A web app created with Code On Time may function as an application server for a client on any platform.
Let’s create a native Windows Forms application that will allow browsing and searching products available at http://demo.codeontime.com/Northwind/Pages/Products.aspx.
This is how a Quick Find search is performed by the web app. The native Windows client will provide a similar presentation and search facility.
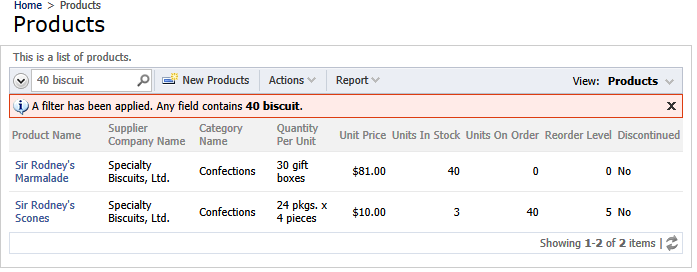
Click on the following link and you will see a response in XML format from the REST service of the web application:
http://demo.codeontime.com/northwind/appservices/Products?_q=40%20biscuit
The response will look similar to this sample.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Products totalRowCount="2" pageSize="100" pageIndex="0" rowCount="2">
<items>
<item ProductName="Sir Rodney's Marmalade" SupplierID="8" CategoryID="3"
QuantityPerUnit="30 gift boxes" UnitPrice="$81.00" UnitsInStock="40"
UnitsOnOrder="0" ReorderLevel="0" Discontinued="False" ProductID="20"
SupplierCompanyName="Specialty Biscuits, Ltd."
CategoryCategoryName="Confections" />
<item ProductName="Sir Rodney's Scones" SupplierID="8" CategoryID="3"
QuantityPerUnit="24 pkgs. x 4 pieces" UnitPrice="$10.00" UnitsInStock="3"
UnitsOnOrder="40" ReorderLevel="5" Discontinued="False" ProductID="21"
SupplierCompanyName="Specialty Biscuits, Ltd."
CategoryCategoryName="Confections" />
</items>
</Products>
The “_q” parameter represents the Quick Find argument of the web resource. If the parameter is not specified, then the first 100 items are returned. Other parameters for sorting, paging, and filtering are also supported.
The native Windows client of the Northwind application server will construct a similar URL to retrieve data for presentation.
Start Visual Studio and select File | New Project option. Choose Windows Forms Application under Visual C# or Visual Basic template group, enter “ProductBrowser” in the name, and click OK to create project files.
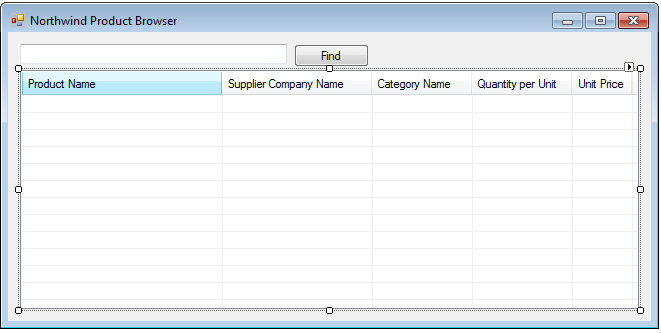
Drop TextBox, Button, and ListView components from toolbox on the design surface of Form1 and have them arranged as shown next.
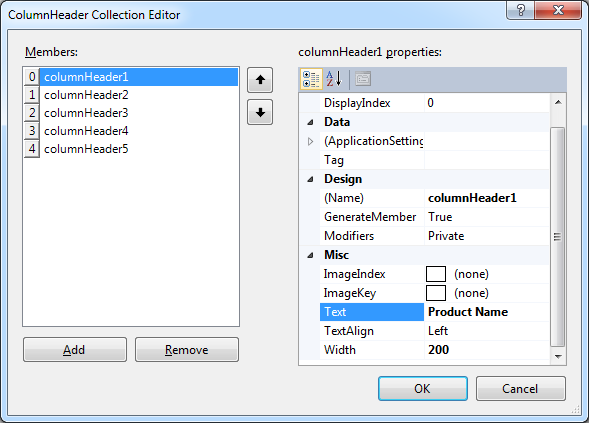
Use Properties Window to modify the Columns collection of listView1. Create five columns Product Name, Supplier Company Name, Category Name, Quantity per Unit, and Unit Price to capture a few properties of products.
