The When Client Script property allows controlling the display of an action based on a JavaScript expression. When the expression evaluates to true, the action is displayed. When it evaluates to false, the action is hidden. This property can be used to prevent users from editing a record based on certain conditions.
The property may be manually set in the Project Designer for every action that needs to be hidden. However, this may result in a large number of changes to be made. If the requirements of the web application were to change, all actions would need to be modified.
A simpler method would be to use virtualization node set plugins. The data controllers will be virtualized to conditionally add a When Client Script parameter for a subset of actions. When project requirements change, the virtualization code can be modified once.
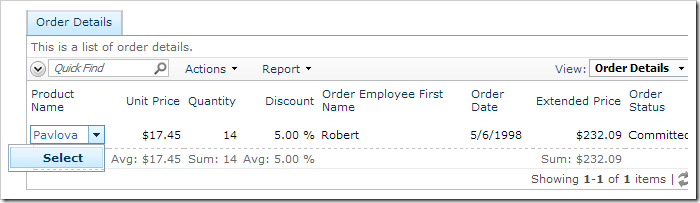
For example, suppose that the web application described in the When Client Script tutorial has been created. The three Edit actions in the Orders controller are not displayed when the Status field of the order is set to “Committed”.
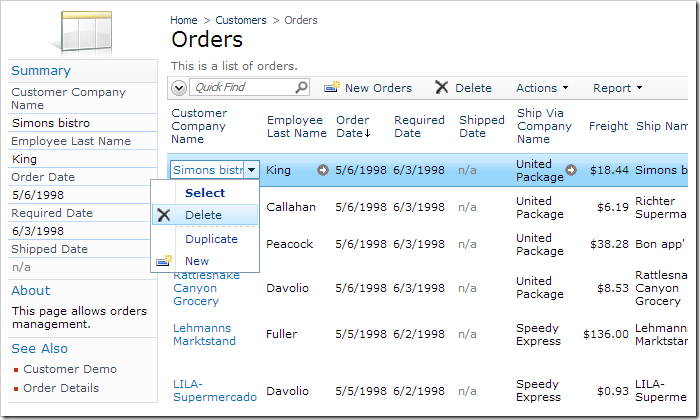
However, orders may still be deleted and order details can be modified. Let’s implement virtualization node set plugins to ensure that the user cannot make any changes to committed orders.
First, make sure to clear any When Client Script values that have been set previously.
Including Status Field in Order Details Controller
In order to prevent order details from being edited, the Status field must be included in the Order Details controller using denormalization.
Start the web application generator. Click on the project name, select Settings, and activate Business Logic Layer. Select Denormalization Map from the list, and make the highlighted addition:
| dbo.Order Details => dbo.Orders
OrderDate
RequiredDate
ShippedDate
ShipVia
Freight
ShipName
ShipAddress
ShipCity
ShipRegion
ShipPostalCode
ShipCountry
Status dbo.Orders => dbo.Employees
FirstName |
Press Finish to navigate to the Summary page. Click on Refresh, and check the box next to OrderDetails controller. Press Refresh and confirm.
On the Summary page, press Design to activate the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab. Double-click on OrderDetails / Fields node.
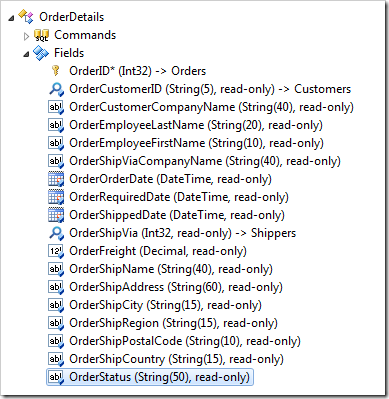
Mark the field as hidden.
| Property | New Value |
| The field is hidden from users. | true |
Press OK to save. Drop OrderStatus (String(50), read-only) field node onto OrderDetails / Views / grid1 node.
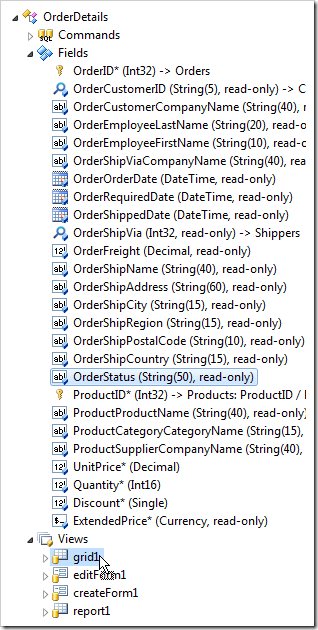
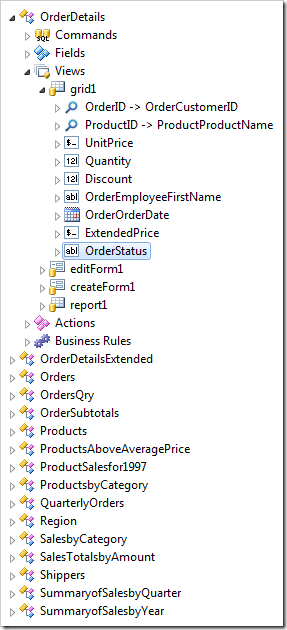
Adding Business Rule
Right-click on Orders controller node and press Edit Handler in Visual Studio.
