Workflows in Line-of-Business Applications
Workflow is a repeatable pattern of business activity. Business applications mirror the real-world patterns through data collection performed in sequences of user-interface screens.
Software developers create hard-coded data structures and data entry forms based on the input from business users. A line-of-business application represents the current understanding of a business process by a development team.
A successful line-of-business application eventually evolves to match the requirements of business processes in organization. The dynamic nature of a business life-cycle will require constant tweaks and fine tuning even in a successful implementation.
Application customization and deployment are very expensive and frequently disruptive. Line-of-business applications must include built-in tools to allow changing application behavior without modifying the core application code.
Procedural Workflows
Many software packages include implementations of procedural workflows. Procedural Workflow allows non-developers to describe sequences of application operations with optional conditions and loops. Procedural workflows can be presented as visual workflow diagrams or text-based scripts. Procedural workflows offer a great tool that allows altering application behavior without changing the core application.
Complexity of procedural workflows grows exponentially when business users are trying to express various exceptions that exist in real-world business processes. Procedural workflows do not offer the means of limiting access to data.
State Machine Workflows
State Machine workflows are composed of rules triggered by the state of data, user identity, and time. Each rule defines a test that allows inspecting the state of data. If the test has passed, then the rule is “triggered”. The triggered rules affect application behavior. If there is no state test, then a rule is considered to be “triggered” by the mere fact of association with the current user identity.
A state-driven rule effects a specific type of application functionality. For example, a rule with Allow type can define a filter that reduces a set of records to a smaller subset based on user identity. If the rule is “triggered”, then the filter is applied to any SQL statement reading data from the application database. A rule with Transform type may remove data modification actions from a data entry form. If the rule is triggered, then the end user will not be able to Edit, Delete, Import or create New data records.
A large collection of rules affecting application behavior can be developed. Developers organize related rules in groups. Groups of rules are associated with users and optional schedules. Association of end users with rule groups and scheduling can be outsourced to application administrators.
The standard end user experience is defined by the implementation of line-of-business application. The rules of the state machine workflow will alter user experience based on user identity, time, and state of data.
State-based rules hide the complexity of the real-world business processes by breaking them down into small and manageable bits of functionality. State-based rules are great when it comes to implementing real-world exception. A state-based rule can define data filters, user interface alterations, business rule injection, and much more.
Adaptive Line-of-Business Apps
For the past few years we have worked on an integrated solution that will enable declarative state-machine workflows in the generated applications out-of-the-box. The goal is to enable adaptive customization of live apps without making changes to the code that require re-deployment.
We have identified the following customization requirements that must be available in a live application:
- Ability to define Allow/Deny filtering rules that can be applied to any data retrieved by application.
- Ability to create customization rules applied to XML definition of a data controller.
- Ability to replace an entire data controller with a substitute.
- Ability to create “content” and “data” pages in a live app.
Several prototypes have been developed but appeared too complex to operate.
Meanwhile developers working with Code On Time had an option to implement requirements (1), (2), and (3) on their own:
- Dynamic Access Control Rules - http://codeontime.com/learn/security/multi-tenant-applications/dynamic-access-control-rules
- Data Controller Virtualization - http://codeontime.com/learn/workflow/virtualization-node-set-plugins
- Substitution of controllers - http://codeontime.com/learn/data-controllers/virtualization
Requirement (4) can be satisfied in SharePoint Factory and DotNetNuke Factory Projects. Both products are content management systems that allow creating pages at runtime.
This year we have finally arrived to a solution that will become integrated in the apps created as Azure Factory, Mobile Factory, Web App Factory, or Web Site Factory projects.
The solution will be rolled into a single feature called “Workflow Register”.
It will include an integrated Content Management System (CMS) as a core component of generated apps. CMS will allow creating dynamic “data” and “content” pages at runtime.
“Data” pages will include markup that uses “data-“ attributes to define data views. For example, master-detail page at http://demo.codeontime.com/northwind/Pages/Categories.aspx is defined as follows:
<div data-flow="NewRow">
<div id="view1" data-controller="Categories" data-view="grid1" data-show-in-summary="true"></div>
</div>
<div data-flow="NewRow" style="padding-top: 8px">
<div data-activator="Tab|Products">
<div id="view2" data-controller="Products" data-view="grid1"
data-filter-source="view1" data-filter-fields="CategoryID"
data-page-size="5" data-auto-hide="container" data-show-modal-forms="true"></div>
</div>
</div>
“Content” pages may contain arbitrary HTML.
Here is the screen shot of a “content” page based on popular Bootstrap framework, which will be integrated in the Code On Time release 8.0.9.0 due out at the end of September 2014.