Also set the following properties of listView1 component:
| Property |
Value |
| FullRowSelect |
True |
| GridLines |
True |
| View |
Details |
| VirtualMode |
True |
The list view is configured to behave as a virtual view.
If the property VirtualListSize is set to a value other than zero then the virtual list view will request items from the application as needed.
The list view will continuously request items representing a visible subset of data rows as a user scrolls the list.
Right-click Form1 node in the Solution Explorer and select View Code option in the context menu.
Add the highlighted namespaces to the top of code file:
C#:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Net;
using System.Xml.XPath;
using System.IO;
namespace ProductBrowser
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
}
}
Visual Basic:
Imports System.Net
Imports System.Xml.XPath
Imports System.IO
Public Class Form1
End Class
The namespaces will link required .NET library components used by Windows native client to communicate with the web app.
Add fields _dataPage, _query, _cache, and method GetDataPage to the definition of class Form1.
C#:
protected XPathNavigator _dataPage;
protected string _query;
private SortedDictionary<int, XPathNavigator> _cache = new SortedDictionary<int, XPathNavigator>();
protected XPathNavigator GetDataPage(int pageIndex)
{
XPathNavigator result = null;
if (!_cache.TryGetValue(pageIndex, out result))
{
Cursor = Cursors.WaitCursor;
try
{
WebRequest request = WebRequest.Create(String.Format(
"http://demo.codeontime.com/northwind" +
"/appservices/Products?_pageIndex={0}&_pageSize=10&_q={1}",
pageIndex, _query));
request.Method = "GET";
using (WebResponse response = request.GetResponse())
{
using (Stream stream = response.GetResponseStream())
result = new XPathDocument(stream)
.CreateNavigator().SelectSingleNode("/Products");
}
_cache.Add(pageIndex, result);
}
finally
{
Cursor = Cursors.Default;
}
}
return result;
}
Visual Basic:
Protected _dataPage As XPathNavigator
Protected _query As String
Private _cache As SortedDictionary(Of Integer, XPathNavigator) =
New SortedDictionary(Of Integer, XPathNavigator)
Protected Function GetDataPage(pageIndex As Integer) As XPathNavigator
Dim result As XPathNavigator = Nothing
If Not (_cache.TryGetValue(pageIndex, result)) Then
Cursor = Cursors.WaitCursor
Try
Dim request As WebRequest = WebRequest.Create(String.Format(
"http://demo.codeontime.com/northwind" +
"/appservices/Products?_pageIndex={0}&_pageSize=10&_q={1}",
pageIndex, _query))
request.Method = "GET"
Using response As WebResponse = request.GetResponse()
Using stream As Stream = response.GetResponseStream()
result = New XPathDocument(stream).
CreateNavigator().SelectSingleNode("/Products")
_cache.Add(pageIndex, result)
End Using
End Using
Finally
Cursor = Cursors.Default
End Try
End If
Return result
End Function
The implementation of method GetDataPage creates a web request and retrieves the page of data from the web app if the page has not been found in the dictionary of cached data pages. The method parses the XML response received from the web app and stores an instance of XPathNavigator class initialized with a page data in the _cache field. The web request URI incorporates the requested page index and search criteria in _pageIndex and _q parameters accordingly.
Select listView1 in form designer and activate Properties Window, choose Events button, and double click RetrieveVirtualItem event.
