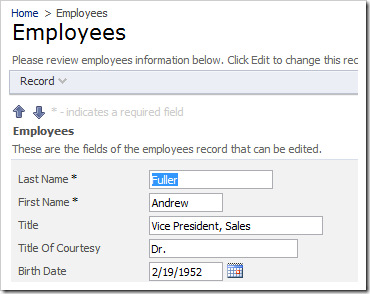
Let’s examine two tables in the Northwind database, Employees and Orders. Each order is linked to an employee via the EmployeeID foreign key relationship.
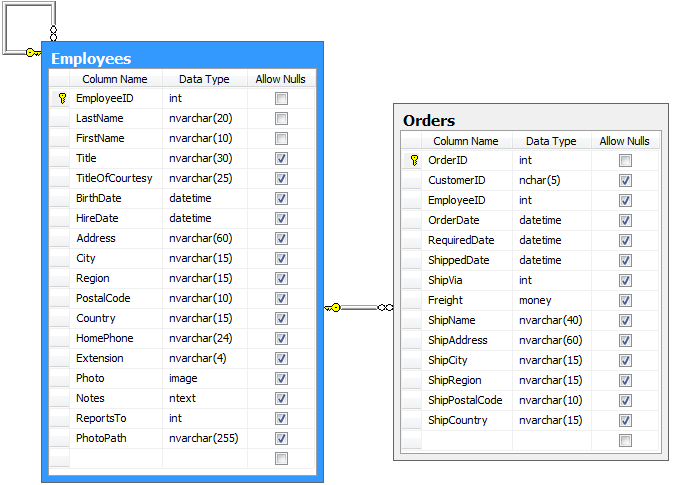
A Code On Time web application will perform automatic denormalization and use the LastName field as alias for EmployeeID. This field is shown below, labeled “Employee Last Name”.
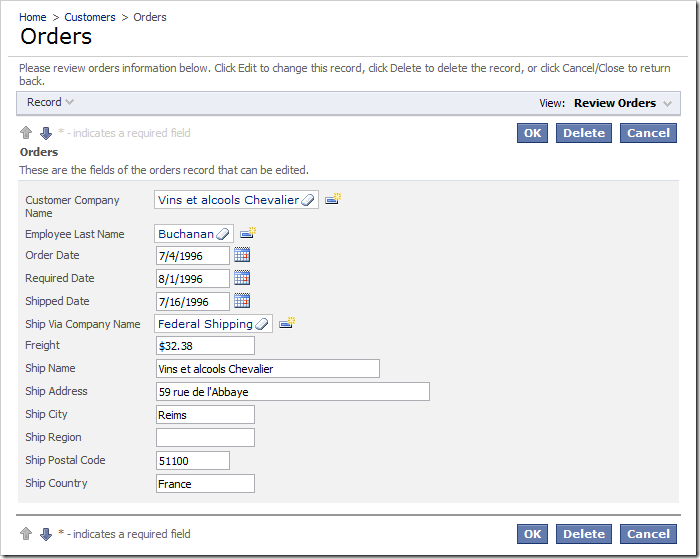
The end user may want to see the full name of the employee instead.
Let’s create a calculated field that combines First Name and Last Name of the employee, and use this field as an alias for EmployeeID in both Employees and Orders controllers.
Creating the Calculated Field in Employees Controller
Activate the Project Designer. In the Explorer, switch to Controllers tab. Let’s take a look at the command of Employees controller. Double-click on Employees / Commands / command1 node.
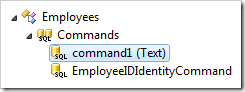
Take a look at the text of the command.
