One method to implement separation of “draft” and “committed” data is to add a log table to the database. This table will store a list of references to data that has not been committed. For example, new orders created in a database will be referenced in the dedicated DraftOrderLog table. The application will ensure that draft orders are only visible on the order entry page. When a user submits an order, the reference to it will be removed from the log table.
Adding Log Table
Start SQL Server Management Studio. In the Object Explorer, right-click on Databases / Northwind node, and press New Query.
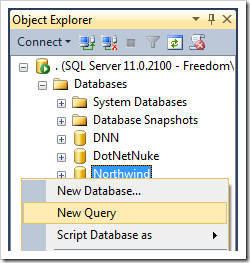
Paste in the following query:
create table DraftOrderLog
(
OrderID int not null primary key,
Created datetime default getdate()
)
go
The query will create the “DraftOrderLog” table with two columns. Column “OrderID” will record the ID of the draft order, and column “Created” will reflect the date when the order was logged.
On the toolbar, press Execute to run the query.
Controlling Display of Draft Orders
Start the web app generator. Select the project name and click Settings. Press Business Logic Layer and enable shared business rules. Click Finish and regenerate the project.
Start the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab. Right-click on Orders controller, and press Edit Handler in Visual Studio.
The shared business rule file will open in Visual Studio. Replace the existing code with the following:
C#:
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using MyCompany.Data;
namespace MyCompany.Rules
{
public partial class SharedBusinessRules : MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
{
public SharedBusinessRules()
{
}
protected override void EnumerateDynamicAccessControlRules(string controllerName)
{
if (Context.Request.UrlReferrer != null)
{
if (Context.Request.UrlReferrer.ToString().ToLower().Contains("orderform.aspx"))
RegisterAccessControlRule("OrderID",
"select OrderID from DraftOrderLog",
AccessPermission.Allow);
else
RegisterAccessControlRule("OrderID",
"select OrderID from DraftOrderLog",
AccessPermission.Deny);
}
}
}
}
Visual Basic:
Imports MyCompany.Data
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.Data
Imports System.Linq
Namespace MyCompany.Rules
Partial Public Class SharedBusinessRules
Inherits MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
Public Sub New()
MyBase.New()
End Sub
Protected Overrides Sub EnumerateDynamicAccessControlRules(controllerName As String)
If Context.Request.UrlReferrer <> Nothing Then
If Context.Request.UrlReferrer.ToString().ToLower().Contains("orderform.aspx") Then
RegisterAccessControlRule("OrderID",
"select OrderID from DraftOrderLog",
AccessPermission.Allow)
Else
RegisterAccessControlRule("OrderID",
"select OrderID from DraftOrderLog",
AccessPermission.Deny)
End If
End If
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
The implementation will conditionally register a dynamic access control rule that will be applied to a view of any data controller with an OrderID data field. If the user is interacting with the ~/Pages/OrderForm.aspx application page, then only data with OrderID that matches a record in the DraftOrderLog table will be included in the returned data set. All other pages will show data that is not linked to a logged order.
Save the file.
Adding Business Rule to Update Log Table
Switch back to the Project Designer. Right-click on Orders / Business Rules node, and press New Business Rule.
Assign the following values:
| Property |
Value |
| Type |
SQL |
| Command Name |
Insert |
| Phase |
After |
| Script |
insert into DraftOrderLog (OrderID)
values (@OrderID)
|
The business rule will insert a reference to the new order in the DraftOrderLog table. Press OK to save the business rule.
Adding “Submit Order” Action
Right-click on Orders / Actions / ag2 (Form) node, and press New Action.
Give this action the following properties:
| Property |
Value |
| Command Name |
Custom |
| Command Argument |
SubmitOrder |
| Header Text |
Submit Order |
Press OK to save. Drop a101 – Custom, SubmitOrder | Submit Order node to the left side of a100 – Report | Order Report to place it first on the form.
Right-click on Orders / Business Rules node, and press New Business Rule.
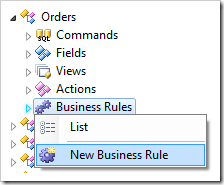
Assign these values:
| Property |
Value |
| Type |
SQL |
| Command Name |
Custom |
| Command Argument |
SubmitOrder |
| Phase |
Execute |
| Script |
delete from DraftOrderLog
where OrderID = @OrderID
set @Result_NavigateUrl = 'OrderForm.aspx'
|
This business rule will remove the reference to a submitted order from the DraftOrderLog table when the Submit Order action is activated. The browser will be instructed to navigate to ~/Pages/OrderForm.aspx page.
Press OK to save the business rule.
