Many organizations adopt security systems that require their users to enter a numeric time-based verification code generated by an authenticator app installed on the user’s mobile device. The unique secret key is associated with the user account in the application database. Authenticator app uses the same secret to generate a new verification code periodically and does not require a network interaction with the application. The server-side code generates the verification code in real time and compares it to the one provided by the user. If the correct verification code is not provided at the time of sign in, then the access to the application is not granted even if the user is entering the correct username and password combination.
The username, password, verification code in the text message or email, and the phone with the authenticator app with optional fingerprint scan or face recognition are the components of the multi-factor authentication.
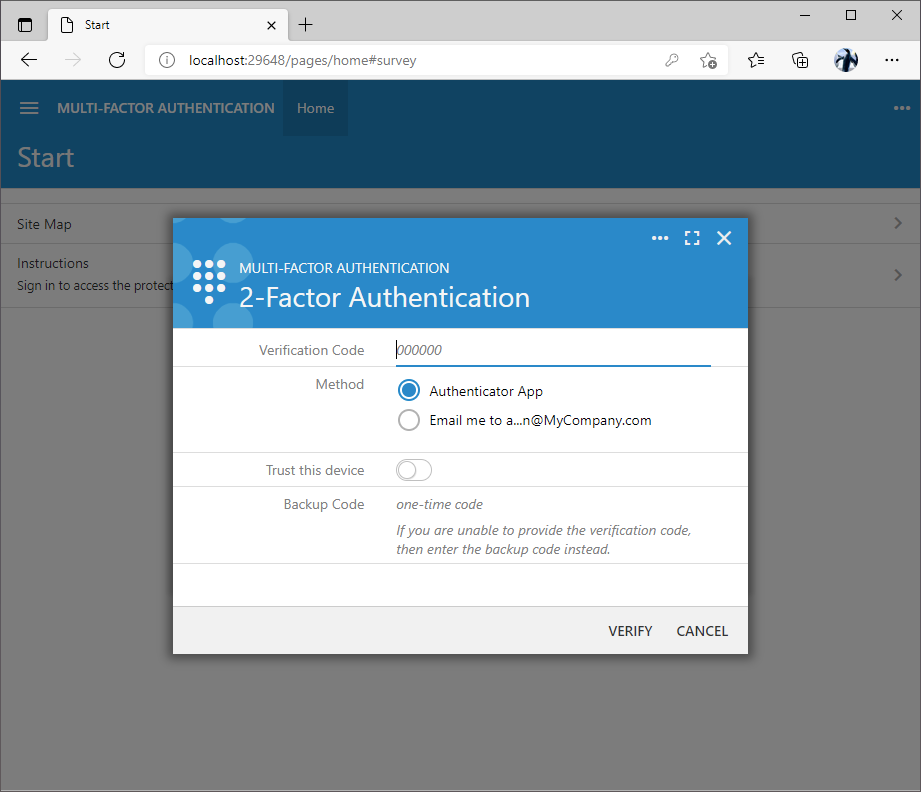
The prompt to enter a verification code is displayed after the successful confirmation of the username and password. Users must enter the verification code displayed on the screen of their mobile device in the authenticator app or request the verification code through other available methods. The backup codes are accepted in the Backup Code input.
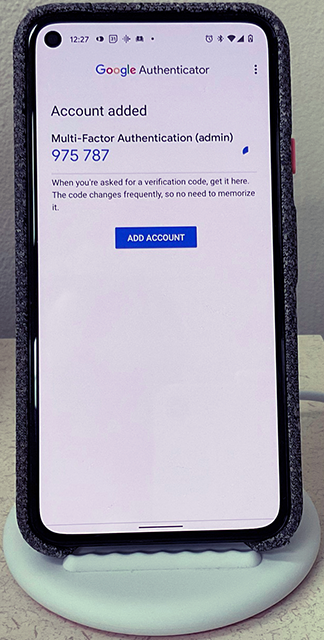
The Google Authenticator app in the picture shows the verification code after the QR code was scanned in the 2-Factor Authentication setup form of an application created with Code On Time. The name of the app and the username are displayed above the code. This makes it easy to locate the verification code of a specific application.