Fast paced and hectic business days exert a high toll on information workers. Having summary views of the current task items replaces digging and searching through numerous screens in a line-of-business application.
Well constructed summary task views will reflect the actual workflow of the business process. Summary views ensure happy and productive business users. Throw in automatic task view refreshing without any intervention and the level of happiness in application users is likely to increase even more.
Objective
Consider the home page of the Northwind sample. We can greatly improve the life of folks working in the shipping department by replacing the standard site map and login instructions with the summary of orders waiting to ship and orders that were shipped late. Both workflow task views will refresh at predefined intervals.
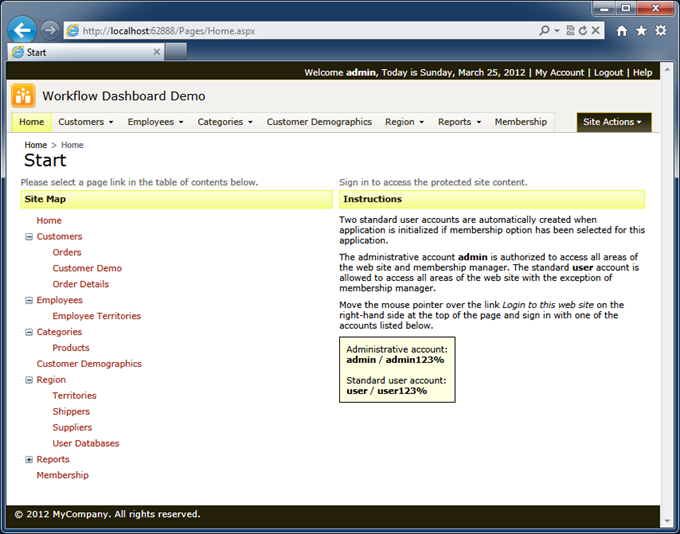
This is how the home page of the application may look.
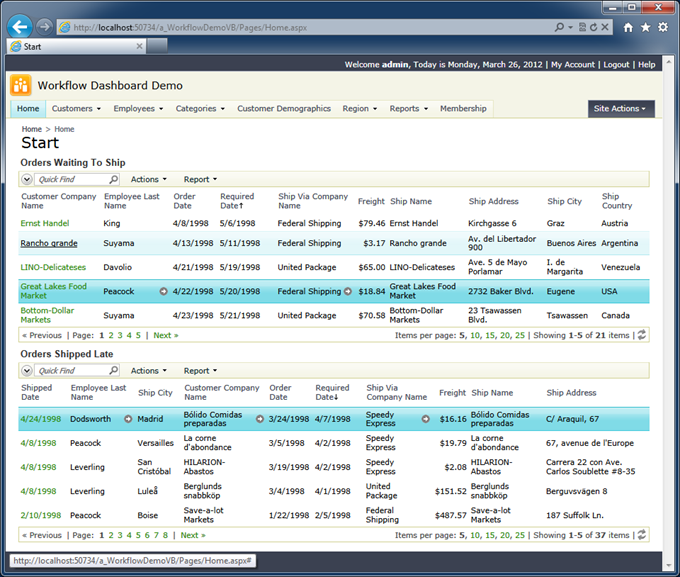
Changing Home Page
Select the project name on the start page of the web application generator and click Design.
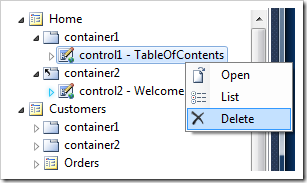
Expand the Home node in the Project Explorer and delete the user control instances Home / container1 / control1 and Home / container2 / control2. Right-click each control node and choose Delete option to delete a control instance.
Change the properties of Home / container2 as follows and click OK button.
| Property | Value |
| Flow | New Row |
| CSS Style Properties | margin-top:8px; |
Right-click Home / container1 and add a new data view to the container.
