Code On Time web applications designed for Internet access have an option to include a built-in Membership Manager. This tool works on top of Microsoft ASP.NET Membership to simplify user and role management in generated apps. It uses exactly the same data controller architecture as the rest of data controllers in a project.
Data controllers aspnet_Membership and aspnet_Roles are automatically created in a web application if the membership feature is enabled.
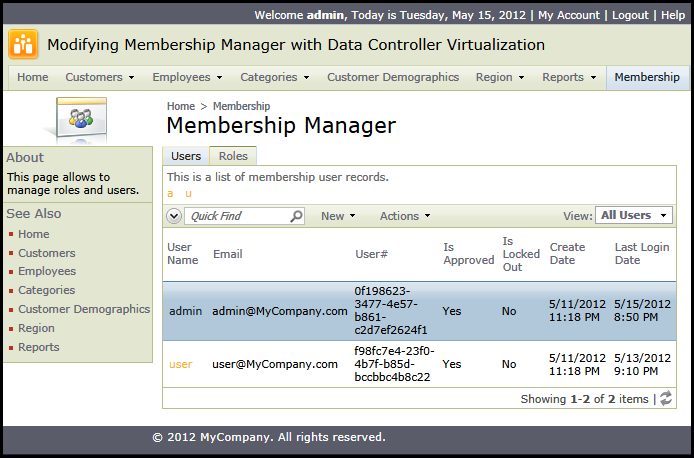
This is a typical view of Membership Manager presented if you sign in as admin and navigate to Membership page.
The data controller files can be changed in Visual Studio but the changes will be overwritten by the application generator.
Instead, consider the data controller virtualization when you need to modify the membership manager.
Select the project name on the start page of the generator and choose Develop option. Visual Studio will load the project for editing. Create a new code file Class1.cs(vb) under ~/App_Code/Security folder of your project.
Enter the following definition of the partial class MembershipBusinessRules to virtualize the data controller definition at runtime.
C#:
using System;
using MyCompany.Data;
namespace MyCompany.Security
{
public partial class MembershipBusinessRules
{
public override bool SupportsVirtualization(string controllerName)
{
return true;
}
protected override void VirtualizeController(string controllerName)
{
// remove lookup capability from the field "UserId"
NodeSet().SelectField("UserId")
.SetItemsStyle(null)
.SetItemsController(null)
.SetItemsNewView(null);
// select "grid1" view
NodeSet().SelectView("grid1")
// add data field "UserId"
.CreateDataField("UserId")
.SetReadOnly(true)
// delete data field "Comment"
.SelectDataField("Comment")
.Delete();
// select "grid1" view
NodeSet().SelectView("grid1")
// re-arrange the data fields
.ArrangeDataFields("UserUserName", "Email", "UserId");
}
}
}
Visual Basic:
Imports MyCompany.Data
Imports System
Namespace MyCompany.Security
Partial Public Class MembershipBusinessRules
Public Overrides Function SupportsVirtualization(controllerName As String) As Boolean
Return True
End Function
Protected Overrides Sub VirtualizeController(controllerName As String)
' remove lookup capability from the field "UserId"
NodeSet().SelectField("UserId") _
.SetItemsStyle(Nothing) _
.SetItemsController(Nothing) _
.SetItemsNewView(Nothing)
' select "grid1" view, add data field "UserId", and delete data field "Comment"
NodeSet().SelectView("grid1") _
.CreateDataField("UserId") _
.SetReadOnly(True) _
.SelectDataField("Comment") _
.Delete()
' select "grid1" view and re-arrange the data fields
NodeSet().SelectView("grid1") _
.ArrangeDataFields("UserUserName", "Email", "UserId")
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
The new partial class complements the standard class MembershipBusinessRulesBase included in the application framework. It is possible to override any standard methods such as SignUpUser or UpdateUser. The implementation above overrides the data controller virtualization methods only.
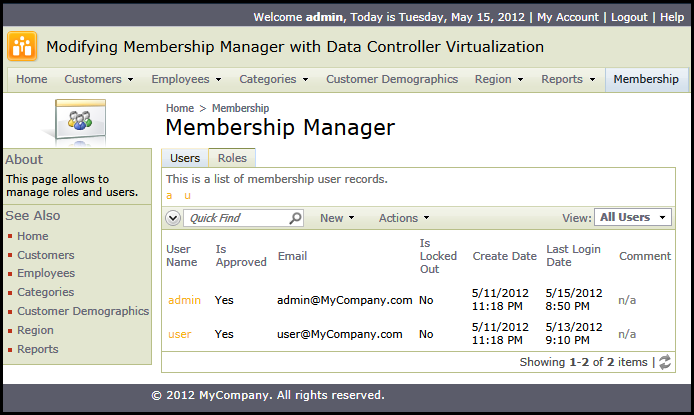
Save the code file and navigate to Membership Manager.
You will see the global unique ID of each user. The data field Comment is not visible anymore. The remaining data fields are re-arranged.