select
"Employees"."EmployeeID" "EmployeeID"
,"Employees"."LastName" "LastName"
,"Employees"."FirstName" "FirstName"
,"Employees"."Title" "Title"
,"Employees"."TitleOfCourtesy" "TitleOfCourtesy"
,"Employees"."BirthDate" "BirthDate"
,"Employees"."HireDate" "HireDate"
,"Employees"."Address" "Address"
,"Employees"."City" "City"
,"Employees"."Region" "Region"
,"Employees"."PostalCode" "PostalCode"
,"Employees"."Country" "Country"
,"Employees"."HomePhone" "HomePhone"
,"Employees"."Extension" "Extension"
,"Employees"."Photo" "Photo"
,"Employees"."Notes" "Notes"
,"Employees"."ReportsTo" "ReportsTo"
,"ReportsTo"."LastName" "ReportsToLastName"
,"Employees"."PhotoPath" "PhotoPath"
from "dbo"."Employees" "Employees"
left join "dbo"."Employees" "ReportsTo" on "Employees"."ReportsTo" = "ReportsTo"."EmployeeID"
You can see the alias “Employees” in front of the LastName and FirstName columns. You will need to use this alias when referring to columns of the Employees table in the SQL Formula of the calculated field.
Make sure not to modify and/or save the command – the code generator
will stop automatically updating the command if you do so.
Let’s create the new field. Right-click on Employees / Fields node and select New Field option.
Give this field the following settings:
| Property |
Value |
| Name |
EmployeeFullName |
| Allow Null Values |
True |
| The value of this field is computed at run-time by SQL expression. |
"Employees"."LastName" + ', ' + "Employees"."FirstName"
|
| Label |
Employee Full Name |
| Values of this field cannot be edited |
True |
| Allow Query-by-Example |
True |
| Allow Sorting |
True |
Press OK to save the new field.
Now let’s change the data fields in the grid view. In the Project Explorer, double-click on Employees / Views / grid1 / LastName data field node.
Make the following change:
| Property |
New Value |
| Field Name |
EmployeeFullName |
Press OK to save the data field. In the Project Explorer, right-click on Employees / Views / grid1 / FirstName data field node, and choose Delete option. Select OK to confirm the delete operation.
Creating the Calculated Field in Orders Controller
Before creating the “EmployeeFullName” field in Orders controller, we’ll need to find the alias of the Employees tables in the command text.
Double-click on Orders / Commands / command1 node.
Take a look at the text of the command.
select
"Orders"."OrderID" "OrderID"
,"Orders"."CustomerID" "CustomerID"
,"Customer"."CompanyName" "CustomerCompanyName"
,"Orders"."EmployeeID" "EmployeeID"
,"Employee"."LastName" "EmployeeLastName"
,"Orders"."OrderDate" "OrderDate"
,"Orders"."RequiredDate" "RequiredDate"
,"Orders"."ShippedDate" "ShippedDate"
,"Orders"."ShipVia" "ShipVia"
,"ShipVia"."CompanyName" "ShipViaCompanyName"
,"Orders"."Freight" "Freight"
,"Orders"."ShipName" "ShipName"
,"Orders"."ShipAddress" "ShipAddress"
,"Orders"."ShipCity" "ShipCity"
,"Orders"."ShipRegion" "ShipRegion"
,"Orders"."ShipPostalCode" "ShipPostalCode"
,"Orders"."ShipCountry" "ShipCountry"
from "dbo"."Orders" "Orders"
left join "dbo"."Customers" "Customer" on "Orders"."CustomerID" = "Customer"."CustomerID"
left join "dbo"."Employees" "Employee" on "Orders"."EmployeeID" = "Employee"."EmployeeID"
left join "dbo"."Shippers" "ShipVia" on "Orders"."ShipVia" = "ShipVia"."ShipperID"
You can see that this data controller refers to Employees using “Employee”, which is different than the Employees data controller reference of “Employees”. The SQL Formula of the calculated field will need to use the alias of the command text in Orders data controller.
Make sure not to save any changes to the command. Right-click on Orders / Fields node, and choose New Field.
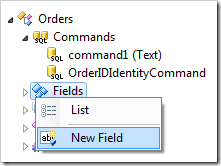
Use the following settings for the new field:
| Property |
Value |
| Name |
EmployeeFullName |
| Allow null values |
True |
| The value of this field is computed at run-time by SQL Expression |
"Employee"."LastName" + ', ' + "Employee"."FirstName"
|
| Label |
Employee Full Name |
| Values of this field cannot be edited |
True |
| Allow Query-by-Example |
True |
| Allow Sorting |
True |
Press OK to save the field.
