Web applications may maintain a collection of session variables on the server and use the variables when a user navigates between pages. A session variable is usually initialized when a user signs in or when a certain action is performed. The variables exist on the server for a duration of the browsing session and expire when user closes a browser or logs out.
There are also the client-side variables that are typically passed as URL arguments when users navigate from one page to another.
SQL Business Rules can access both types of variables and manipulate their values.
Consider the the following example that demonstrates creation and use of a session variable in the Northwind sample.
Start Project Designer and right-click Suppliers / Actions /ag1 (Grid) node in the Project Explorer on Controllers tab. Select New Action option.
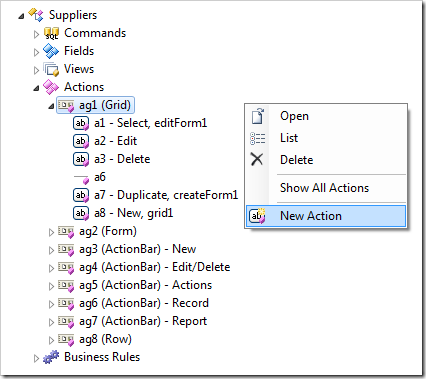
Enter these property values and click OK to create the new action.
| Property | Value |
| Command Name | SQL |
| Header Text | Show Supplier Products |
| Data | set @Session_SupplierID = @SupplierID
set @Result_ShowAlert =
'Primary key of supplier "' + @CompanyName +
'" has been stored in the user session. ' +
'You will be redirected to products.'
set @Result_NavigateUrl = 'Products.aspx?FilterBy=Suppliers'
|
The Suppliers data controller hierarchy will look as follows
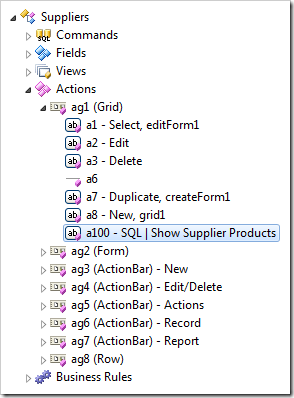
Now the application can make use of the session variable SupplierID and URL variable FilterBy.
Let’s limit the list of products rendered on the Products page to those that have their SessionID column value equal to the value stored in the session variable. The filtering will only take place if FilterBy=SupplierID is detected in the URL of the Products page. The page has to provide an explanation that the list of products is filtered to avoid any confusion on a part of user.
Select Products / Views / grid1 view node on the Controllers tab in Project Explorer.
Enter the Filter Expression and save the changes.
| Property |
New Values |
| Filter Expression |
@Url_FilterBy is null or
@Url_FilterBy = 'Suppliers' and SupplierID = @Session_SupplierID
|
The entire filter expression is embedded in the WHERE clause of SELECT statement created by the application framework at runtime.
Right-click the Products / Business Rules node. Select New Business Rule option and enter the following properties of the new rule.
| Property |
Value |
| Command Name |
Select |
| View |
grid1 |
| Name |
ExplainFilter |
| Type |
SQL |
| Phase |
Before |
| Script |
if @Session_SupplierID is not null and @BusinessRules_Tags is null
begin
-- tag the client-side view to render explanation once
set @BusinessRules_Tags = 'Explained'
-- find the supplier company name
declare @Supplier nvarchar(40)
select @Supplier = CompanyName
from Suppliers
where SupplierID = @Session_SupplierID
-- display a "view message" in the web browser
set @Result_ShowViewMessage =
'The supplier of these products is "' +
@Supplier + '".'
end
|
Press OK to save the business rule. The hierarchy of the Products data controller will change.
Click Browse and navigate to Products page. The entire list of products will be displayed as if the project has never changed.
Navigate to Suppliers page and open a context menu of any supplier. Choose Show Supplier Products option.
