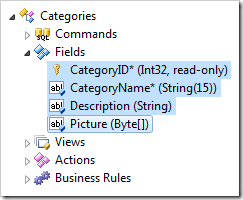
A field represents a column of a data row. There are physical and virtual fields. Virtual fields are not derived from a physical column of a data table – their values are computed at runtime. Bindings of fields to views are called data fields.
In the Project Explorer, fields are contained under the Fields node of a controller. If an asterisk (*) is present after the name of the field, the field is required. The field type and length are displayed in parentheses. Some fields fields may display “read-only” label.
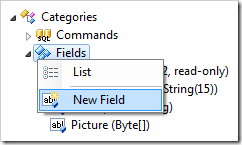
Creating a Field
A field can be created by using the New Field context menu option on the Fields node.
Moving Fields
Fields can be moved using drag and drop operations.
Dropping a field node onto another field node will place the field after the target field.
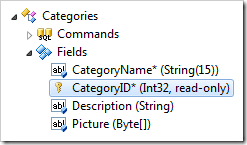
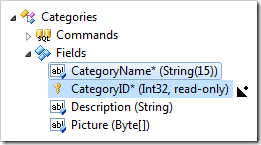
Dropping a field node on the right side of another field node will place it after the target field.
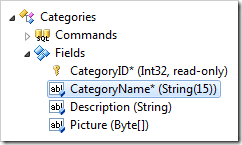
Dropping a field node on the left side of another field node will place it before the target field.
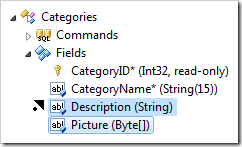
Fields can be copied to a different controller by dragging onto the controller or Fields node. The original field will not be deleted.
Creating Data Fields
When fields are dropped onto a view or category, they will be instantiated as data fields in the target view. When the field is dropped onto a form view, the data fields will be appended to the last category.
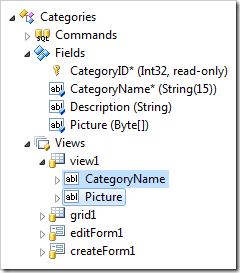
Cloning a Field
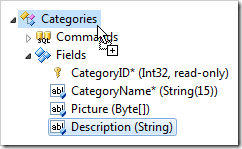
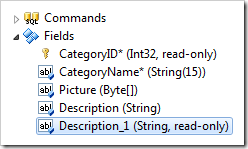
A field can be copied by dropping onto the controller or Fields node while holding Ctrl key. The name of the clone will be appended with a number, and the new field will be configured as a calculated field that reflects the physical column in the database. Use context menu option Copy on the field and use Paste on the controller or Fields node to create a clone.
Create Standard Validator and Converter
Validation and conversion business rules can be quickly created using the Add Validator and Add Converter context menu options. Code, SQL, and JavaScript options are available.
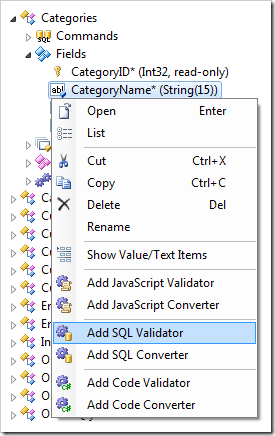
When an option is selected, the field is configured as calculated, and a business rule will be created.
Deleting a Field
Fields can be deleted using the context menu option Delete. This will also remove all data fields, items, and field outputs.