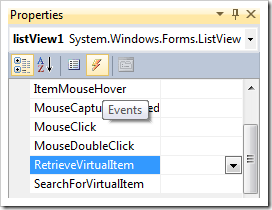
Enter the following definition of the method listView1_RetrieveVirtualItem as shown next.
C#:
private void listView1_RetrieveVirtualItem(object sender, RetrieveVirtualItemEventArgs e)
{
// analyze the current page item range
int pageIndex = Convert.ToInt32(_dataPage.GetAttribute("pageIndex", String.Empty));
int pageSize = Convert.ToInt32(_dataPage.GetAttribute("pageSize", String.Empty));
int rowCount = Convert.ToInt32(_dataPage.GetAttribute("rowCount", String.Empty));
int firstAvailableRowIndex = pageIndex * pageSize;
int lastAvailableRowIndex = firstAvailableRowIndex + rowCount - 1;
// if the current page does not contain the item then retrieve the page from the app
if (!(firstAvailableRowIndex <= e.ItemIndex && e.ItemIndex <= lastAvailableRowIndex))
{
pageIndex = e.ItemIndex / pageSize;
firstAvailableRowIndex = pageIndex * pageSize;
_dataPage = GetDataPage(pageIndex);
}
// create a virtual list item
XPathNavigator dataRow = _dataPage.SelectSingleNode(
String.Format("items/item[{0}]", e.ItemIndex - firstAvailableRowIndex + 1));
e.Item = new ListViewItem(dataRow.GetAttribute("ProductName", String.Empty));
e.Item.SubItems.Add(dataRow.GetAttribute("SupplierCompanyName", String.Empty));
e.Item.SubItems.Add(dataRow.GetAttribute("CategoryCategoryName", String.Empty));
e.Item.SubItems.Add(dataRow.GetAttribute("QuantityPerUnit", String.Empty));
e.Item.SubItems.Add(dataRow.GetAttribute("UnitPrice", String.Empty));
}
Visual Basic:
Private Sub listView1_RetrieveVirtualItem(sender As System.Object,
e As System.Windows.Forms.RetrieveVirtualItemEventArgs) Handles listView1.RetrieveVirtualItem
' analyze the current page item range
Dim pageIndex As Integer = Convert.ToInt32(_dataPage.GetAttribute("pageIndex", String.Empty))
Dim pageSize As Integer = Convert.ToInt32(_dataPage.GetAttribute("pageSize", String.Empty))
Dim rowCount As Integer = Convert.ToInt32(_dataPage.GetAttribute("rowCount", String.Empty))
Dim firstAvailableRowIndex As Integer = pageIndex * pageSize
Dim lastAvailableRowIndex As Integer = firstAvailableRowIndex + rowCount - 1
' if the current page does not contain the item then retrieve the page from the app
If Not (firstAvailableRowIndex <= e.ItemIndex And e.ItemIndex <= lastAvailableRowIndex) Then
pageIndex = e.ItemIndex \ pageSize
firstAvailableRowIndex = pageIndex * pageSize
_dataPage = GetDataPage(pageIndex)
End If
' create a virtual list item
Dim dataRow As XPathNavigator = _dataPage.SelectSingleNode(
String.Format("items/item[{0}]", e.ItemIndex - firstAvailableRowIndex + 1))
e.Item = New ListViewItem(dataRow.GetAttribute("ProductName", String.Empty))
e.Item.SubItems.Add(dataRow.GetAttribute("SupplierCompanyName", String.Empty))
e.Item.SubItems.Add(dataRow.GetAttribute("CategoryCategoryName", String.Empty))
e.Item.SubItems.Add(dataRow.GetAttribute("QuantityPerUnit", String.Empty))
e.Item.SubItems.Add(dataRow.GetAttribute("UnitPrice", String.Empty))
End Sub
Consult the sample of XML response at the top of article to understand the method implementation.
