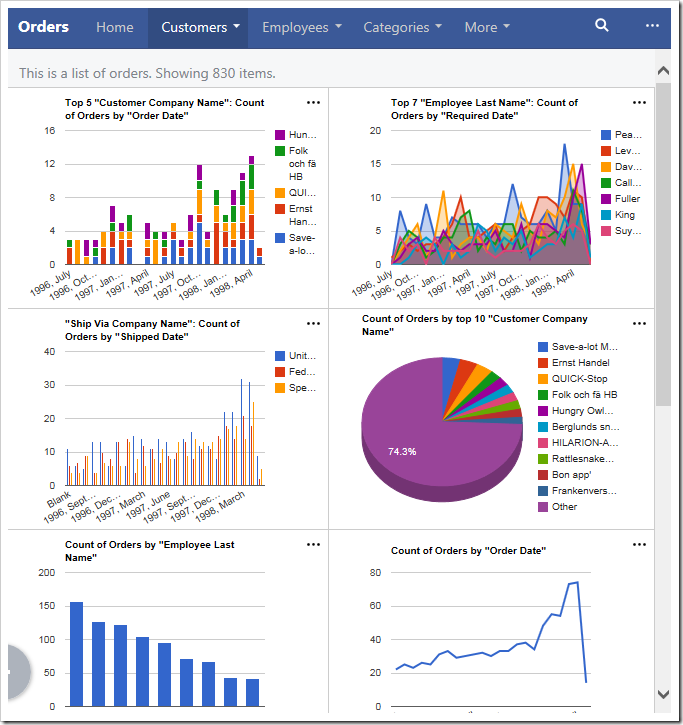
If the window is shrunk to a moderate size or the device is a tablet, two columns of charts will be shown instead.
Smaller devices will display one chart at a time.
If the device or window has a short height (or if your phone is rotated horizontally), then the charts will be shrunk vertically in order to fit at least one chart at a time on the screen.
Sizing Charts
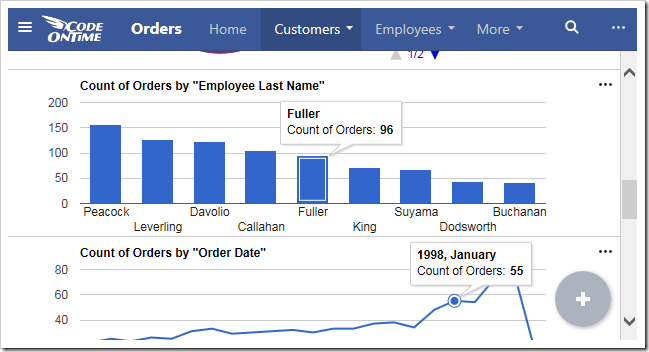
Charts can also be individually resized. Each chart is set to “Small” by default. This will render three columns on large screens, two columns on medium screens, and one column on small screens. If only one chart is present for the view, then that chart will always be maximum size available for the device.
The user can change the size of each chart by clicking on the three dot context menu “…” in the top right corner of the chart. Large devices will have access to “Small”, “Medium” and “Large” sizes.
Select “Large” to display a chart at full width and height of the screen. “Large” charts will scale down to “Medium” size on moderately sized devices, and to “Small” if the device cannot fit medium charts.