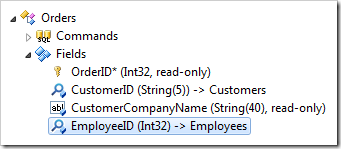
Let’s change the alias of the EmployeeID data fields in each view so that Employee Full Name is displayed. In the Explorer, double-click on Orders / Fields / EmployeeID field node.
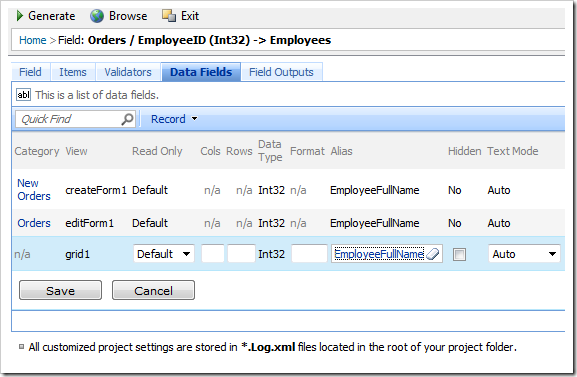
At the top, switch to Data Fields tab. For all three data fields, make the following change:
| Property |
New Value |
| Alias |
EmployeeFullName |
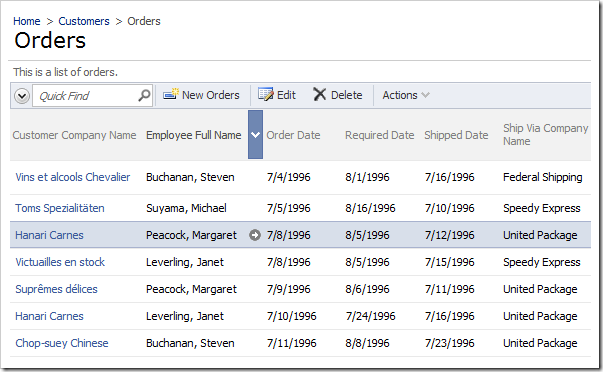
On the tool bar, press Browse to generate the web application. When it opens in your default web browser, navigate to Orders page. The EmployeeID field now shows the full name of each employee, instead of just the last name.
If you edit a record and activate the lookup for Employee Full Name, you will see that the grid view will show the Employee Full Name in the first column.
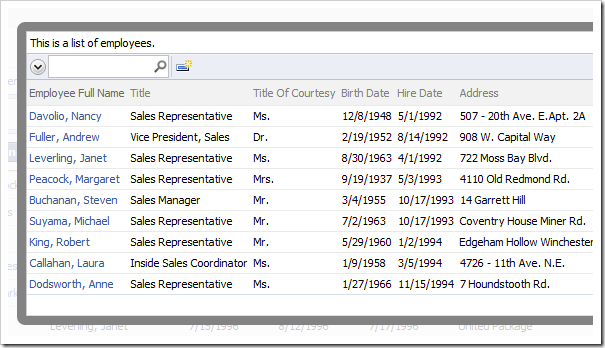
Selecting a record from the grid will insert the full name into the lookup field.
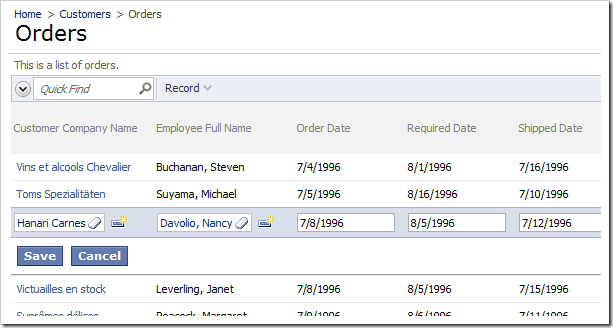
Navigate to the Employees page of the web application. If you activate inline edit mode on the grid view, you will not be able to edit the Employee Full Name field.
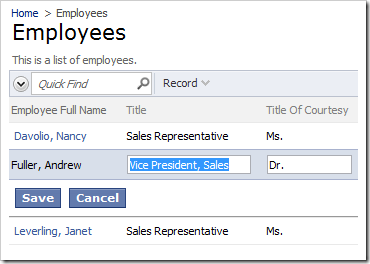
However, if you edit a record using form view, the original First Name and Last Name fields are still there.