Viewing the Results
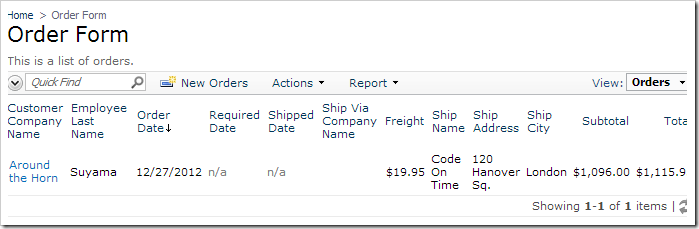
On the toolbar, press Browse. Navigate to the Order Form, and create a new order. Notice that only the new draft order is listed.
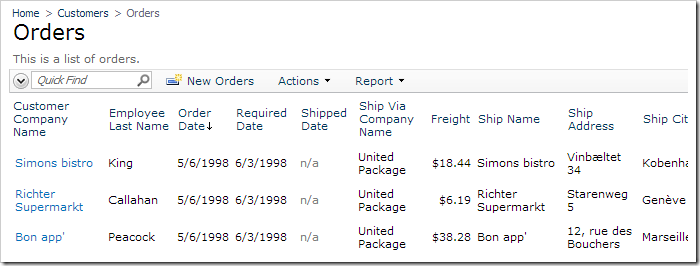
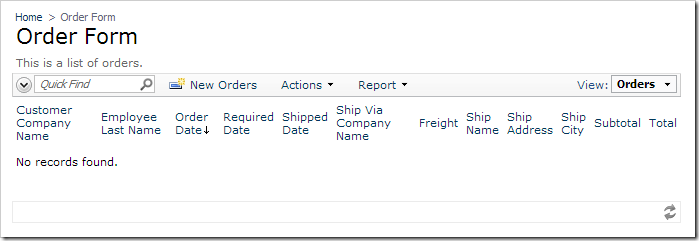
Navigate to the Orders page. All orders except the draft order are displayed.
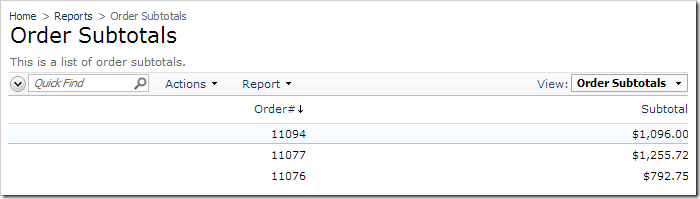
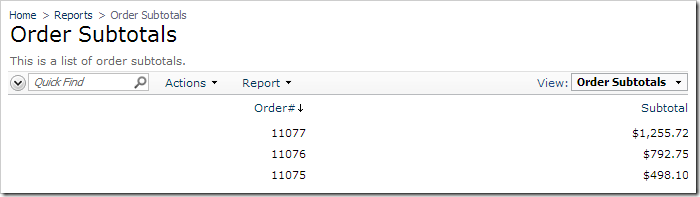
The draft order will not be visible in any data controller based on a database view that relates to orders. For example, the page Reports | Order Subtotals does not display the new order.
Switch back to the Order Form page, and select the draft order. Activate the Submit Order button.
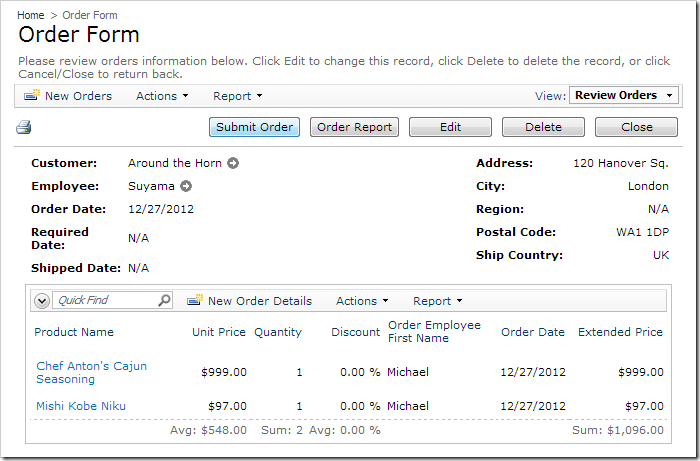
The application will refresh the page and display an empty list of orders.
The submitted order will now appear on Orders page.
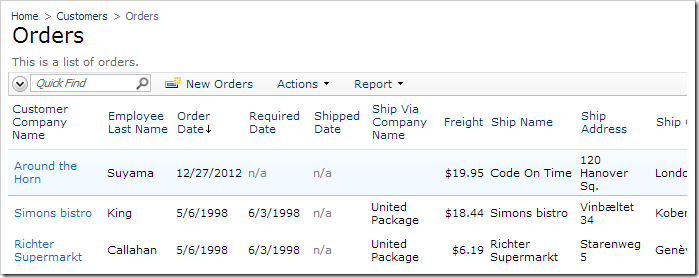
It will also appear on pages linked to data controllers related to orders.