Every user of a computer has experienced a situation when they really wish they could wind back time. From hardware failure losing recent work, to changes made to a file that need to be undone, this capability is necessary to ensure productivity is not lost.
Software development is no different. The most common solution to this problem is through the use of source control systems such as Git, Microsoft Team Foundation Services (TFS), or Apache Subversion (SVN). These solutions will monitor a specific set of files, and allow the user to “commit” a version of files to a repository. When necessary, the user can revert to older versions of these files. Even better, it allows the development of software projects among multiple users.
Code OnTime app generator makes it easy to use source control with your project. When the type of source control is specified, the generator will create requisite files that allow easy exchange of application files and changes made to project configuration.
Getting Started With Source Control
Let’s place our sample Northwind project under source control using Git. On the home page of the app generator, click on the project name. Select “Settings” from the Project Action screen, and then select “Source Code and UI”.
From the Source Control dropdown, select “Git”.
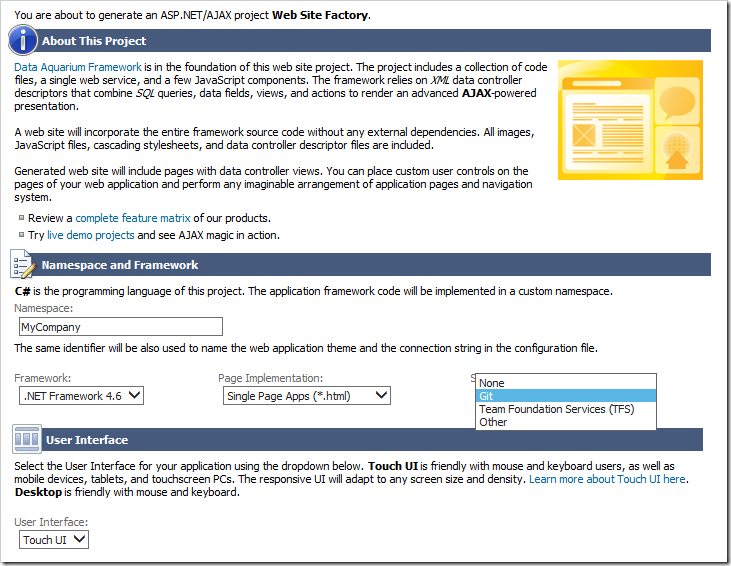
Press the Finish button, and then press “Generate” to generate the application. If the project folder is inspected, two files have been added to the root.
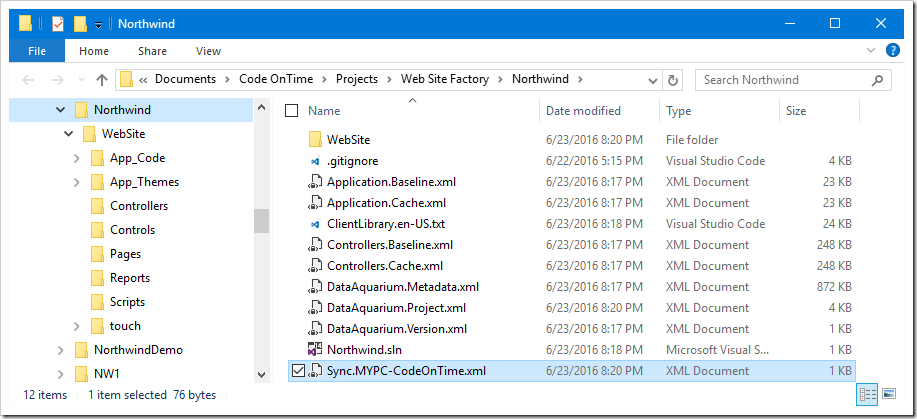
A default “.gitignore” file is added, based on the standard file created by Visual Studio, with several Code OnTime files listed at the bottom. If TFS source control was selected, a corresponding “.tfignore” file will be added.
The other file will be named “Sync.[Machine Name]-[User Name].xml”. This file holds all transactions made in the Project Designer by the current user and machine. When the application is refreshed, all “Sync.XXX.xml” files at the root of the project will be merged together and sorted by transaction timestamp. The merged file is used to create the “Controllers.Log.xml” and “Application.Log.xml”, which hold transactions that are applied to controllers and application pages, controls, and data views, respectively.