The implementation makes an assumption that a page of XML data is stored in the _dataPage instance of XPathNavigator. The property e.ItemIndex specifies the index of the item that the virtual list view needs. The code tries to determine if the current data page contains the item. If the item is not in current page _dataPage, then the application will retrieve a page of data from the web app by invoking GetDataPage method. The method will either find the page in the cache or reach out to the web app with a web request for data.
Next, the event handler will create an instance of a ListViewItem. Its sub-items represent the values displayed in the columns of the list view. The instance of the ListViewItem is assigned to e.Item property.
At this point the entire mechanism of populating the list view with data has been implemented.
The only remaining step is to collect user input for the search criteria and to assign a value to the VirtualListSize property of listView1.
Activate the design surface of Form1 and double-click the Find button. This will create an event handler that shall be defines as explained below.
C#:
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// assign the search criteria
_query = textBox1.Text;
// remove any previously cached data pages
_cache.Clear();
// get the first page of data with index "zero"
_dataPage = GetDataPage(0);
// figure the total number of rows in the virtual listview
int totalRowCount = Convert.ToInt32(_dataPage.GetAttribute("totalRowCount", String.Empty));
listView1.VirtualListSize = totalRowCount;
}
Visual Basic:
Private Sub button1_Click(sender As System.Object, e As System.EventArgs) Handles button1.Click
' assign the search criteria
_query = textBox1.Text
' remove any previously cached data pages
_cache.Clear()
' get the first page of data with index "zero"
_dataPage = GetDataPage(0)
' figure the total number of rows in the virtual listview
Dim totalRowCount As Integer = Convert.ToInt32(_dataPage.GetAttribute("totalRowCount", String.Empty))
listView1.VirtualListSize = totalRowCount
End Sub
The implementation of button1_Click method copies the search criteria from the text box in the field _query. Then it clears the previously cached data pages and obtains the first page of data. Last, the method will figure the size of the virtual list.
In less than a hundred lines of code a remarkable functionality has been brought to life.
Press F5 to start the Northwind Product Browser for Windows. Click the Find button.
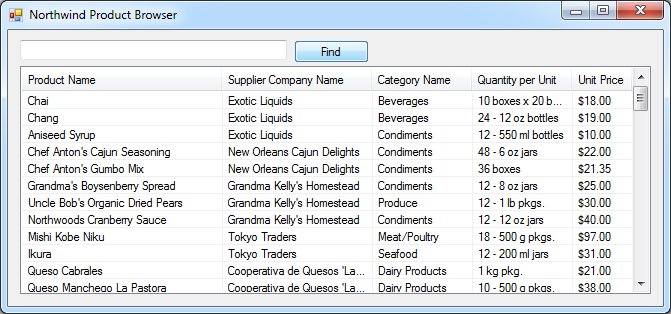
Try scrolling the list of products. The Windows client will make at the most 8 requests to retrieve the 77 products from the Northwind database sample. The page size in this implementation is deliberately set to 10 items to ensure that a client-server interaction does occur upon scrolling. If the page size is not specified then the default page size of 100 will be used.
Enter “40 biscuit” in the text box textBox1 and hit the button one more time. The two products matching the search criteria will be retrieved. Compare the result to the web app screenshot at the top.
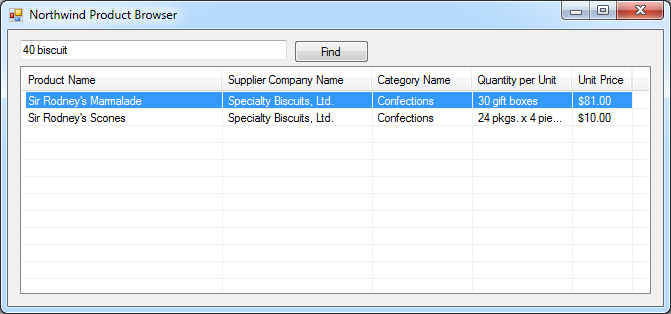
The same technique of data paging can be used in any application that supports XML or JSON data formats. That includes Java applications and mobile native Android and iPhone/iPad apps.