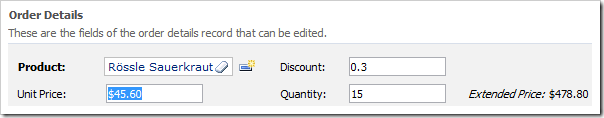
The picture below shows the Order Details form in edit mode.
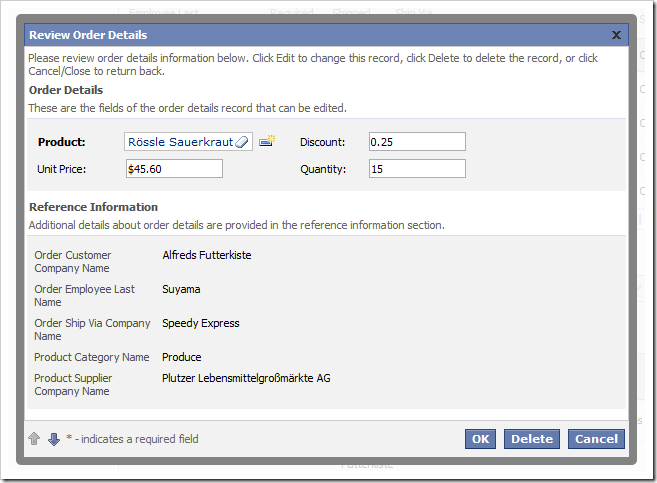
Let’s create a calculated field called Extended Price that will display the extended price of the Order Details item.
Calculated fields are also known as virtual fields. The field value is not stored in the database - it is calculated at runtime based on values of other fields in the data row.
Creating the virtual Field
Activate the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab. Right-click on OrderDetails / Fields node, and press New Field.
Assign the following values:
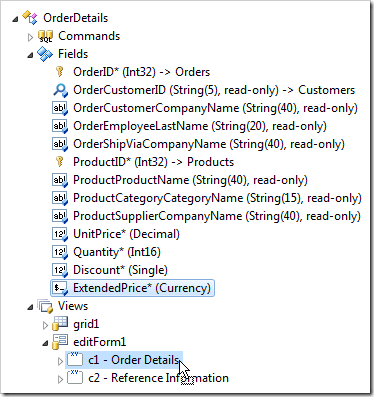
Press OK to save. Drag OrderDetails / Fields / ExtendedPrice node onto OrderDetails / Views / grid1 node to bind the field to the view grid1.
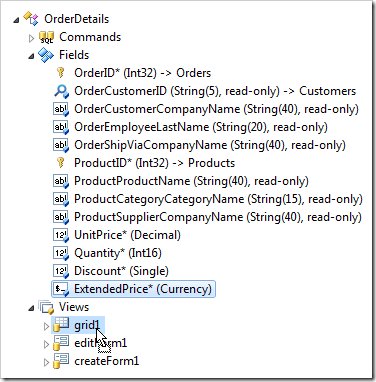
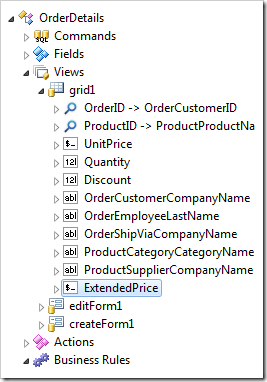
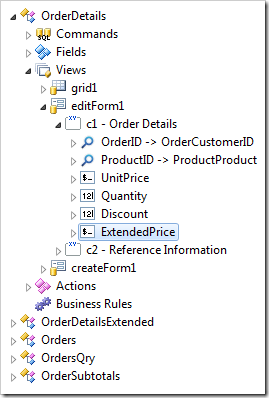
Drag OrderDetails / Fields / ExtendedPrice node onto OrderDetails / Views / editForm1 / c1 – Order Details node to bind the field to view editForm1.
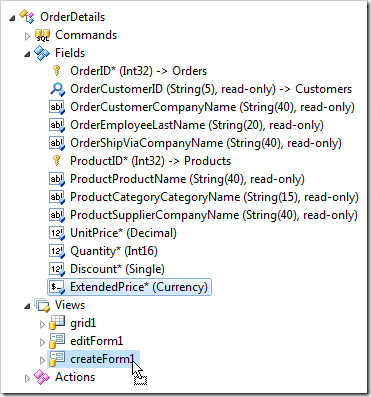
Finally, drag OrderDetails / Fields / ExtendedPrice node onto OrderDetails / Views / createForm1 node.
