Session variables provide a context for the current user activities. The common use for session variables is to perform automatic data filtering and to facilitate data input.
The Session and URL Variables example explains how to store an ID of a supplier in a session variable. The stored Supplier ID is used for product filtering.
It is easy to use the same session variable to assign a supplier when a new product is entered.
Add a new SQL Business Rule to the Products data controller and enter its properties as follows.
| Property | Value |
| Command Name | New |
| Type | SQL |
| Phase | Execute |
| Script | -- assign the Supplier ID
set @SupplierID = @Session_SupplierID
-- assign default values to other fields
select
@SupplierCompanyName = CompanyName, -- Supplier alias field
@UnitsOnOrder = 0, -- Unit On Order
@Discontinued = 0 -- "Discontinued" flag
from Suppliers
where SupplierID = @SupplierID
-- assign default Reorder Level as the maximum reorder level
-- for the products of this supplier
select @ReorderLevel = max(ReorderLevel)
from Products
where SupplierID = @SupplierID
|
Click OK button to save the business rule.
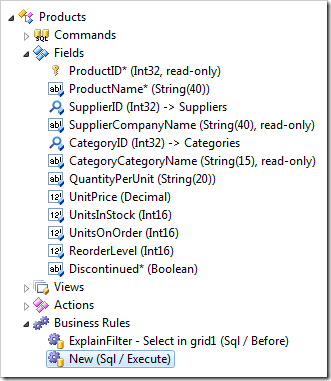
The script definition uses the value stored in the session variable SupplierID to assign the initial values to the lookup field SupplierID and its alias SupplierCompanyName when a new product record is created. It also figures ReorderLevel as a maximum reorder level of supplier products. The script assigns default values to the fields UnitsOnOrder and Discontinued.
The hierarchy of Products data controller will look as shown in the picture.
Click Browse to generate the app. Navigate to Suppliers page and choose Show Supplier Products in the context of any data row.
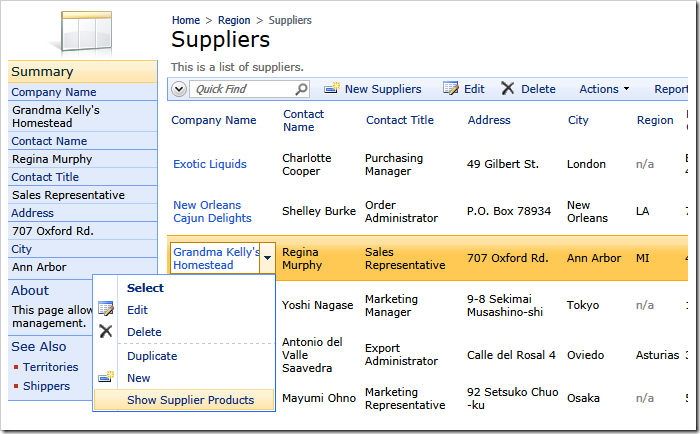
The supplier ID will be stored in the session variable and the web browser will redirect to Products page.
Start creating a new product. The default supplier field values will be automatically entered in the new data record.
The application framework executes business rules that match the New command name. It returns all changed “field” parameter values as the values of a new data row to the web browser. The client library renders a new data row in a presentation view.
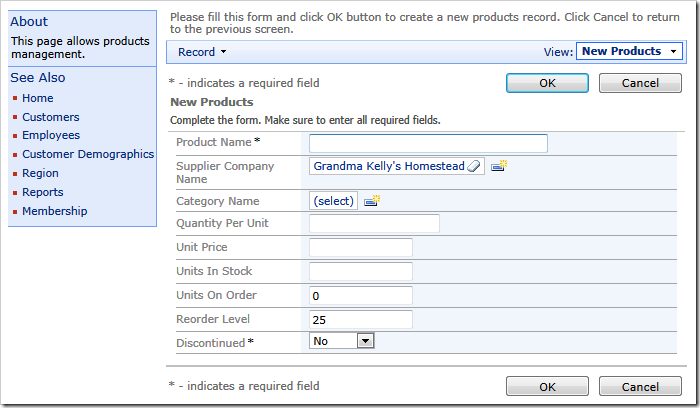
You can visit other application pages. The value of the session variable SessionID will remain the same. If you arrive to Products page directly without choosing another supplier, then the same supplier stored in the session variable will be assigned to the new product record.