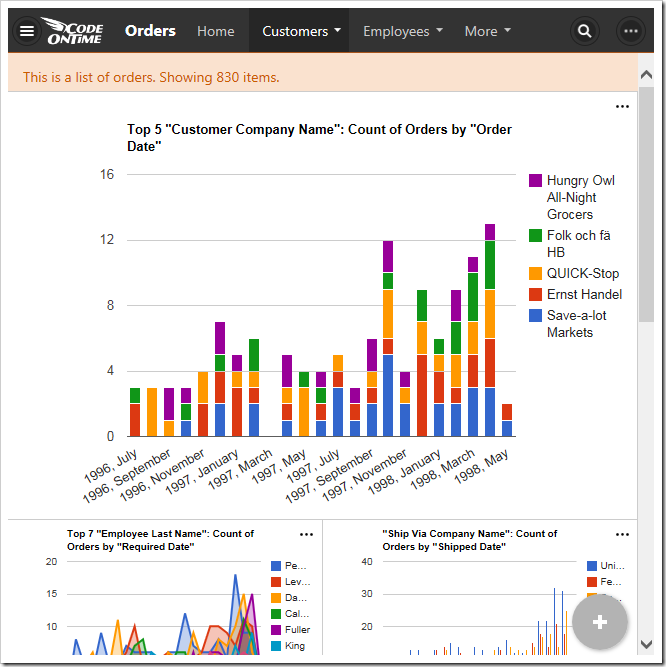
“Medium” chart size uses two thirds of the width and height a large screen, leaving space for one small chart in each dimension.
Medium charts on a medium size device will take the full width and two thirds of the height, leaving room for one chart above or below.
Default chart sizes can also be specified by the developer at design time.
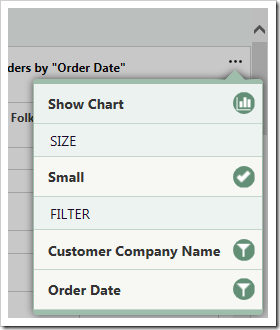
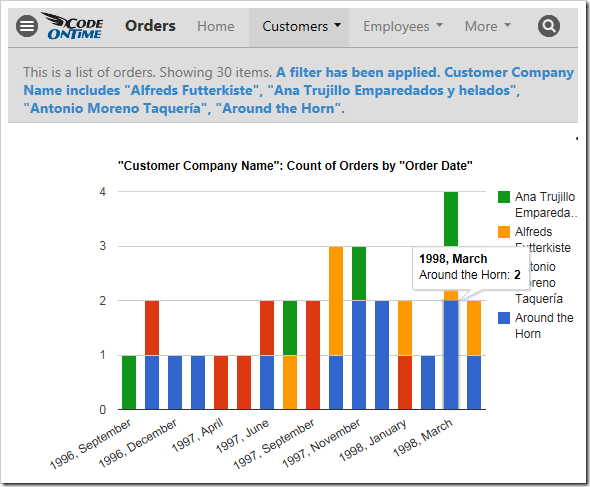
Filtering with Charts
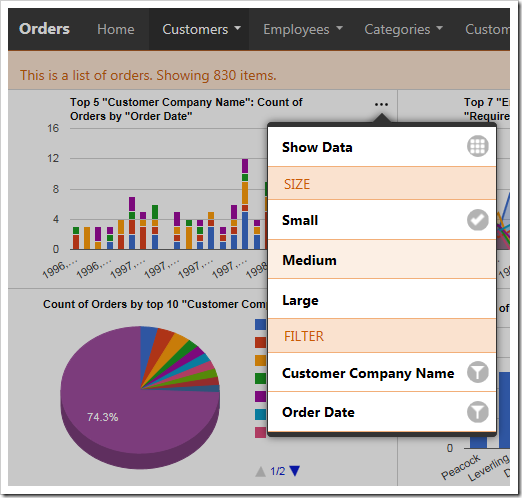
Any filters applied to the data view will be used by the charts. Quick filter options are available for the relevant fields in the context menu of each chart.
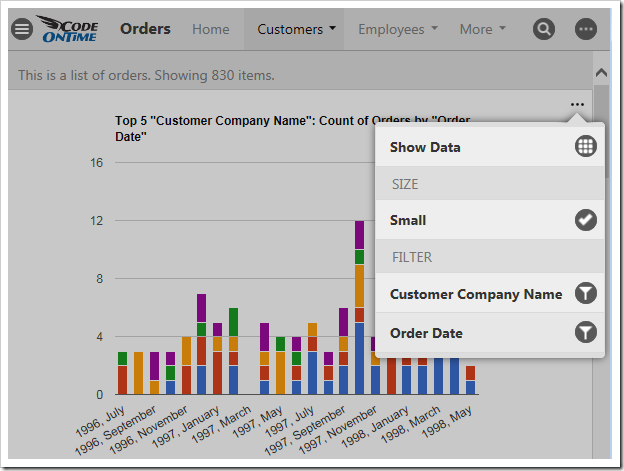
Clicking on the name of a field will open the filter panel for that field.
