Web applications created with Code On Time include default reporting actions when reporting has been enabled.
When a user activates a Report action, the application framework will transform the relevant data controller XML file into a report definition file (RDLC) with the help of a default report template written in XSLT. The report definition and dataset with active filters and sort order will be passed to Microsoft Report Viewer. The Viewer will produce a report output in PDF, Excel (XLS), Image (TIFF), or Word (DOC) format.
The pictures below shows samples of default reports rendered in PDF and Word formats.
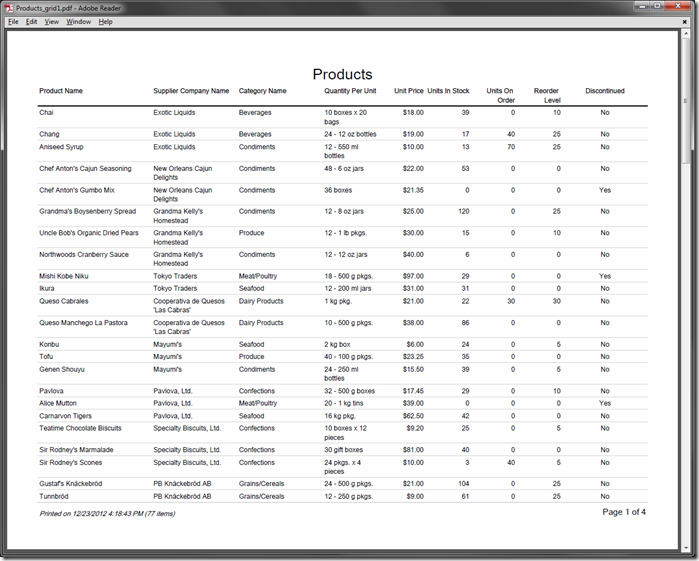
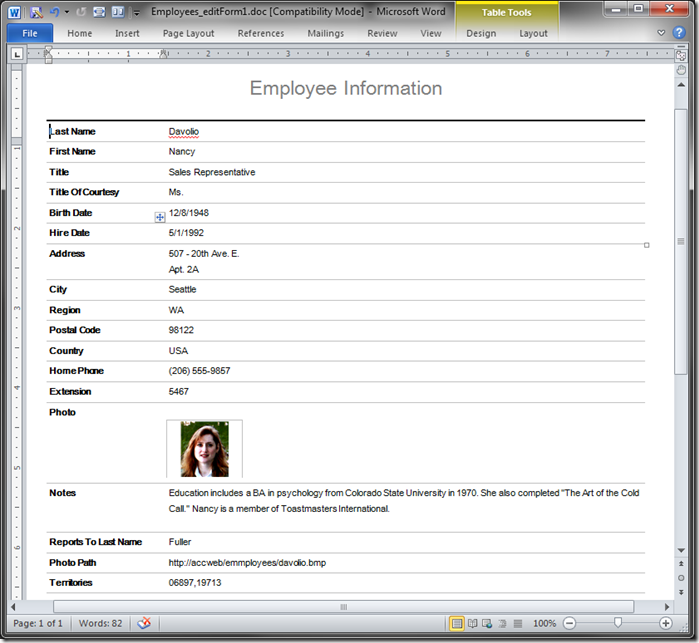
Several properties of the data controller view can alter automatic construction of the report definition file:
| Property | Description |
| Report Font | Changes the size of the font in the report. Options available are X-Large, Large, Medium, Small, X-Small. The default is “Medium”. |
| Report Label | Specifies the text displayed in the header of the report. |
| Report Orientation | Manually specifies the orientation of the page. By default, reports with more than seven fields will be rendered in landscape mode. Otherwise, the report will be portrait. |
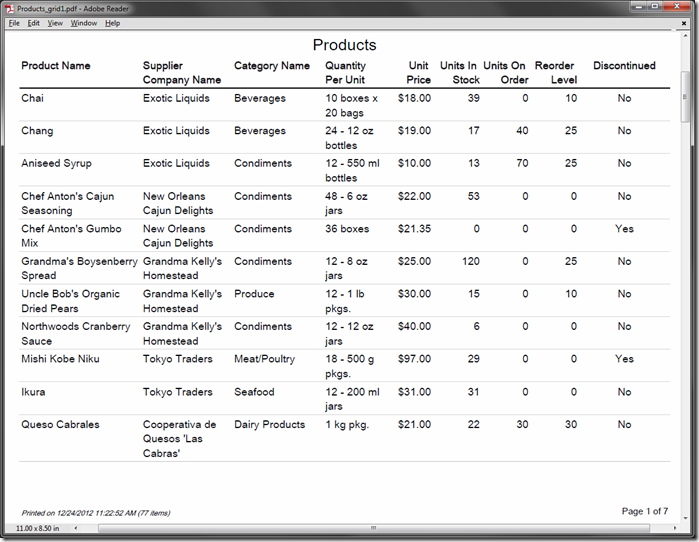
For example, the next picture uses a Report Font of “X-Large”.