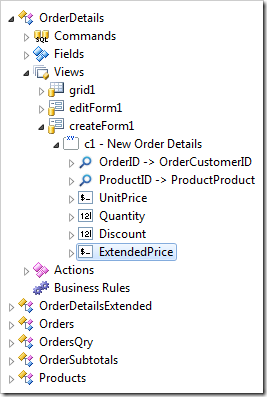
A binding of field to a view is called a data field.
On the toolbar, press Browse and navigate to the Order Manager page. The Extended Price data field is visible in the grid and in the form views of Order Details. However, the field is rendered as blank.
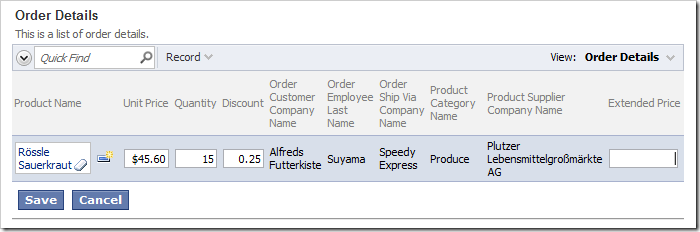
Note that if you have a custom category template associated with the form view, then the field will not be visible automatically. In that case, the custom category template for editForm1 needs to be updated to display the data field.
Read the next section to learn how to include the new virtual data field in the template, or skip to the following section discussing how to provide an SQL Formula for the field.
Updating the Custom Category Template
Switch to the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Pages tab. Right-click on Order Manager / c103 / control1 node and press Edit in Visual Studio.
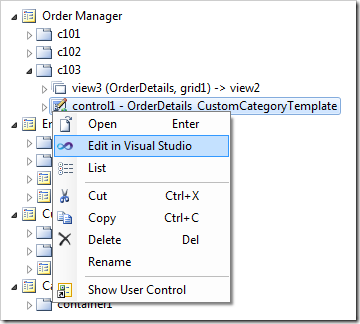
The template file will be opened in Visual Studio. Replace the existing code after the <%@ Control %> element with the following:
<div style="display: none;">
<div id="OrderDetails_editForm1_c1">
<table>
<tr>
<td style="padding-right: 36px;font-weight:bold;">Product:</td>
<td style="padding-right: 18px;">
<span class="FieldPlaceholder DataOnly">{ProductID}</span>
</td>
<td style="padding-right: 18px;">Discount:</td>
<td>
<span class="FieldPlaceholder DataOnly">{Discount}</span>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Unit Price:</td>
<td>
<span class="FieldPlaceholder DataOnly">{UnitPrice}</span>
</td>
<td>Quantity:</td>
<td>
<span class="FieldPlaceholder DataOnly">{Quantity}</span>
</td>
<td style="padding-left:18px;"><i>Extended Price:</i></td>
<td>
<span class="FieldPlaceholder DataOnly">{ExtendedPrice}</span>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</div>
Save the file, and refresh the webpage. The Extended Price data field will be displayed in edit form.
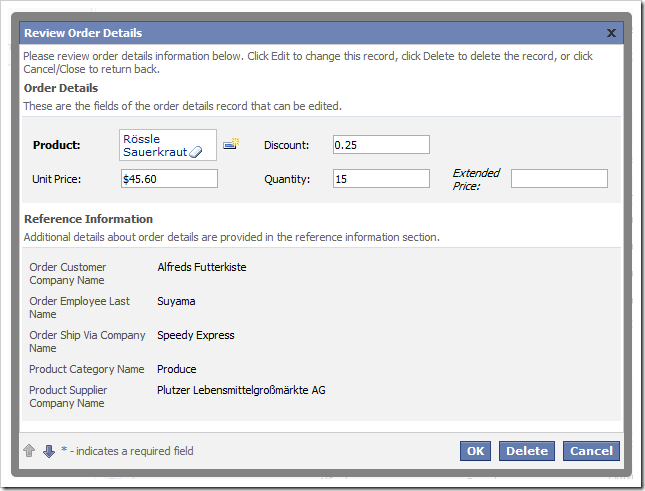
SQL Formula
Let’s provide an SQL expression evaluated when the data rows of order details are selected from the database.
In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab and double-click on OrderDetails / Fields / ExtendedPrice node.
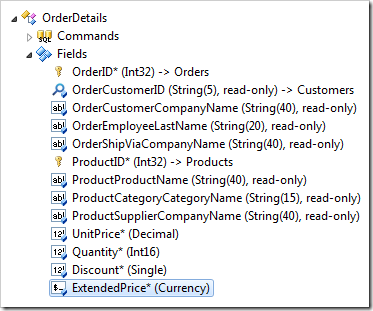
Change the following:
| Property |
New Value |
| The value of this field is computed at run-time by SQL expression. |
true |
| SQL Formula |
OrderDetails.UnitPrice * OrderDetails.Quantity * (1 - OrderDetails.Discount)
|
| Values of this field cannot be edited |
true |
| Data Format String |
c |
Press OK to save the field. On the toolbar, press Browse. The Extended Price field will not be editable, and the value will be presented when the form is rendered.
