The application framework of each project is generated in C# or Visual Basic. The business rules engine of the framework takes care of executing SQL, Email, and JavaScript business rules in response to actions defined in the data controller. Naturally, developers can create business rules written in the programming language of the project to tap in the power of the business rules engine and vast Microsoft.NET library.
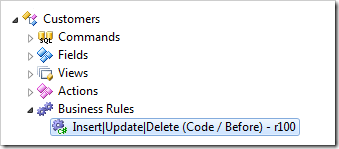
For example, the “Code” business rule defined in the project configuration will result in the code file generated in the project output folders.
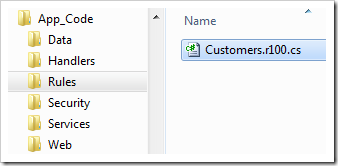
The business rule file provides a method template linked to the data controller business rule with Rule attribute. The file will not be re-created during subsequent code generation sessions. Any modifications to the file will become a permanent extension of the application framework.
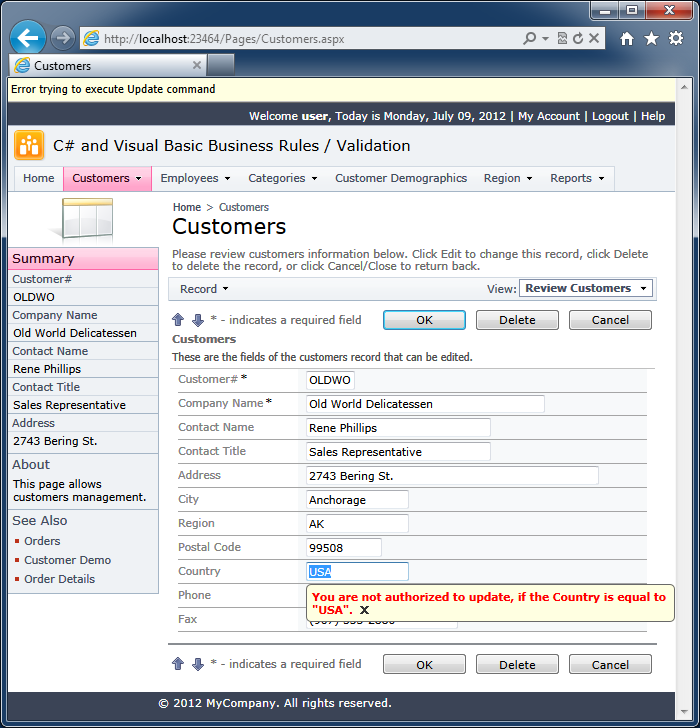
Let’s implement a validation business logic. Note that the highlighted text indicates the conditional expression inserted in the automatically generated business rule method template.
C#:
using System;
using MyCompany.Data;
namespace MyCompany.Rules
{
public partial class CustomersBusinessRules : MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
{
/// <summary>
/// This method will execute in any view before an action
/// with a command name that matches "Insert|Update|Delete".
/// </summary>
[Rule("r100")]
public void r100Implementation(string customerID, string companyName,
string contactName, string contactTitle, string address, string city,
string region, string postalCode, string country, string phone, string fax)
{
// This is the placeholder for method implementation.
if (country == "USA")
{
// tell the application framework to skip the execution of update, insert, or delete
PreventDefault();
// set the focus to the field "Country" and display an error message
Result.Focus("Country",
"You are not authorized to {0}, " +
"if the Country is equal to \"USA\".",
Arguments.CommandName.ToLower());
// show an additional information in the message bar at the top of the page
Result.ShowMessage("Error trying to execute {0} command",
Arguments.CommandName);
}
}
}
}
Visual Basic:
Imports MyCompany.Data
Imports System
Namespace MyCompany.Rules
Partial Public Class CustomersBusinessRules
Inherits MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
''' <summary>
''' This method will execute in any view before an action
''' with a command name that matches "Insert|Update|Delete".
''' </summary>
<Rule("r100")> _
Public Sub r100Implementation(ByVal customerID As String, ByVal companyName As String,
ByVal contactName As String, ByVal contactTitle As String, ByVal address As String,
ByVal city As String, ByVal region As String, ByVal postalCode As String,
ByVal country As String, ByVal phone As String, ByVal fax As String)
' This is the placeholder for method implementation.
If (country = "USA") Then
' tell the application framework to skip the execution of update, insert, or delete
PreventDefault()
' set the focus to the field "Country" and display an error message
Result.Focus("Country",
"You are not authorized to {0}, " &
"if the Country is equal to ""USA"".",
Arguments.CommandName.ToLower())
' show an additional information in the message bar at the top of the page
Result.ShowMessage("Error trying to execute {0} command",
Arguments.CommandName)
End If
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
The pattern of implementation is following closely the pattern of SQL and JavaScript business rules. Both of these alternatives are actually built on top of the same infrastructure demonstrated in this example.
The screenshot shows the “code” business rule in action.