It is a requirement for every database web application to perform data validation. SQL business rules can be used to extend the functionality of basic database validation to ensure that the user enters values that conform to business requirements.
Server-side validation has the benefit of direct access to database and sophisticated APIs of the server-side operating system and database engine. One major limitation is the inability to have a conversation with the user – the server-side code cannot ask questions of the user without complex chained internet callbacks. If the business rule implementation requires confirming certain aspects of validation by directly requesting information from the application user, then a validating JavaScript business rule must be implemented. If a “conversational” validation business logic requires access to the database, then consider utilizing the RESTful application server of your web app.
Consider the following example below. The default Northwind web application allows users to select a product and enter any unit price, quantity, and discount. The database engine will validate the constraints and raise an exception if an error occurs.
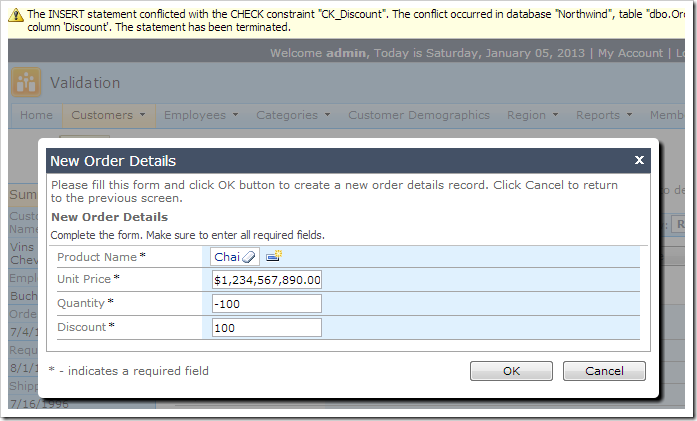
However, the database server will not test for logical violations, such as absurd unit price or quantity.
Let’s implement an SQL business rule that will perform multi-step validation.
Configuring Fields
Start the Project Designer. Switch to the Controllers tab in the Project Explorer. Double-click on OrderDetails / Fields / ProductID* (Int32) –> Products node.
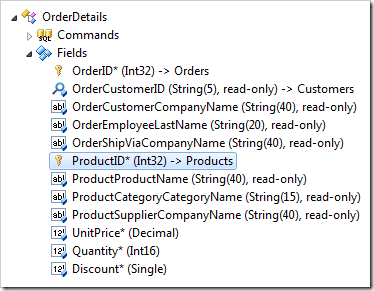
Change the following:
| Property | Value |
| Copy | UnitPrice=UnitPrice |
Press OK to save. Next, double-click on UnitPrice* (Decimal) field node.
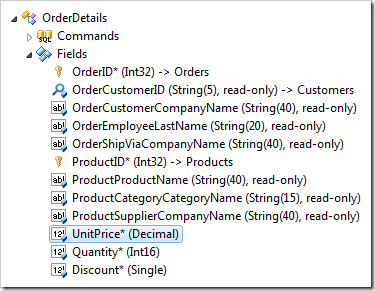
Make the following changes:
| Property | Value |
| The value of this field is calculated by a business rule expression. | true |
| Context Fields | ProductID, UnitPrice, Quantity, Discount |
Press OK to save.
Configuring Business Rule
Right-click on OrderDetails / Business Rules node, and press New Business Rule.
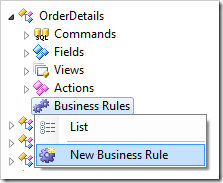
Assign the following values:
| Property | Value |
| Type | SQL |
| Command Name | Calculate|Insert|Update |
| Phase | Execute |
Paste in the following script:
-- 1. If the collected values are not valid then do not enforce the rule.
