Every application requires a list of user accounts that have been granted (or denied) access to the data. In order to maintain membership consistency, every user needs to be associated with a password. Recommended practices for passwords dictate that every password must be unique, contain a long series of mixed alphanumeric characters, and that users should change their passwords regularly. It is likely that many users do not follow these recommended practices, and tend to reuse simple and easy to remember passwords across various systems. This can lead to a security issue if one of the systems becomes compromised – malicious users can then gain access to all systems that share the same password.
In an attempt to solve solutions to the problems mentioned above, authentication can be delegated to a “higher authority”. Application admins can register their app to accept responses from a federated authentication server. When a new user attempts to sign up to the application, they can choose to register an account using their federated account. They will be redirected to the authentication server’s login page, and grant permission for the app to gain access to their email. This information is then used to automatically create an account in the app and sign them in. Therefore, the user simply has to ensure that their account in the federated system is secure.
Applications created with Code On Time can use OAuth 2.0 to register their users. Simply define a resource under the Content Management System (CMS) that lists your client ID, client secret, and redirect URI. A local redirect URI can be defined for testing purposes.
Registering Your App With Facebook
The first step to configuring Facebook Login is to register your app with Facebook. Navigate to https://developers.facebook.com. In the top-right corner, hover over “My Apps” and press “Add a New App”.
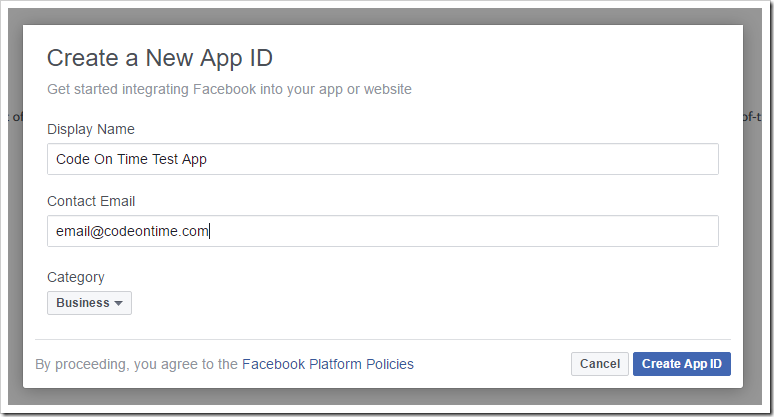
Specify a Display Name, Contact Email, and Category, and press “Create App ID”.
On the “Add Product” screen, press “Get Started” next to “Facebook Login”.
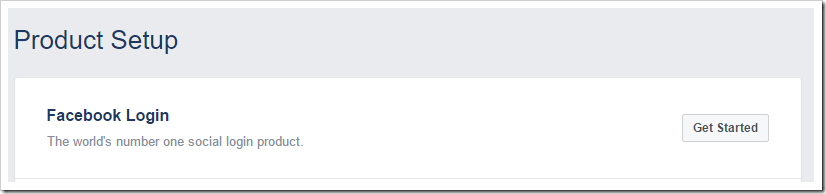
Under “Valid OAuth redirect URIs”, add a URI for your app URL, with the path “/appservices/saas/facebook”. It is recommended to add a test redirect URI when running the app locally on your PC.
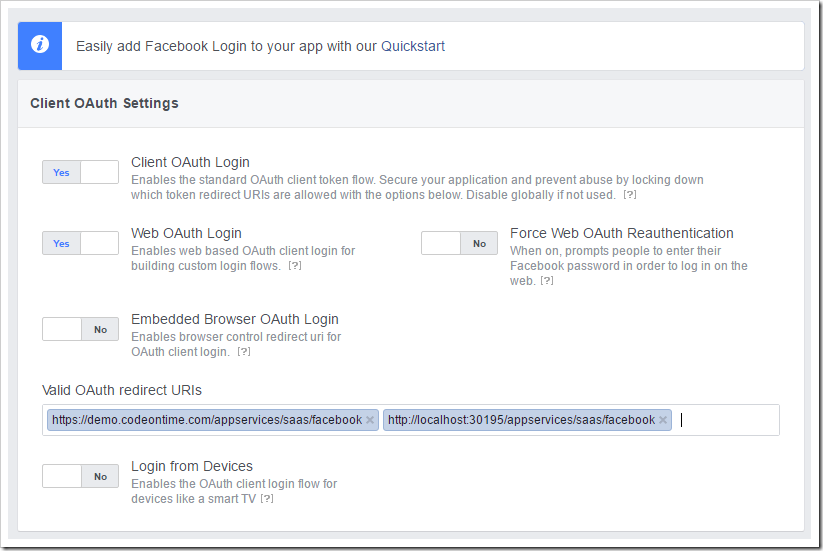
Next, press “Dashboard” section on the navbar on the left side of the screen. Take note of the App ID and App Secret values.
Enabling Facebook Authentication in your App
Navigate to your website, and navigate to your Site Content page. Create a new record with the following properties:
Make sure to replace the values in the “Text” property with the correct values for your app. Save the new record, and log out of the app.
Logging In With Facebook
On the login screen, the “LOGIN WITH FACEBOOK” action will now be displayed at the top of the form.
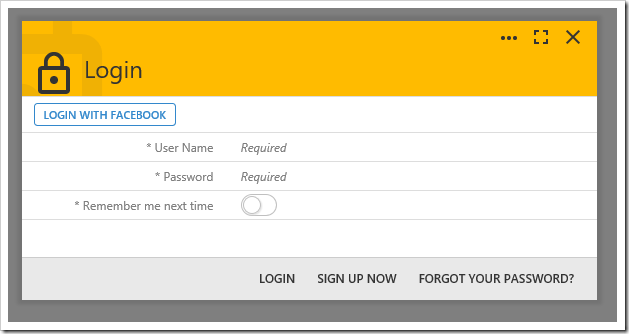
Press the “LOGIN WITH FACEBOOK” button, and the app will redirect to authenticate with Facebook. Once signed in, it will display a permissions popup.
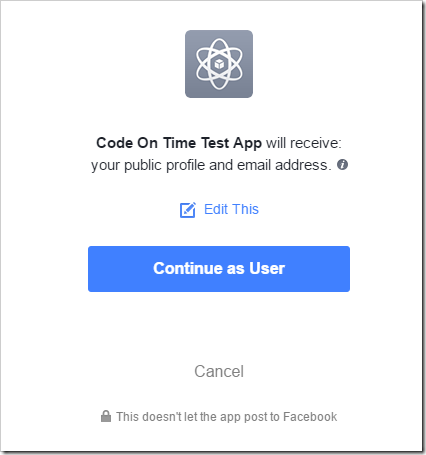
Press “Continue as XXX” button to grant access to your profile and email address for that app. It will redirect back to your app and attempt to log in as a user with that email. If the user does not exist, it will be created. The password and password answer will be randomly generated.
Note that in order to allow Facebook users other than the app creator to authenticate with the app, the app must be marked as “Public” under the App Review section of the developer site.