In businesses that require a lot of driving and tracking packages, it is invaluable to estimate a driving distance between two different addresses or sets of latitude/longitude. Starting in release 8.5.11.0, C# and Visual Basic business rules now have access to the CalculateDistance() method. This method will query the Google Distance Matrix API to estimate driving distance.
It is required to obtain and add a Maps API Identifier to your project in order to use this feature.
Please make sure to follow Google Maps APIs Terms Of Service. Of note is section 10.5.d, which restricts long-term storage of Content.
Let’s add a custom action to the Employees page that, when pressed, will display how far the employee lives from the main office using a code business rule.
First, we need to add an action that will be accessible to the user in order to trigger the code.
Start the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab. Right-click on “Employees / Actions / ag1 (Grid)” node, and press New Action.
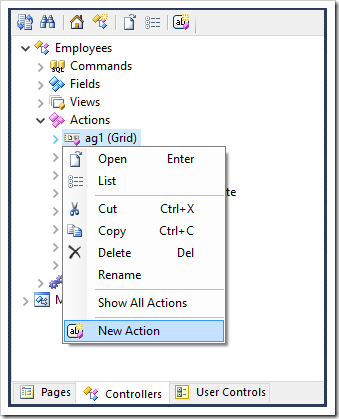
Enter the following settings:
| Property | Value |
| Command Name | Custom |
| Command Argument | DistanceFromHQ |
| Header Text | Distance From HQ |
| When Key Selected | Yes |
Press OK to save. Next, let’s create a business rule that will be triggered when the user presses the action. Right-click on “Employees / Business Rules”, and press New Business Rule.
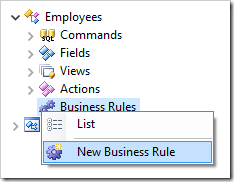
Enter the following properties:
| Property | Value |
| Type | C# / Visual Basic |
| Command Name | Custom |
| Command Argument | DistanceFromHQ |
| Phase | Execute |
Press OK to save the business rule. On the toolbar, press Browse to generate the application and create the rule file.
When generation is complete, press “Edit Rule” on the action bar to open the file in Visual Studio.
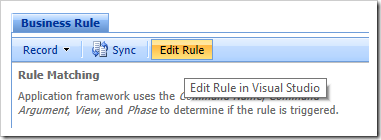
Replace the contents with the following:
C#:
using System.Data;
using MyCompany.Data;
using MyCompany.Models;
namespace MyCompany.Rules
{
public partial class EmployeesBusinessRules : MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
{
/// <summary>
/// This method will execute in any view for an action
/// with a command name that matches "Custom"
/// and argument that matches "DistanceFromHQ".
/// </summary>
[Rule("r100")]
public void r100Implementation(EmployeesModel instance)
{
// combine address pieces with ","
string sourceAddress = string.Join(",", instance.Address, instance.City,
instance.Region, instance.PostalCode, instance.Country);
string destinationAddress = "1 Microsoft Way,Redmond,Washington";
// get distance and calculate miles
decimal meters = CalculateDistance(sourceAddress, destinationAddress);
decimal miles = meters * 0.00062137m;
// show result
if (meters == 0)
Result.ShowAlert("No path found.");
else
Result.ShowAlert("Distance from HQ is " + meters
+ " meters, or " + miles + " miles");
}
}
}
Visual Basic:
Imports MyCompany.Data
Imports MyCompany.Models
Namespace MyCompany.Rules
Partial Public Class EmployeesBusinessRules
Inherits MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
''' <summary>
''' This method will execute in any view for an action
''' with a command name that matches "Custom"
''' and argument that matches "DistanceFromHQ".
''' </summary>
<Rule("r100")>
Public Sub r100Implementation(ByVal instance As EmployeesModel)
' combine address pieces with ","
Dim sourceAddress = String.Join(",", instance.Address, instance.City,
instance.Region, instance.PostalCode, instance.Country)
Dim destinationAddress = "1 Microsoft Way,Redmond,Washington"
' get distance and calculate miles
Dim meters = CalculateDistance(sourceAddress, destinationAddress)
Dim miles = meters * 0.00062137D
' show result
If (meters = 0) Then
Result.ShowAlert("No path found.")
Else
Result.ShowAlert("Distance from HQ is " & meters &
" meters, or " & miles & " miles")
End If
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
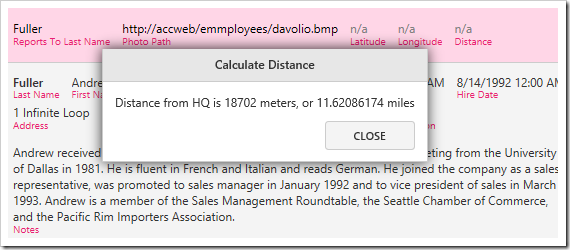
Switch back to the web browser, and press the three dot menu button next to any row to reveal the grid action menu.
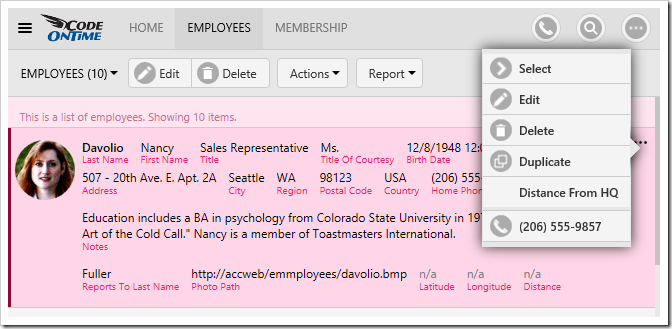
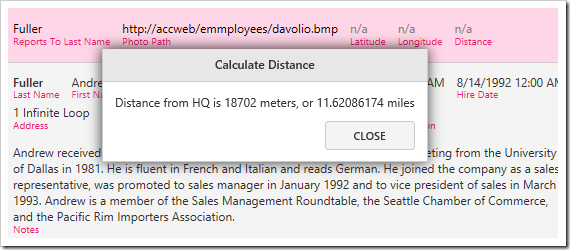
Press “Distance From HQ” action, and a message box will display the distance.
Note that it is also possible to pass a latitude and longitude by separating the values with a comma, such as in the following example:
CalculateDistance(instance.Latitude + "," + instance.Longitude, destinationAddress)