-- The client library will instruct the user to correct the input.
declare @Success nvarchar (5) = 'true'
-- 2. Reset the base price for calculation of price limits
-- if the product selection has changed or if an existing
-- data row has been selected for editing
if (@ProductID != @Session_ProductID or @Session_ProductID is null)
begin
declare @BasePrice decimal = @UnitPrice
if (@Arguments_Trigger != 'ProductID')
begin
set @BasePrice = @UnitPrice_OldValue
end
set @Session_UnitPrice = @BasePrice
set @Session_ProductID = @ProductID
if (@Arguments_Trigger = 'ProductID')
begin
set @Quantity = 1
set @Discount = 0
set @Result_Focus = 'Quantity'
end
end
-- 3. Adjusting base price for an existing record
declare @OriginalUnitPrice float = @Session_UnitPrice
if (@Session_UnitPrice is null)
begin
set @OriginalUnitPrice = @UnitPrice_OldValue
set @Session_UnitPrice = @OriginalUnitPrice
end
-- 4. Validate Unit Price Field
declare @MinPrice float = @OriginalUnitPrice
declare @MaxPrice float = (@OriginalUnitPrice * 1.05)
if (@UnitPrice is null)
set @Result_Focus = 'UnitPrice, Please enter the price.'
else
if (@UnitPrice < @MinPrice or @UnitPrice >= @MaxPrice)
set @Result_Focus = 'UnitPrice, The price must be between $'
+ cast(convert(money, @MinPrice) as nvarchar(50)) + ' and $'
+ cast(convert(money, @MaxPrice) as nvarchar(50)) + '.'
set @Success = 'false'
-- 5. Validate Quantity Field
if (@Quantity is not null and @Quantity <= 0)
begin
set @Result_Focus = 'Quantity, The quantity must be greater than zero.'
set @Success = 'false'
end
-- 6. Validate Discount Field
if (@Discount > 1)
set @Discount = (@Discount / 100)
-- 7. Confirm Discount is between 0.00 and 0.99
if (@Discount is not null and (@Discount < 0.00 or @Discount > 0.99))
begin
set @Result_Focus = 'Discount, The discount must be between 0.00 and 0.99 (0% - 99%).'
set @Success = 'false'
end
-- 8. Wrapping up
if (@Arguments_CommandName = 'Calculate' or @Success = 'false')
set @BusinessRules_PreventDefault = 1
The business rule will be fired when a user inserts a new record, updates an existing record, and every time a field value is changed. The client library will first ensure that the values are valid. Then the script will be sent to the database server. The field values are bound by the application framework as @FieldName. Session variables are introduced to the web application by using @Session_FieldName. The name of the field that triggered the command is recorded in @Arguments_Trigger, and the command is saved in @Arguments_Command. The client library is instructed to display messages next to fields using @Result_Focus. The parameter @BusinessRules_PreventDefault will prevent the default behavior of the web application from continuing.
There are eight distinct steps to this business rule:
1. Initial Input Validation
When a user enters an invalid value in the Order Details form, the client library will display an error and prevent execution of the business rule – no code needs to be written for this to occur.
The variable @Success is declared in order to remember the status of validation. By default, it is set to “true”. If any of the later steps fail to validate, this variable will be changed to “false” and the last step will ensure that the user cannot apply changes.
declare @Success nvarchar (5) = 'true'
The picture below shows an example of automatic client-side validation.
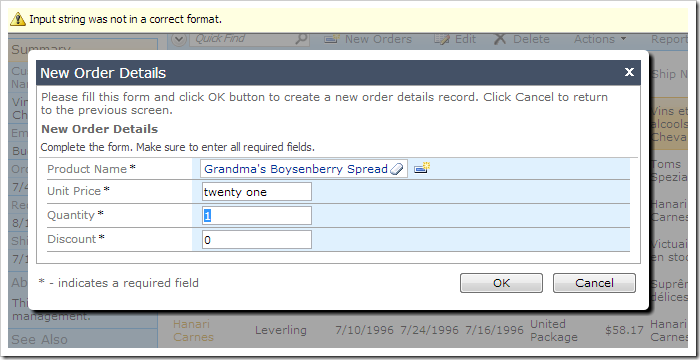
2. Determination of the “Base” Price
This query will memorize the last ProductID and UnitPrice values in session variables, as well as the UnitPrice of the selected product when it is copied over. This UnitPrice will be saved as @BasePrice, and will be used to prevent price inflation by more than 5%. When the ProductID is changed, the Quantity and Discount fields will be reset to default values of 1 and 0.
if (@ProductID != @Session_ProductID or @Session_ProductID is null)
begin
declare @BasePrice decimal = @UnitPrice
if (@Arguments_Trigger != 'ProductID')
begin
set @BasePrice = @UnitPrice_OldValue
end
set @Session_UnitPrice = @BasePrice
set @Session_ProductID = @ProductID
if (@Arguments_Trigger = 'ProductID')
begin
set @Quantity = 1
set @Discount = 0
set @Result_Focus = 'Quantity'
end
end
The screenshot below shows the form after the product has been changed.