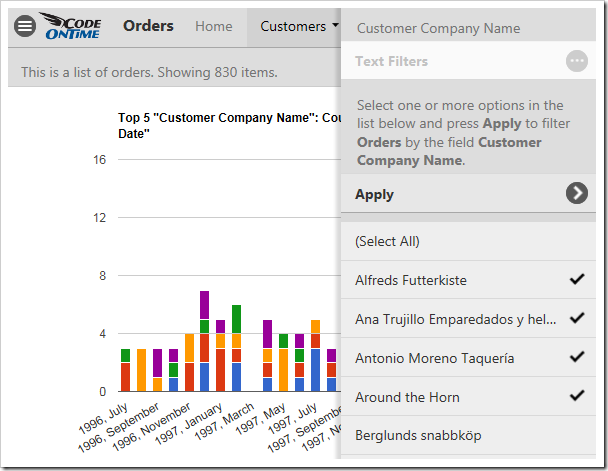
Select several options from the panel and press “Apply” to filter. The charts will refresh with the new, filtered data.
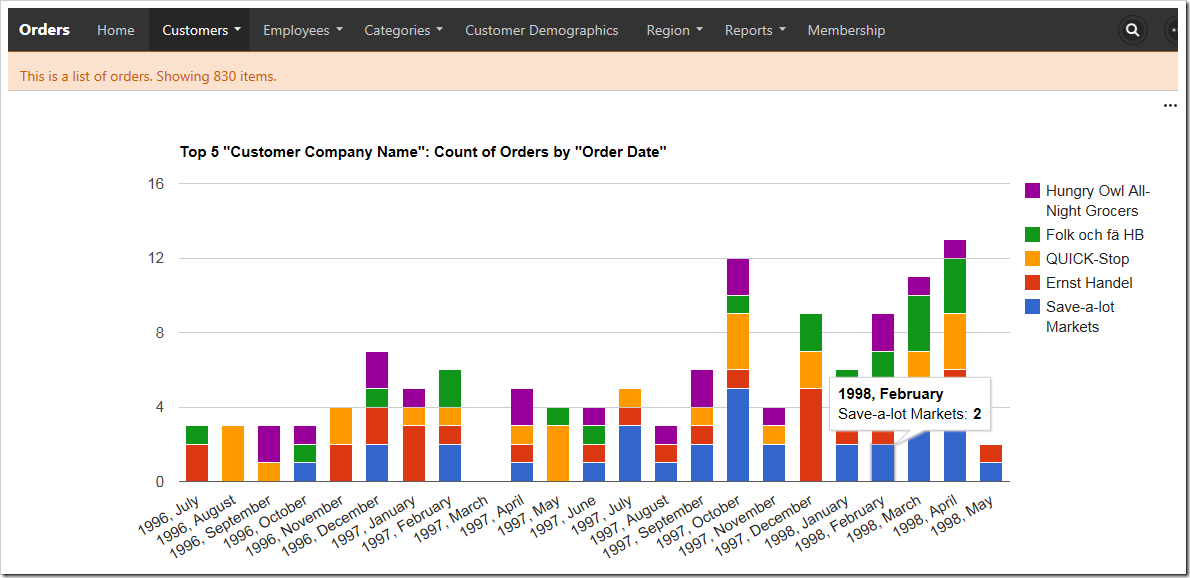
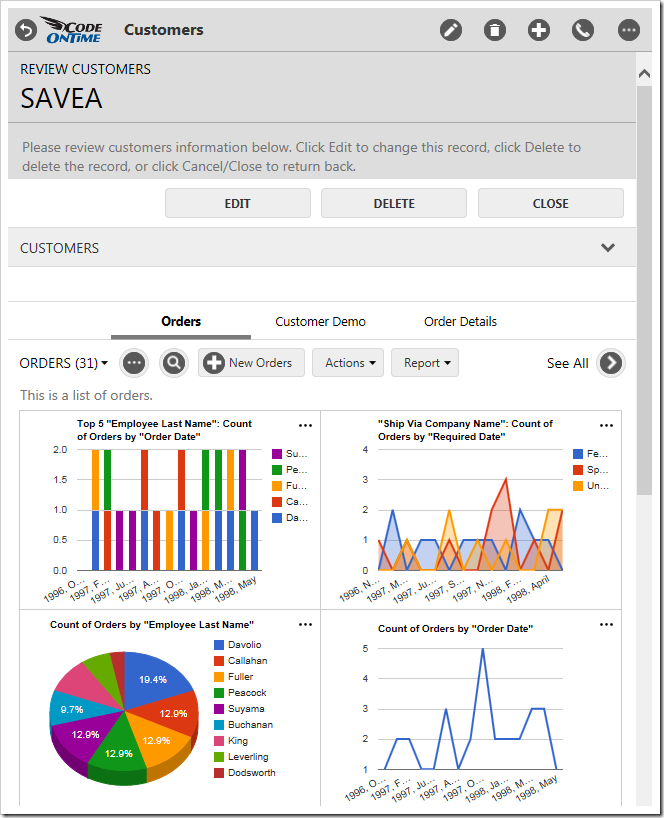
Child data views also derive the filter from the selected master record. The screen below shows charts giving insight to the orders from the customer “Save-a-lot Market” – Davolio seems to be the preferred employee.
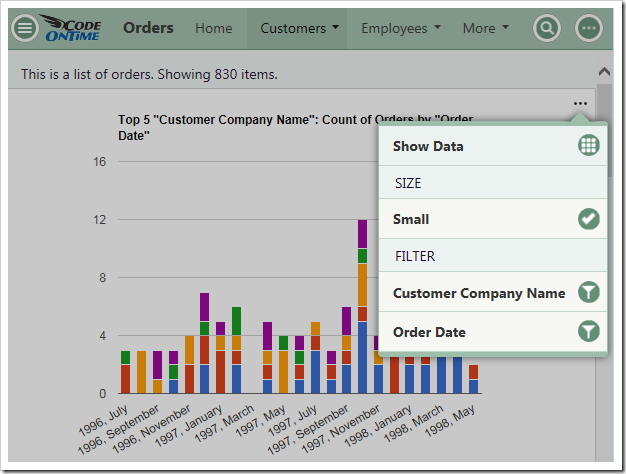
Viewing the Data Behind the Chart
Users also have the option to view the pivoted data that the chart is based on in a table. Click on the three dot context menu “…” in the top right corner of a chart. Select “Show Data” option.
The chart will be replaced by a table that shows the data. A miniature chart preview will be shown in the top left corner.
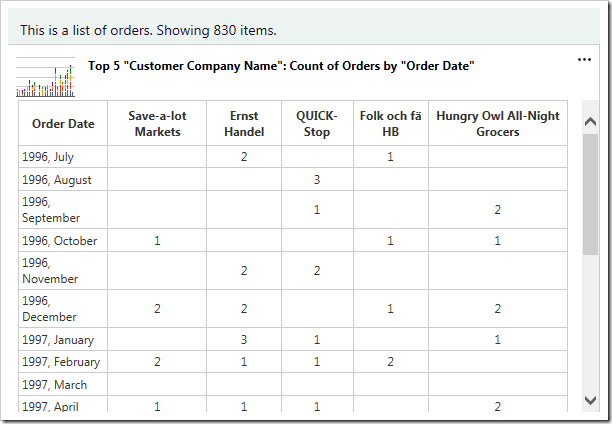
Clicking on the mini chart in the top left hand corner will restore the chart. The user can also use the “Show Chart” option in the context menu.