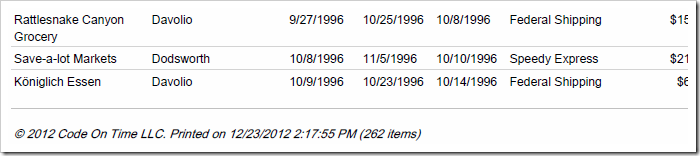
The default XSLT report template can be customized in order to change the automatically constructed report definition files. When this template is changed, all reports will reflect the changes. For example, the picture below shows the modified footer element that now includes a copyright message.
When it is necessary to create a fully custom report beyond the available options, a custom report template may be created for the view. This will generate a report template at design-time. The RDLC file can be designed in Visual Studio.
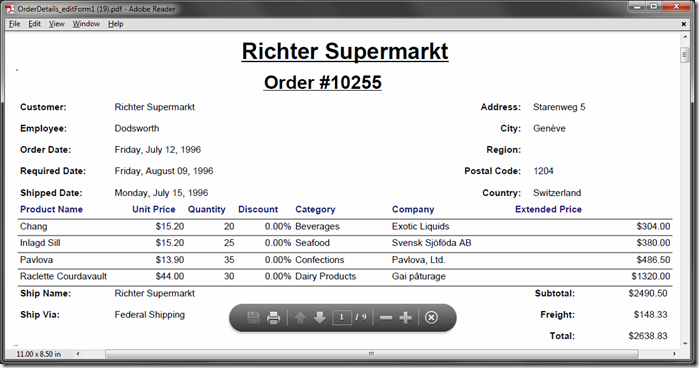
For example, the Order Form Sample shows how to create a custom Order Report. This report will group order details by customer, and then by order. It has multiple calculated fields, such as Extended Price, Subtotal, and Total.
Development of a custom report definition file involves either an extended field dictionary of a data controller, or a brand new data controller based on a database view. A dedicated report view must be defined to provide the field model for a custom report. The developer can remove the pre-configured elements from the custom report definition file or rearrange them in Visual Studio.
The simplest implementation of a master-detail report requires setting up a tablix element and placing master fields in the header and footer of the report. The report definition language offers rich field formatting capabilities supported in Visual Studio.
The last step is to configure a Report action in a data controller to activate the custom report.
A custom report may be implemented with multi-level grouping when data rows of multiple logical entities are included in the report data set. These reports can be activated from multiple data controllers with controller-specific filters.
The reporting actions may have a custom handler that will produce an arbitrary output. Custom parameters can be collected from the application user, data row selected on the client, or URL in the address bar of the browser. These parameters will be passed to the report handler.
A web application created with Code On Time can be integrated with third-party reporting solutions with the help of Navigate action. Another alternative is to configure a Hyperlink Format String for a data field in the view.