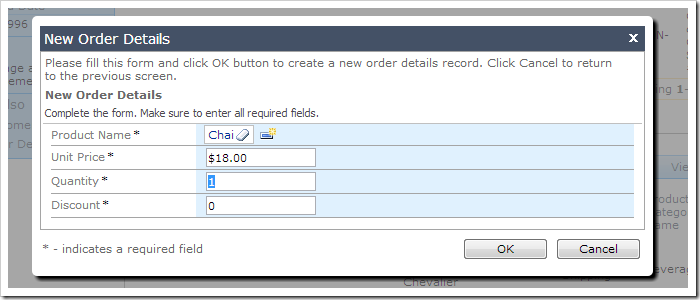
3. Adjusting Base Price for Existing Records
If the user is editing an existing record, then the original UnitPrice value is memorized using a session variable.
declare @OriginalUnitPrice float = @Session_UnitPrice
if (@Session_UnitPrice is null)
begin
set @OriginalUnitPrice = @UnitPrice_OldValue
set @Session_UnitPrice = @OriginalUnitPrice
end
4. Price Validation
The minimum and maximum price is calculated. If the price is blank, the user is directed to enter a value. If the price is out of range, the user is forced to correct the problem.
declare @MinPrice float = @OriginalUnitPrice
declare @MaxPrice float = (@OriginalUnitPrice * 1.05)
if (@UnitPrice is null)
set @Result_Focus = 'UnitPrice, Please enter the price.'
else
if (@UnitPrice < @MinPrice or @UnitPrice >= @MaxPrice)
set @Result_Focus = 'UnitPrice, The price must be between '
+ cast(@MinPrice as nvarchar(50)) + ' and '
+ cast(@MaxPrice as nvarchar(50)) + '.'
set @Success = 'false'
The form below shows price validation in action.
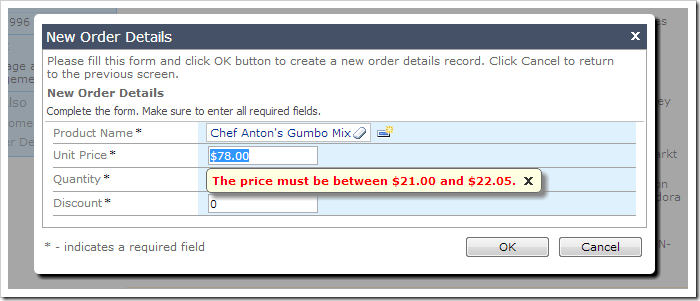
Here is validation in data sheet view.
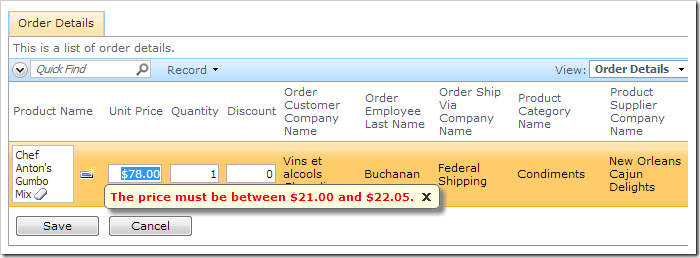
5. Quantity Validation
Validation will ensure that a positive value is entered into Quantity field.
if (@Quantity is not null and @Quantity <= 0)
begin
set @Result_Focus = 'Quantity, The quantity must be greater than zero.'