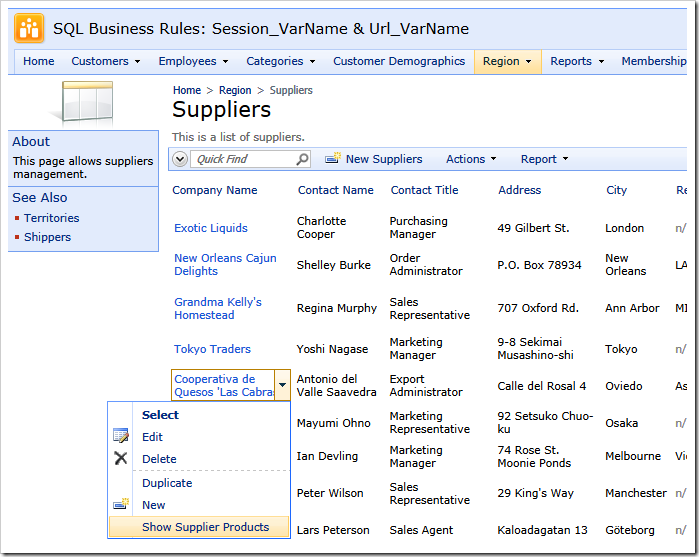
The browser alert window will be displayed. At that time the relevant Supplier ID has been stored in the session variable by application server.
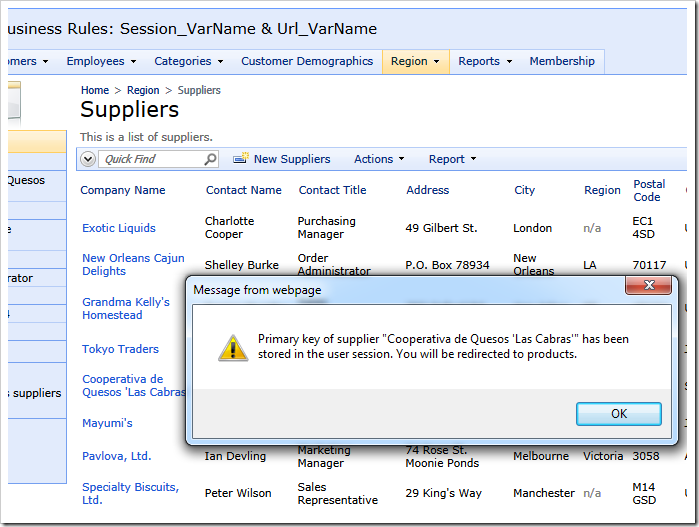
Click OK and the web browser will navigate to Products page.
Notice the FilterBy=Supplier fragment in the address bar.
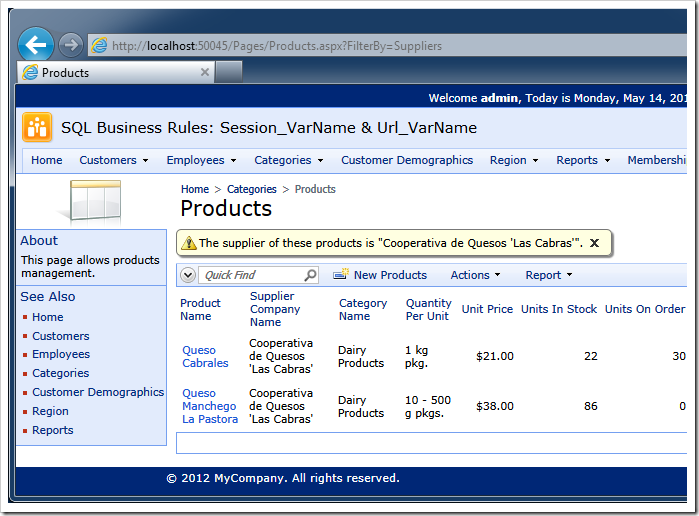
The filter expression specified in the Products / Views / grid1 view node is evaluated whenever users interact with the data on the Products page.
If the FilterBy argument is not specified in the URL of the page, then the value of parameter @Url_FilterBy is equal to NULL.
The parameter named @Session_SupplierID is equal to the value assigned by SQL action Suppliers / Actions / ag1 (Grid) / a100 – SQL | Show Supplier Products. If the action has not been executed, then the value of parameter @Session_SupplierID is null.
Once assigned, a session variable value is available in data views of all application pages.