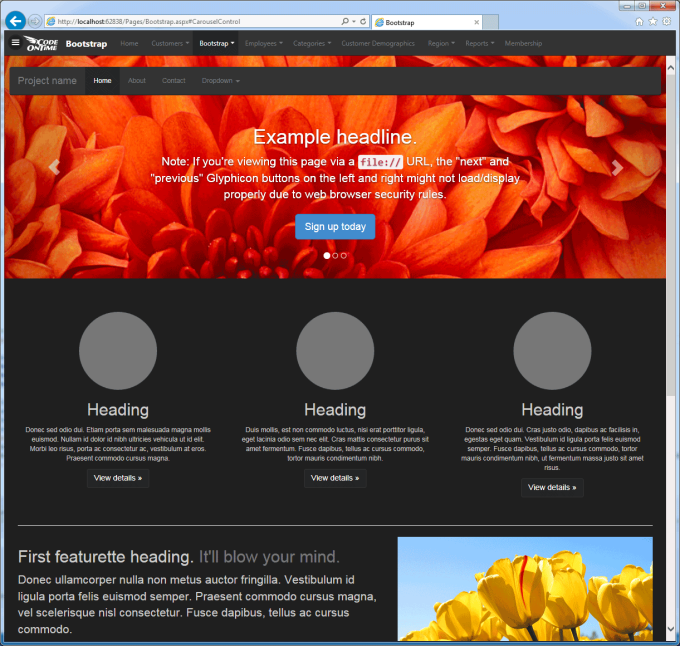
If workflow Register is enabled in a project, then the app generator will install a custom database schema to the primary database. The tables will have “ease_” prefix. The schema includes tables to support the following features:
- Workflows - specifies Allow, Deny, Transform, Define rules that are applied to various application components, such as pages, menu items, controllers, etc.
- Content Management System – provides storage for dynamic content, such as pages and menu items.
- Register - global registry that associates user identity references (user IDs and roles) with workflows and optional schedules.
- Permissions – a collection of workflow rules associated with users.
Register
The purpose of workflow Register is to enable management of various permissions by application administrators at runtime.
All users will have access to the Register entries associated with their user ID. Only administrators will have access to all entries in the Register.
Entries created by administrators have “Approved” status. Users will also be able to assign workflows to themselves. Such entries will be created with “Pending” status. Only “Approved” workflow register entries will be taken into account by the application framework.
A person assigning a workflow to a user or role does not need to know the details of workflow implementation. An entry in Register may read:
Workflow Human Resources is assigned to John Doe on Tuesday, Wednesday, and Thursday starting on November 15, 2014 and ending on February 1, 2015.
User John Doe will have have access to human resources pages on the specified dates. The workflow may allow or deny access to data records exposed on the pages.
Developers will be able to create workflow rules that delegate management of Register entries to the users other than administrators.
Workflow Register comes with pre-defined data controllers and management pages exposed through “Register” menu option in generated apps.
Workflows
Workflows are collections of rules defined by application developers. A developer can create a set of pre-defined workflows as a part of application at design time. New workflow rules can be created and existing ones can be customized at runtime as needed.
Rules may affect application behavior in multiple ways. For example:
- A filter that allows or denies access to data can be specified
- New pages can be made available to end users
- Data controller actions defined in the application can be dynamically altered at runtime.
- New SQL, JavaScript, and Email business rules can be introduced in data controllers.
The rule definition system if very simple and exceptionally extensible to fit the most demanding customization requirements.
Content Management System
Content management system allows populating an application with new “content” and “data” pages.
CMS may also store images, style sheets, JavaScript, and any other files or documents.
Application workflows determine access to the content. Content may be publicly available or limited to specific individuals or groups of users.
Permissions
Permissions are collections of workflow rules matched to a user identity.
Permissions are evaluated by application framework when users access various applications resources. Application framework matches workflow Register entries with the user identity and resource type. Matched workflow rules are automatically engaged by application framework.
For example, if “Allow” rule defines a filter limiting visibility of customer records, then the filter is included in SELECT statements executed by the framework when application tries to read a list of customers.
If a workflow assignment has an associated schedule, then permission engagement will be time-sensitive.
Permissions are created by application framework on-demand directly from the workflow Register entries. Permissions are refreshed when associated workflows are changed.
Availability
We are planning to release various components of Workflow Register with each upcoming release.
The upcoming release 8.0.9.0 due out by the end of month in September will include several elements of Workflow Register:
- Support for content pages.
- Support for declarative data pages.
- Integrated Bootstrap framework to allow creation of compelling responsive content pages.
- One-to-One entities support in data controllers. This particular feature is introduced to support “ease_” database tables.
Our production schedule indicates that Workflow Register will become available in November of 2014 or a sooner.