set @Success = 'false'
end
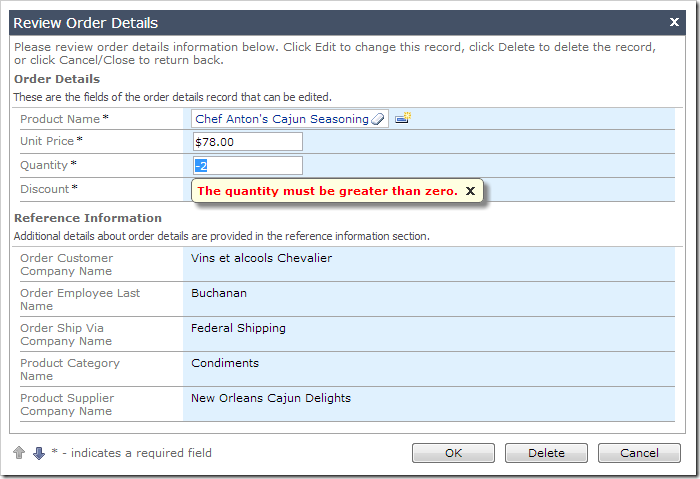
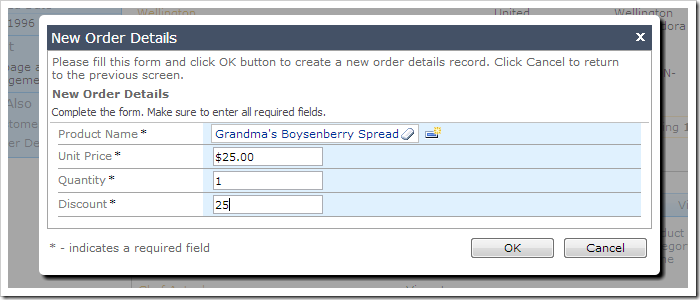
6. Automatic Conversion of Discount
When the user enters a value greater than 1, the business rule will automatically convert the value to a fraction of 100.
if (@Discount > 1)
set @Discount = (@Discount / 100)
For example, a value of “25” has been entered in the New Order Details screen shown below.
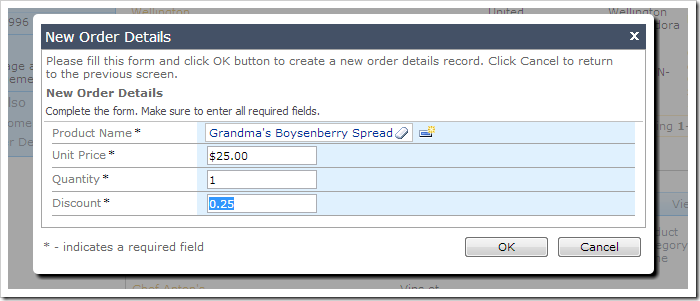
When focus is shifted from the field, the value is converted to a percentage.
7. Discount Range Validation
A validation error will be displayed if the Discount value is not within range after automatic conversion.
if (@Discount is not null and (@Discount < 0.00 or @Discount > 0.99))
begin
set @Result_Focus = 'Discount, The discount must be between 0.00 and 0.99 (0% - 99%).'
set @Success = 'false'
end
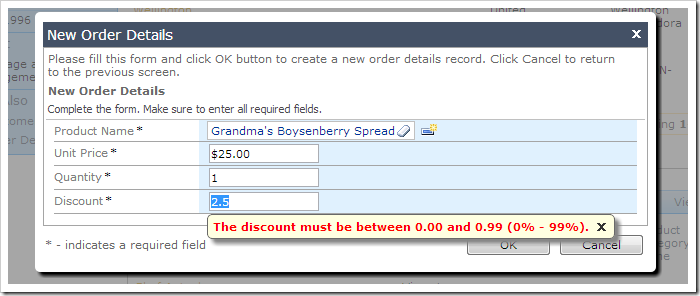
8. Wrapping Up
The default behavior of the application server will be to continue processing the Insert or Update action triggered by the user. If any of the validations have failed or the command was Calculate, the default behavior will be halted.
-- 8. Wrapping up
if (@Arguments_CommandName = 'Calculate' or @Success = 'false')
set @BusinessRules_PreventDefault = 1