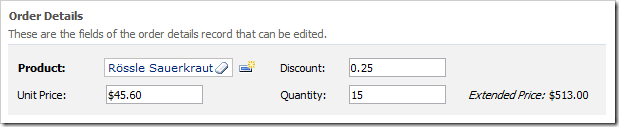
SQL Formula provides the highest possible performance for the calculation since it is being evaluated by the database engine. The complexity of calculated fields depends on the capabilities of the database engine. There are numerous built-in functions that the developer can take advantage of.
Fields based on SQL Formula can be sorted and filtered with the highest possible performance as well.
Calculating Field Values Just-in-Time
Extended Price is not recalculated when a user changes values of Unit Price, Discount, or Quantity fields.
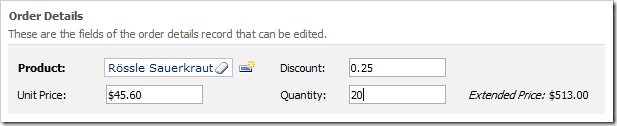
The SQL Formula of the Extended Price field is evaluated only when the data is selected from the database. If the user makes changes in the browser window, the values will not be submitted to the server until the record is saved. Developers can implement a server-side or client-side calculation that will be performed just-in-time as users change the values of the formula’s base fields.
The application framework includes a business rule engine that allows implementing rules in SQL, C#/Visual Basic, or JavaScript.
SQL and C#/Visual Basic business rules require a round-trip between the web browser and the web server. They can look up database information and interact with external systems when necessary.
JavaScript business rules are executed in the browser and provide the highest possible performance when server-side data is not required for calculation.
Let’s consider implementing the calculation using all three flavors of business rules. Note that the developer needs only one of them to accomplish just-in-time calculation of Extended Price.
SQL Business Rule
In the Project Explorer, double-click on OrderDetails / Fields / ExtendedPrice node.
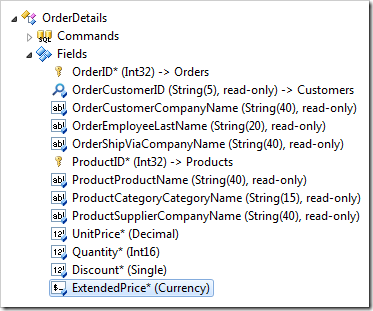
Make the following changes:
| Property |
New Value |
| The value of this field is calculated by a business rule expression. |
true |
| Context Fields |
UnitPrice,Quantity,Discount |
Press OK to save. Right-click on OrderDetails / Business Rules node, and press New Business Rule.
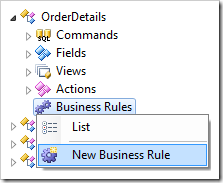
Assign these values:
| Property |
Value |
| Type |
SQL |
| Command Name |
Calculate |
| Phase |
Execute |
| Script |
set @ExtendedPrice = @UnitPrice * @Quantity * (1 - @Discount)
|
Press OK to save. On the toolbar, press Browse. Select and start editing an Order Details record.
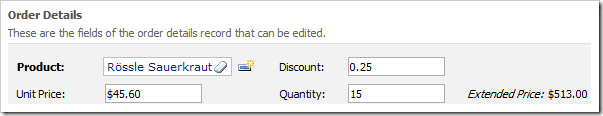
Change the value in Quantity field. Press Enter or shift the focus to a different field. The Extended Price will be updated.
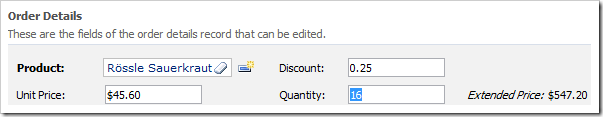
The client library executes Calculate action, which causes transfer of field values to the server. The application framework will pass the business rule script along with the parameter values to the database engine for execution. Then, it evaluates parameters and returns changed values to the client web browser.
SQL business rules involve client, application server, and database engine tiers. The advantage of SQL business rules is the ability to access any database information when necessary.
Code Business Rule
The business rule can also be implemented using C# or Visual Basic.
If you have the SQL business rule created in the previous section, then you will need to delete or rename the business rule. Double-click on OrderDetails / Business Rules / Calculate node.
Change the Command Name property:
| Property |
Value |
| Command Name |
DoNotRun |
Press OK to save. Alternatively, business rule r100 can be deleted.
Right-click on OrderDetails / Business Rules node, and press New Business Rule.