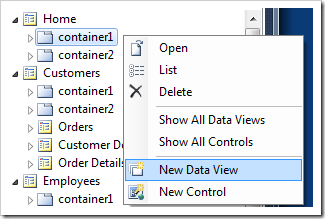
Enter the properties of the data view as shown in the table and save changes.
| Property | Value |
| Controller | Orders |
| View | grid1 |
| Tag | OrdersWaitingToShip |
| Text | Orders Waiting to Ship |
| Page Size | 5 |
| Show View Description | False |
| Show View Selector | False |
| Refresh Interval | 30 |
Add another data view to Home / container2. This time the properties of the data view are slightly different.
| Property | Value |
| Controller | Orders |
| View | grid1 |
| Tag | OrdersShippedLate |
| Text | Orders Shipped Late |
| Page Size | 5 |
| Show View Description | False |
| Show View Selector | False |
| Refresh Interval | 300 |
Click OK button to save the properties of the second data view. The Home page node in the Project Explorer will look as follows.
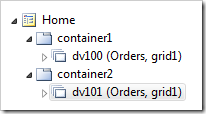
Click Browse button to preview the changes.
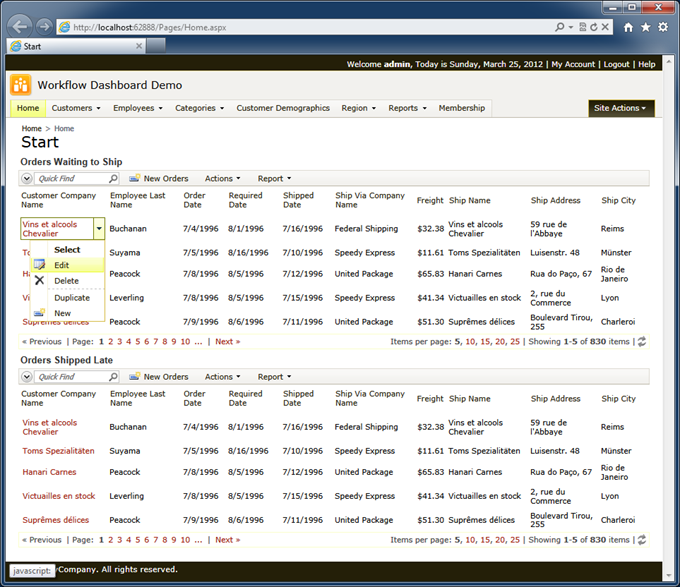
The start page of the application shows two identical data views of Orders. Both views allow changing any orders on screen and show the entire set of orders stored in the database.
Enabling Dedicated Login Page
The home page of the Northwind sample application is not protected. Anonymous users can see the contents of the page. Users are authenticated by entering name and password in the fly-over login window. The login window is activated when users hover over the “Login” link in right-hand corner of the membership bar at the top of the page.
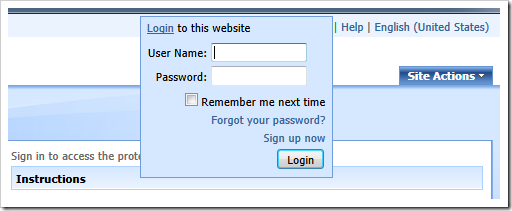
Perform the following steps to hide the home page from anonymous users.
Exit the Project Designer and click Settings.
Select Authentication and Membership option in the menu and proceed to Login Window section. Enable a dedicated login page instead of a fly-over login window.
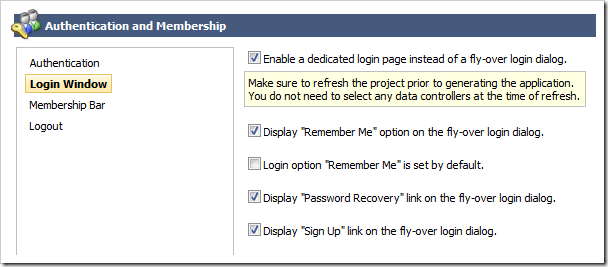
Click Finish to save the changes.
The application baseline needs to be refreshed. Select Refresh option on the project Summary page. The Refresh dialog will be displayed with the list of application data controllers.
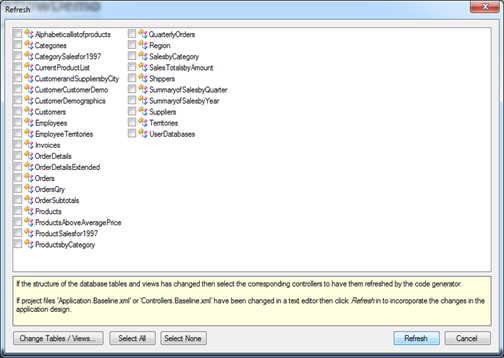
Do not select anything in the list. Simply click the Refresh button at the bottom of the dialog to complete the refresh process. A dedicated login page will be created next time you re-generate the application.
