Code On Time web applications offer impressive adaptive filtering and search capabilities that require zero programming. Consider the following screen shot from the Northwind sample.
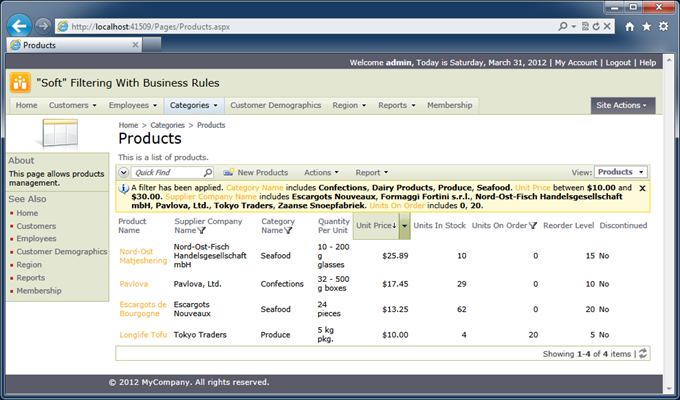
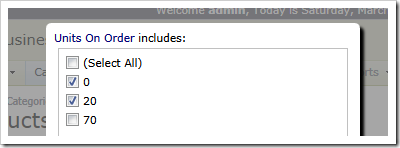
Application user has selected specific categories,
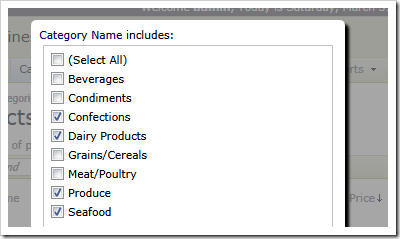
specific suppliers,
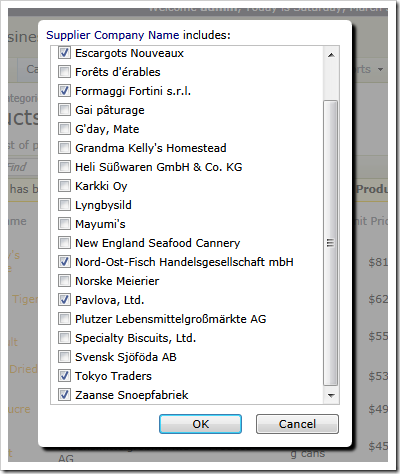
a range of prices,
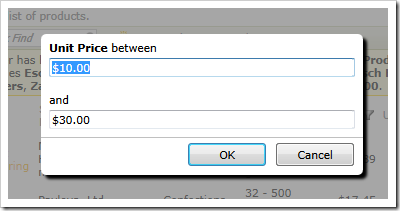
and specific values of product units on order.
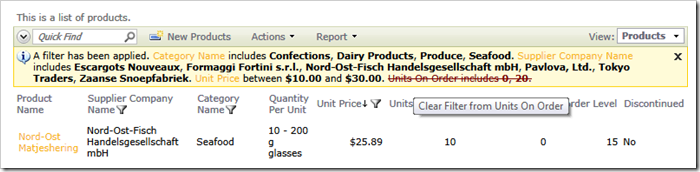
A user can remove the filter at will by either clicking on individual filter elements or dismissing the entire filter.
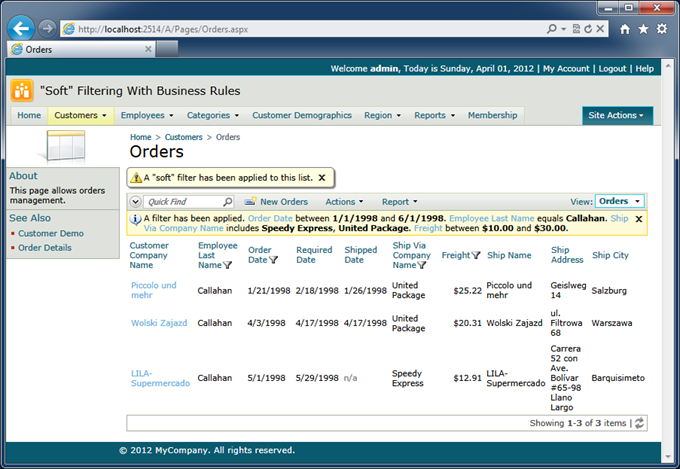
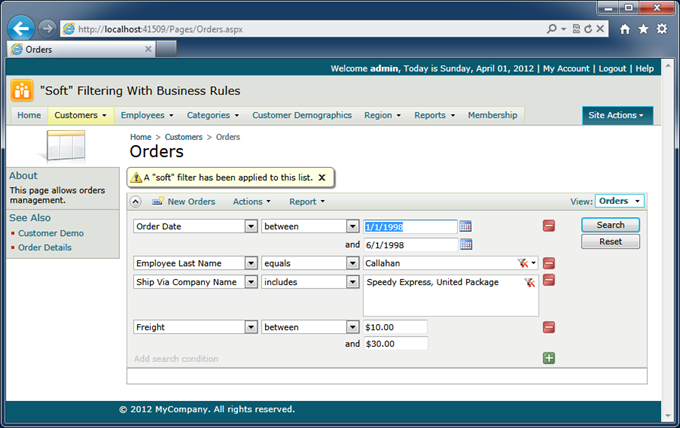
An application developer can also configure a filter based on arbitrary conditions at runtime. The filter can be constructed just before the data is retrieved from the database. Users will see the filter as if they have selected all options on their own. End users can always cancel or adjust the “soft” filter to reveal more data rows.