Assign these values:
| Property |
Value |
| Type |
C# / Visual Basic |
| Command Name |
Calculate |
| Phase |
Execute |
Press OK to save.
Code business rule files do not exist until the application generator has created them. On Project Designer toolbar, press Browse.
When complete, right-click OrderDetails / Business Rules / Calculate business rule node, and press Edit Rule in Visual Studio.
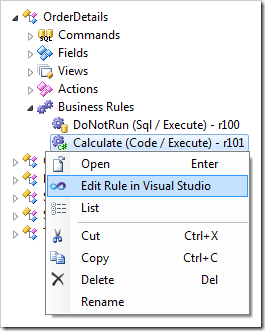
The file will be opened in Visual Studio. The entire class definition and parameters of the business rule method are already defined.
Replace the body of the rule with the call of UpdateFieldValue method:
C#:
using System;
using MyCompany.Data;
namespace MyCompany.Rules
{
public partial class OrderDetailsBusinessRules : MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
{
[Rule("r101")]
public void r101Implementation(int? orderID,
string orderCustomerID, string orderCustomerCompanyName,
string orderEmployeeLastName, string orderShipViaCompanyName,
int? productID, string productProductName, string productCategoryCategoryName,
string productSupplierCompanyName, decimal? unitPrice, short? quantity,
float? discount, decimal? extendedPrice)
{
UpdateFieldValue("ExtendedPrice",
Convert.ToDouble(unitPrice.Value) * quantity.Value * (1 - discount.Value));
}
}
}
Visual Basic:
Imports MyCompany.Data
Imports System
Namespace MyCompany.Rules
Partial Public Class OrderDetailsBusinessRules
Inherits MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
<Rule("r101")> _
Public Sub r101Implementation(
ByVal orderID As Nullable(Of Integer),
ByVal orderCustomerID As String,
ByVal orderCustomerCompanyName As String,
ByVal orderEmployeeLastName As String,
ByVal orderShipViaCompanyName As String,
ByVal productID As Nullable(Of Integer),
ByVal productProductName As String,
ByVal productCategoryCategoryName As String,
ByVal productSupplierCompanyName As String,
ByVal unitPrice As Nullable(Of Decimal),
ByVal quantity As Nullable(Of Short),
ByVal discount As Nullable(Of Single),
ByVal extendedPrice As Nullable(Of Decimal)
)
UpdateFieldValue("ExtendedPrice",
Convert.ToDouble(unitPrice.Value) * quantity.Value * (1 - discount.Value))
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Save the file, and refresh the webpage.
The same behavior as with the SQL business rule will be exhibited every time a context field is changed in the form. The client library will make a short trip to the web server to perform the calculation. The application framework will call the business rules class method which is linked to the business rule defined in OrderDetails data controller.
JavaScript Business Rule
If the values of the base fields are known on the client at the time when a calculation needs to be performed, then the web server round-trip is redundant. JavaScript business rules offer an option to implement complex logic executed by the web browser.
First, disable execution of the previously created C#/Visual Basic business rule. Double-click on OrderDetails / Business Rules / Calculate node.
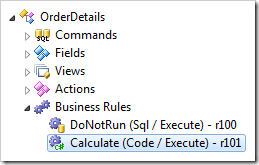
Change the Command Name property:
| Property |
Value |
| Command Name |
DoNotRun |
Press OK to save. Alternatively, business rule r101 can be deleted.
Right-click on OrderDetails / Business Rules node, and press New Business Rule.
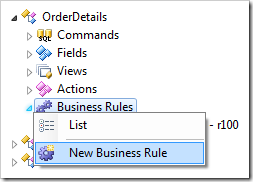
Assign these values:
| Property |
Value |
| Type |
JavaScript |
| Command Name |
Calculate |
| Phase |
Execute |
| Script |
[ExtendedPrice] = [UnitPrice] * [Quantity] * (1 - [Discount]);
this.preventDefault();
|
At runtime, the client library will automatically translate the script into the following JavaScript code:
this.updateFieldValue('ExtendedPrice',
this.selectFieldValue('UnitPrice') *
this.selectFieldValue('Quantity') *
(1 - this.selectFieldValue('Discount')));
this.preventDefault();
Press OK to save. On the toolbar, press Browse. Open the form view of an order detail.
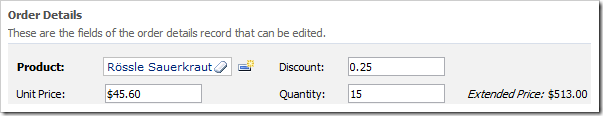
Change a value in one of the fields. Press Tab to shift focus away from the field. The Extended Price will automatically be updated without performing a server request.
The call of the method preventDefault() will prevent the client library from processing the Calculate action on the server.