Enabling Shared Business Rules
We will change the appearance of the Orders on the Home page with the help of data controller virtualization and dynamic access control rules supported in the application framework. This will require writing some code.
For the purpose of this demo we will create a SharesBusinessRules class. Click Settings on the project Summary page and continue to Business Logic Layer. Activate shared business rules and click Finish. You will arrive back to the project Summary page. Proceed to generate the application.
You will be greeted by the dedicated login page when the code generation completes.
The application framework creates an instance of SharedBusinessRules class whenever you access a page that displays data. Page data views send requests to your application. Instances of business rules are created to service each and every request.
You will not see any effect of shared business rules at this time - custom business logic has not been implemented yet.
Altering Presentation of Orders on Home Page
First we will change the appearance of orders waiting to ship and orders that were shipped late.
Select the project name on the start page of the application generator and click Develop. The project source code will be displayed in Visual Studio or Visual Web Developer.
Open the file ~/App_Code/Rules/SharedBusinessRules.cs(vb) in the text editor of your development environment.
Replace the default implementation with the following code.
C#:
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using MyCompany.Data;
namespace MyCompany.Rules
{
public partial class SharedBusinessRules : MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
{
public override bool SupportsVirtualization(string controllerName)
{
if (controllerName == "Orders" && IsTagged("OrdersWaitingToShip",
"OrdersShippedLate"))
return true;
return false;
}
}
}
Visual Basic:
Imports MyCompany.Data
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.Data
Imports System.Linq
Namespace MyCompany.Rules
Partial Public Class SharedBusinessRules
Inherits MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
Public Overrides Function SupportsVirtualization(controllerName As String) As Boolean
If controllerName = "Orders" AndAlso IsTagged("OrdersWaitingToShip",
"OrdersShippedLate") Then
Return True
End If
Return False
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
Our application will detect when Orders data controller is supposed to produce data in response to the requests from the Orders data views located on the Home page. The code verifies the controller name and ensures that the requesting data views are tagged as OrdersWaitingToShip or OrdersShippedLate. If the method SupportsVirtualization returns true then the application framework will give business rules a chance to modify the definition of the Orders data controller.
We do not want any virtualization changes to go beyond the home page. If users visit the automatically generated Orders page, then no unusual behavior will be seen there.
Now it is time to decide what are we going to change in the presentation of orders on the Home page.
We will:
- make the controller read-only by removing editing actions;
- delete all remaining actions in the context menu of the grid view;
- add new 'Navigate' action redirecting application user to the “unchanged” Orders page when an order is selected in grid view;
- hide “ShippedDate” data field in the “orders waiting to ship” view;
- sort “orders waiting to ship” in ascending order of “RequiredDate”;
- add “ShipCountry” data field to the “orders waiting to ship”;
- sort “orders shipped late” in descending order of “RequiredDate”;
- rearrange “orders shipped late” in such a way that “ShippedDate”, “EmployeeID”, and “ShipCity” are displayed first.
These sound like a handful!
The snippet of the Orders controller shows the content that must be affected by our modifications.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<dataController name="Orders" conflictDetection="overwriteChanges" label="Orders"
xmlns="urn:schemas-codeontime-com:data-aquarium">
. . . . .
<views>
<view id="grid1" type="Grid" commandId="command1" label="Orders">
<headerText>$DefaultGridViewDescription</headerText>
<dataFields>
<dataField fieldName="CustomerID" aliasFieldName="CustomerCompanyName" />
<dataField fieldName="EmployeeID" aliasFieldName="EmployeeLastName" />
<dataField fieldName="OrderDate" columns="10" />
<dataField fieldName="RequiredDate" columns="10" />
<dataField fieldName="ShippedDate" columns="10" />
<dataField fieldName="ShipVia" aliasFieldName="ShipViaCompanyName" />
<dataField fieldName="Freight" dataFormatString="c" columns="15" />
<dataField fieldName="ShipName" columns="40" />
<dataField fieldName="ShipAddress" />
<dataField fieldName="ShipCity" columns="15" />
</dataFields>
</view>
. . . . .