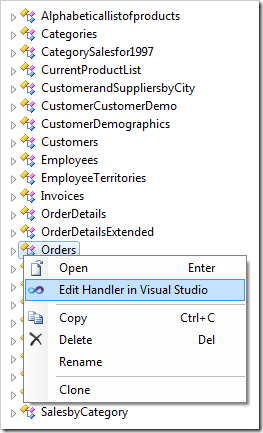
The handler file will open in Visual Studio. Append the SharedBusinessRules class with the two highlighted methods:
C#:
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using MyCompany.Data;
namespace MyCompany.Rules
{
public partial class SharedBusinessRules : MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
{
public SharedBusinessRules()
{
}
protected override void EnumerateDynamicAccessControlRules(string controllerName)
{
if (Context.Request.UrlReferrer != null)
{
if (Context.Request.UrlReferrer.ToString().ToLower().Contains("orderform.aspx"))
RegisterAccessControlRule("OrderID",
"select OrderID from Orders where Status = 'Draft'",
AccessPermission.Allow);
else
RegisterAccessControlRule("OrderID",
"select OrderID from Orders where Status = 'Committed'",
AccessPermission.Allow);
}
}
public override bool SupportsVirtualization(string controllerName)
{
if (controllerName == "Orders" || controllerName == "OrderDetails")
return true;
else
return false;
}
protected override void VirtualizeController(string controllerName)
{
if (controllerName == "Orders")
NodeSet().SelectActions("Edit", "Delete")
.WhenClientScript("[Status] != 'Committed'");
else if (controllerName == "OrderDetails")
NodeSet().SelectActions("Edit", "Delete", "New", "Duplicate")
.WhenClientScript("[OrderStatus] != 'Committed'");
}
}
}
Visual Basic:
Imports MyCompany.Data
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.Data
Imports System.Linq
Namespace MyCompany.Rules
Partial Public Class SharedBusinessRules
Inherits MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
Public Sub New()
MyBase.New()
End Sub
Protected Overrides Sub EnumerateDynamicAccessControlRules(controllerName As String)
If Context.Request.UrlReferrer <> Nothing Then
If Context.Request.UrlReferrer.ToString().ToLower().Contains("orderform.aspx") Then
RegisterAccessControlRule("OrderID",
"select OrderID from Orders where Status = 'Draft'",
AccessPermission.Allow)
Else
RegisterAccessControlRule("OrderID",
"select OrderID from Orders where Status = 'Committed'",
AccessPermission.Allow)
End If
End If
End Sub
Public Overrides Function SupportsVirtualization(controllerName As String) As Boolean
If controllerName = "Orders" Or controllerName = "OrderDetails" Then
Return True
Else
Return False
End If
End Function
Protected Overrides Sub VirtualizeController(controllerName As String)
If controllerName = "Orders" Then
NodeSet().SelectActions("Edit", "Delete").WhenClientScript(
"[Status] != 'Committed'")
ElseIf controllerName = "OrderDetails" Then
NodeSet().SelectActions("Edit", "Delete", "New", "Duplicate").WhenClientScript(
"[OrderStatus] != 'Committed'")
End If
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
The business rule will virtualize the Orders and OrderDetails controllers. For Orders, all Edit and Delete actions will be selected. For OrderDetails, all Edit, Delete, New, and Duplicate actions will be selected. Then, a When Client Script parameter will be assigned to hide the actions when the Status field is equal to “Committed”.
Viewing the Results
Save the file, and run the web application in your browser. Navigate to the Orders page. The Edit and Delete actions are no longer available in the user interface.
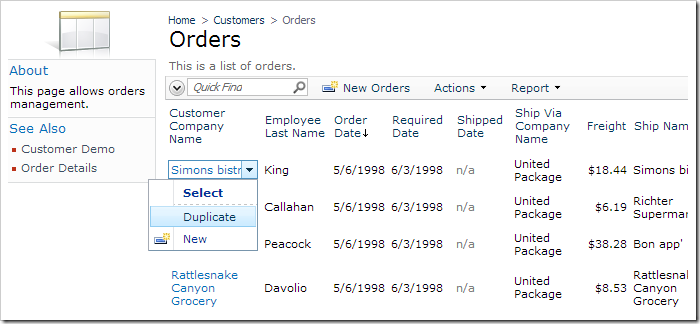
Select an order to view the order details. All Edit, Delete, New, and Duplicate actions will not be available.