Developers rely on a variety of platforms to deliver mobile apps. It is easy to set up the user authorization with an application created with Code On Time. The embedded RESTful API Engine implements OAuth 2.0 protocol with multiple authorization flows. Native applications can be programmed to have enterprise level security with little effort. The lesson explains how to configure Postman, the popular API development tool, to get the access tokens from the RESTful Backend Application. Any native client app will implement a similar pattern of authorization.
Learn to acquire access tokens in the native app via OAuth 2.0 Authorization Code flow with PKCE.
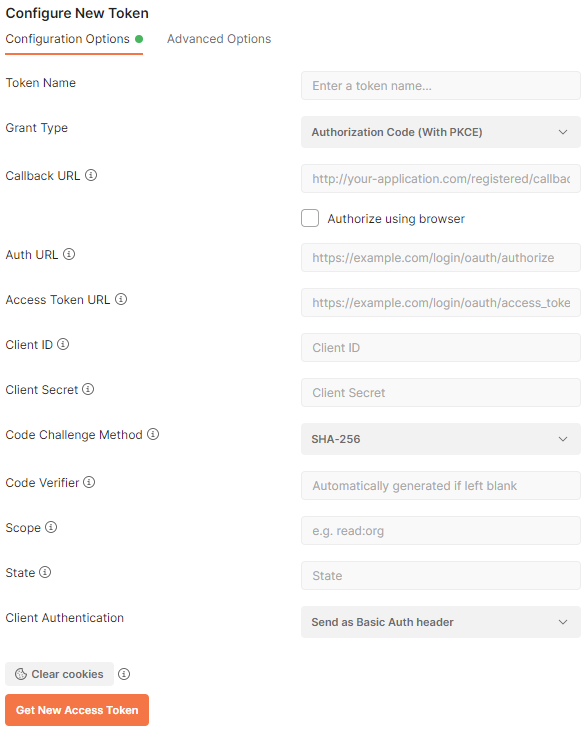
Postman provides the means of capturing the access tokens from any OAuth 2.0 compliant identity server. RESTful API Engine of apps created with Code On Time has the built-in support for OAuth 2.0 authorization flows. Developers can configure Postman to capture the access tokens from a Code On Time application.

Postman provides the means of access token capturing from any OAuth 2.0 compliant identity server. RESTful API Engine of apps created with Code On Time has the built-in support for OAuth 2.0 authorization flows. Developers can configure Postman to capture the access tokens from a Code On Time application.
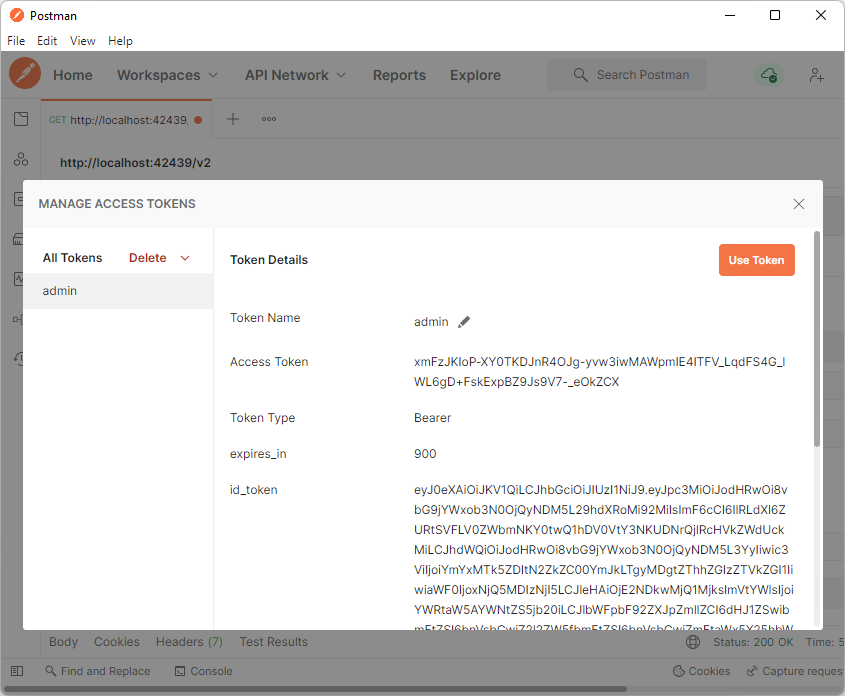
Developers can name the new Access Token and use it for development purposes in the Manage Access Tokens window. Typically the name of the token is the username.