<actions>
<actionGroup id="ag1" scope="Grid">
<action id="a1" commandName="Select" commandArgument="editForm1" />
<action id="a2" commandName="Edit" />
<action id="a3" commandName="Delete" />
<action id="a6" />
<action id="a7" commandName="Duplicate" commandArgument="createForm1" />
<action id="a8" commandName="New" commandArgument="grid1" />
</actionGroup>
<actionGroup id="ag2" scope="Form">
<action id="a1" commandName="Edit" />
<action id="a2" commandName="Delete" />
. . . . .
</actionGroup>
<actionGroup id="ag3" scope="ActionBar" headerText="New" flat="true">
<action id="a1" commandName="New" commandArgument="createForm1" cssClass="NewIcon" />
</actionGroup>
<actionGroup id="ag4" scope="ActionBar" headerText="Edit/Delete" flat="true">
<action id="a1" whenKeySelected="true" commandName="Edit" commandArgument="editForm1"
cssClass="EditIcon" whenView="grid1" />
<action id="a2" whenKeySelected="true" commandName="Delete"
cssClass="DeleteIcon" whenView="grid1" />
</actionGroup>
<actionGroup id="ag5" scope="ActionBar" headerText="Actions">
. . . . .
<action id="a6" commandName="Import" commandArgument="createForm1" />
</actionGroup>
</actions>
</dataController>
Making changes to the data controller in a text editor would not be difficult. One could copy, rename, move, and change various portions of the file to accomplish the desired result.
We don’t want to change the static definition of the data controller.
Multiple versions of the same controller are not welcomed either -
this would become a maintenance nightmare.
Data Controller Virtualization comes to the rescue. It allows conditional modification of the data controller at runtime. Developer becomes a true magician and dynamically alters the actual definition of the controller based on a given use case.
Add the following implementation of the method VirtualizeController to the SharedBusinesRules class. The implementation takes advantage of the method BusinessRules.NodeSet() and molds the data controller definition at runtime according to the specification suggested above.
C#:
protected override void VirtualizeController(string controllerName)
{
if (controllerName == "Orders" && IsTagged("OrdersWaitingToShip", "OrdersShippedLate"))
{
// make the controller read-only by removing editing actions
NodeSet("action[@commandName = $name]",
"New", "Edit", "Delete", "Duplicate", "Import").Delete();
// delete all remaining actions in the 'Grid' scope
NodeSet("actionGroup[@scope='Grid']")
.Select("action").Delete();
// add new 'Navigate' action to the 'Grid' scope
NodeSet("<action>")
.Attr("commandName", "Navigate")
.Attr("commandArgument",
"Orders.aspx?OrderID={OrderID}&_controller=Orders" +
"&_commandName=Edit&_commandArgument=editForm1")
.AppendTo("c:actionGroup[@scope='Grid']");
}
if (IsTagged("OrdersWaitingToShip"))
{
// sort 'grid1' and hide the 'ShippedDate' data field
NodeSet("view[@id='grid1']")
.Attr("sortExpression", "RequiredDate asc")
.Select("dataField[@fieldName='ShippedDate']")
.Attr("hidden", "true");
// add data field 'ShipCountry' to 'grid1' view
NodeSet("<dataField>").Attr("fieldName", "ShipCountry")
.AppendTo("view[@id='grid1']/dataFields");
}
if (IsTagged("OrdersShippedLate"))
// sort and rearrange 'grid1' by placing ShippedDate, EmployeeID, and ShipCity first
NodeSet("view[@id='grid1']")
.Attr("sortExpression", "RequiredDate desc")
.Select("dataField")
.Arrange("@fieldName", "ShippedDate", "EmployeeID", "ShipCity");
}
Visual Basic:
Protected Overrides Sub VirtualizeController(controllerName As String)
If (controllerName = "Orders" AndAlso IsTagged("OrdersWaitingToShip", "OrdersShippedLate")) Then
' make the controller read-only by removing editing actions
NodeSet("action[@commandName = $name]",
"New", "Edit", "Delete", "Duplicate", "Import").Delete()
' delete all remaining actions in the 'Grid' scope
NodeSet("actionGroup[@scope='Grid']") _
.Select("action").Delete()
' add new 'Navigate' action to the 'Grid' scope
NodeSet("<action>") _
.Attr("commandName", "Navigate") _
.Attr("commandArgument",
"Orders.aspx?OrderID={OrderID}&_controller=Orders" +
"&_commandName=Edit&_commandArgument=editForm1") _
.AppendTo("c:actionGroup[@scope='Grid']")
End If
If (IsTagged("OrdersWaitingToShip")) Then
' sort grid1 and hide the 'ShippedDate' data field
NodeSet("view[@id='grid1']") _
.Attr("sortExpression", "RequiredDate asc") _
.Select("dataField[@fieldName='ShippedDate']") _
.Attr("hidden", "true")
' add data field 'ShipCountry' to 'grid1' view
NodeSet("<dataField>").Attr("fieldName", "ShipCountry") _
.AppendTo("view[@id='grid1']/dataFields")
End If
If (IsTagged("OrdersShippedLate")) Then
' sort and rearrange 'grid1' by placing ShippedDate, EmployeeID, and ShipCity first
NodeSet("view[@id='grid1']") _
.Attr("sortExpression", "RequiredDate desc") _
.Select("dataField") _
.Arrange("@fieldName", "ShippedDate", "EmployeeID", "ShipCity")
End If
End Sub
The code only executes when the data is requested from the home page by the views tagged as OrdersWaitingToShip and OrdersShippedLate. Go ahead and take a look at the effect of modifications in the web browser.