This may be useful when a specific data row has to be brought to the application user’s attention. “Soft” filtering will work even better when combined with the auto highlight first row or auto select first row features.
Enable shared business rules in your web application and enter the following code.
C#:
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using MyCompany.Data;
namespace MyCompany.Rules
{
public partial class SharedBusinessRules : MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
{
[ControllerAction("Orders", "grid1", "Select", ActionPhase.Before)]
public void AssignOrdersFilter()
{
if (!IsTagged("Filtered"))
{
AddTag("Filtered");
DateTime startDate = new DateTime(1998, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, DateTimeKind.Utc);
DateTime endDate = new DateTime(1998, 6, 1, 23, 59, 59, DateTimeKind.Utc);
AssignFilter(
new FilterValue("OrderDate",
RowFilterOperation.Between, startDate, endDate),
new FilterValue("EmployeeLastName",
RowFilterOperation.Equal, "Callahan"),
new FilterValue("ShipViaCompanyName",
RowFilterOperation.Includes, "Speedy Express", "United Package"),
new FilterValue("Freight",
RowFilterOperation.Between, 10, 30)
);
Result.ShowViewMessage("A \"soft\" filter has been applied to this list.");
}
}
}
}
Visual Basic:
Imports MyCompany.Data
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.Data
Imports System.Linq
Namespace MyCompany.Rules
Partial Public Class SharedBusinessRules
Inherits MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
<ControllerAction("Orders", "grid1", "Select", ActionPhase.Before)> _
Public Sub AssignOrdersFilter()
If Not IsTagged("Filtered") Then
AddTag("Filtered")
Dim startDate As DateTime = New DateTime(1998, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, DateTimeKind.Utc)
Dim endDate As DateTime = New DateTime(1998, 6, 1, 23, 59, 59,
DateTimeKind.Utc)
AssignFilter(
New FilterValue("OrderDate",
RowFilterOperation.Between, startDate, endDate),
New FilterValue("EmployeeLastName",
RowFilterOperation.Equal, "Callahan"),
New FilterValue("ShipViaCompanyName",
RowFilterOperation.Includes, "Speedy Express", "United Package"),
New FilterValue("Freight",
RowFilterOperation.Between, 10, 30)
)
Result.ShowViewMessage("A ""soft"" filter has been applied to this list.")
End If
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Save the code file and navigate to the page Orders. The method AssignOrdersFilter will be invoked when the data is about to be retrieved. The method will apply a filter one time only in the lifecycle of the page instance displayed in the web browser to prevent interference with application user actions.
Notice that we are filtering by UTC dates to ensure that Microsoft.NET will not try to compensate for the time difference between the server and the web browser.
In the end, the method will display a view-level message rendered just above the grid view informing the app user about the “soft”- filter.
Select data view Customers/ Orders / container1 / view in the Project Explorer.
If you enable Search On Start in the data view properties then the Orders page will open up with the search bar pre-filled with filter values and no data will be displayed. Users will have to click Search to initiate the retrieval of data.
If you have enabled automatic selection or highlighting of the first row in the properties of the page data view then the view will perform the first action in the context menu of the first data row or simulate a click in the first row. This sort of behavior will happen even if you do not “soft” filter the data.
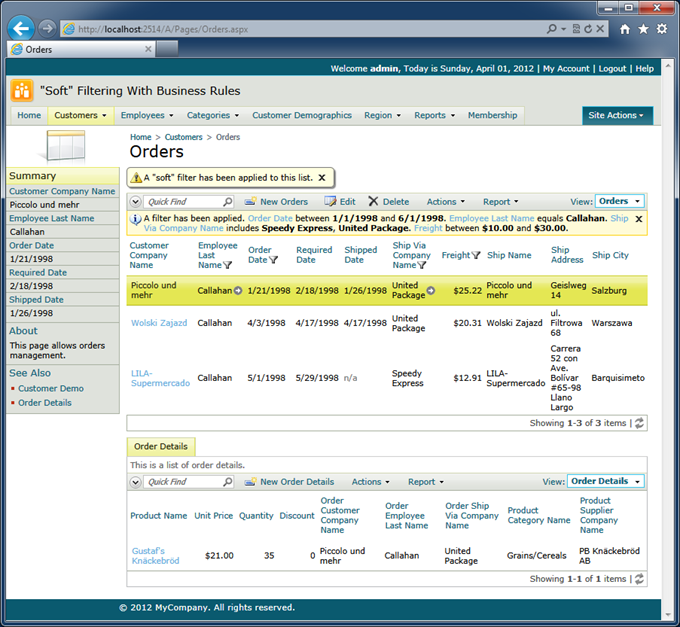
You can also coincide the selection or highlighting of the first row with the assignment of a “soft” filter in business rules by calling Result.SelectFirstRow or Result.HightlightFirstRow right after the call of ShowViewMessage method.
For example, this is the effect of Result.HighlightFirstRow method call.
Developers should use access control rules or filter expressions when the application business logic does not permit cancellation of data filters at will by the application users.