Presenting Orders Waiting To Ship or Shipped Late
We need to filter both home page data views to show a specific subset of orders reflecting the view’s purpose. The following implementation of method EnumerateDynamicAccessControlRules will do the job.
C#:
protected override void EnumerateDynamicAccessControlRules(string controllerName)
{
if (IsTagged("OrdersWaitingToShip"))
RegisterAccessControlRule("OrderID",
"[ShippedDate] is null",
AccessPermission.Allow);
if (IsTagged("OrdersShippedLate"))
RegisterAccessControlRule("OrderID",
"[ShippedDate] is not null and [RequiredDate] < [ShippedDate]",
AccessPermission.Allow);
}
Visual Basic:
Protected Overrides Sub EnumerateDynamicAccessControlRules(controllerName As String)
If (IsTagged("OrdersWaitingToShip")) Then
RegisterAccessControlRule("OrderID",
"[ShippedDate] is null",
AccessPermission.Allow)
End If
If (IsTagged("OrdersShippedLate")) Then
RegisterAccessControlRule("OrderID",
"[ShippedDate] is not null and [RequiredDate] < [ShippedDate]",
AccessPermission.Allow)
End If
End Sub
The data view tagged as OrdersWaitingToShip will show the orders with the empty “ShippedDate”.
The data view tagged with OrdersShippedLate will show the orders that were shipped but the required date is less than the shipped date.
Analyzing Dashboard Capabilities
Here is the dashboard reflecting the business workflow of the shipping department at our fictitious mail order company Northwind.
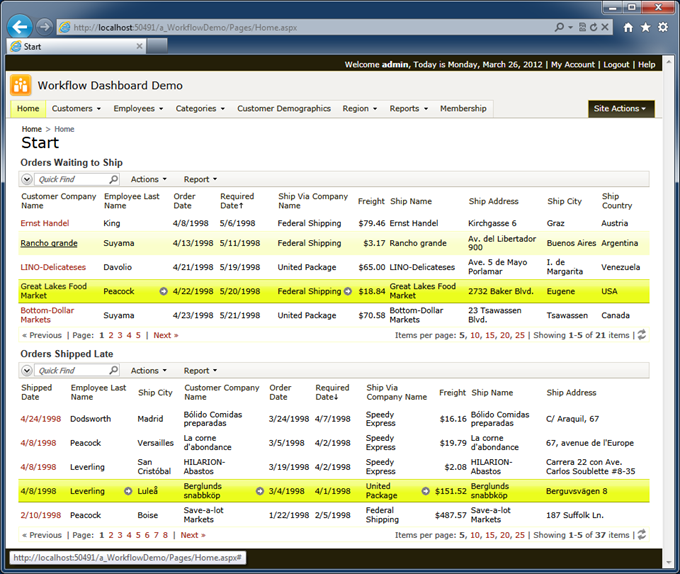
Users are not able to change data in the views. The row context menu is not displayed when users move the mouse pointer over the links in the first column. Action bar does not display New Orders and Import actions.
Columns in the grid views are rearranged.
The top view is sorted in ascending order of “Required Date”. Column “Shipped Date” is not displayed.
The bottom view is sorted in descending order of “Required Date”. The first columns are “Shipped Date”, “Employee ID” (aliased with “Employee Last Name”), and “Ship City”.
The top view is automatically refreshed every 30 seconds. The bottom one is refreshed every 5 minutes. The refreshing happens if user is not interacting with the views longer than their respective refresh intervals.
If a user clicks on any link in the first column of either grid view then the web browser will navigate to the Orders page. The page will open with the selected order presented in edit mode.
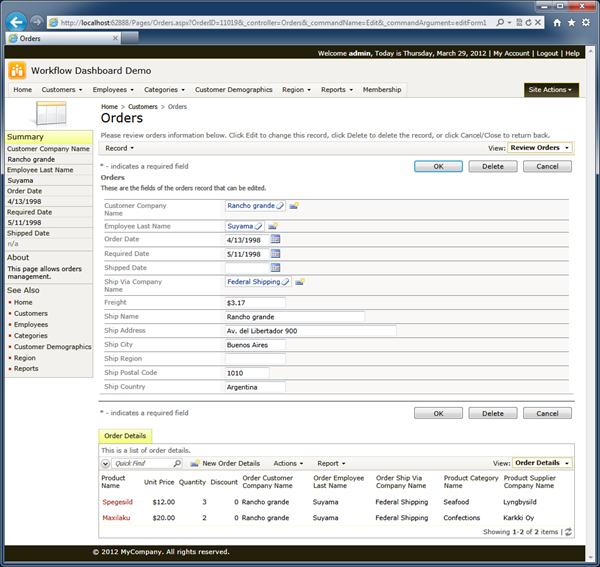
Users can edit or add new Order Details while remaining on the same Orders page.
Users will be transferred back to the home page as soon they click on OK or Cancel buttons in the Orders form.
Notice that the automatically generated Orders page is not affected by virtualization rules. Navigate to the Orders page by selecting Customers / Orders menu option and you will see the default layout of the grid view and data editing commands unchanged.
URL Hashing
Look close at the URL in the address bar of the browser when user navigates to the Orders page. You will see something like this:
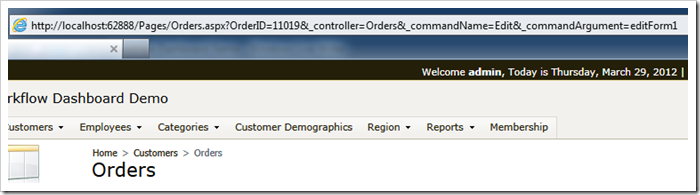
You can easily spot the OrderID and data controller URL parameters activating the edit mode of the order form.
Sometimes you do not wish to reveal this information.
Select the project name on the start page of the application generator and click Settings. Continues to Features and activate EASE Configuration. Enable the URL Hashing option.
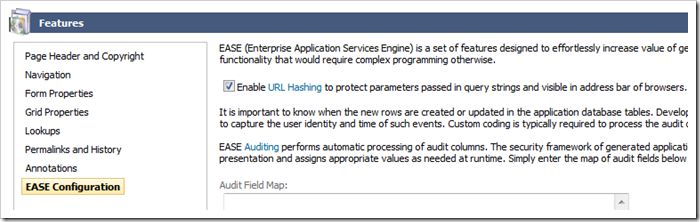
Click Finish button and generate the app. Select any order and observer that the URL is not as revealing as previously.
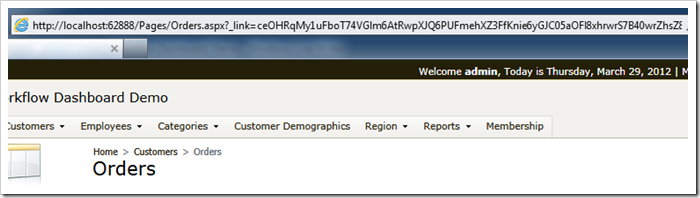
Any attempts to alter the URL will result in Access Denied message. Learn about URL Hashing.
Conclusion
Data Controller Virtualization enables rapid development of complex workflow dashboards. Developers can treat the core application data controllers as a collection of building blocks. Developers can alter the definition of data controllers based on arbitrary conditions such as user identity or use case of the data controller as was explained above.
Virtualization plugins allows rapid development of virtualization rules by eliminating the need to use XML elements in the node sets.