This allows work from multiple machines to be smoothly integrated, without having to deal with manually merging XML files.
Next, let’s push this project to a new repository. This process may differ based on the source control and tool used to initialize the repository.
On the home page of the app generator, select the project name and press Develop to open the project in Visual Studio.
In the Solution Explorer (typically found on the right side of the screen), right-click on the solution node and press “Add Solution to Source Control”.
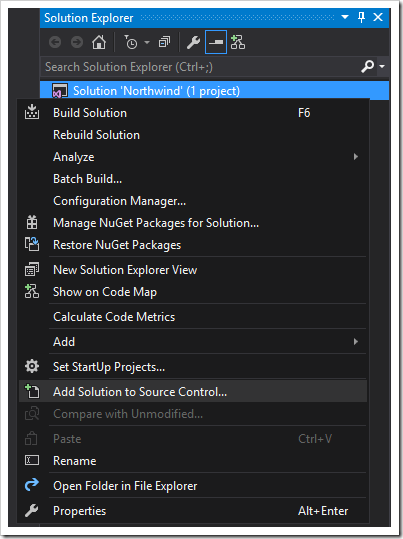
In the “Choose Source Control” popup that opens, select “Git” and press OK.
If the Visual Studio Git Provider has not been used before, it will require configuring your user name and email address. Click the “Configure” link, visible at the top of the Team Explorer window, set your desired settings, and press Update.
Next, enter a commit message, and press Commit to create the first commit in your local repository. Make sure that the necessary files are included in the commit.
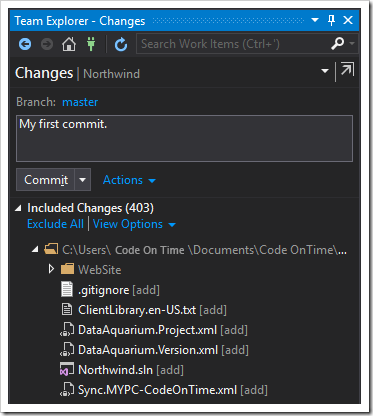
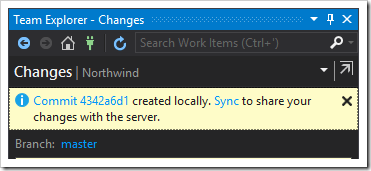
If the commit was successful, a message will appear at the top of the screen, stating that the commit was created. It will also prompt to sync the repository with a server. Click the “Sync” link to sync to a server.
The same screen can be reached by pressing the Home icon from any screen, and selecting “Sync” option.
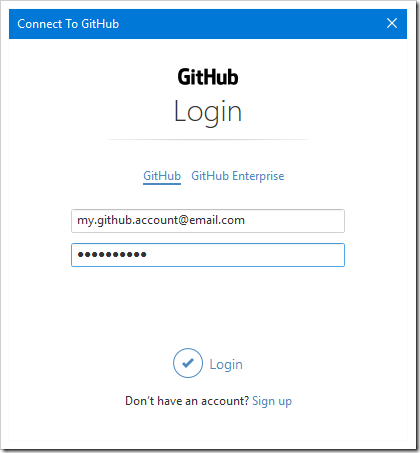
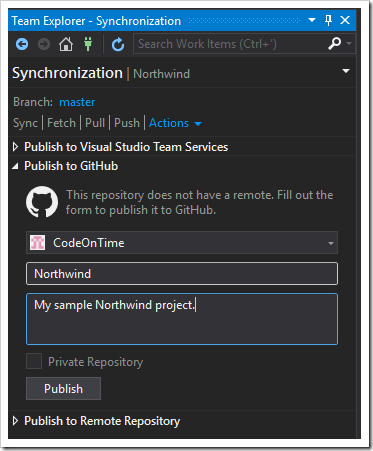
Several options will be available. For this example, we will use GitHub. If you have not logged into GitHub on this computer, click the “Login” button, enter your credentials, and press “Login” again.
Select “Get Started” link under the “Publish to Github” section.
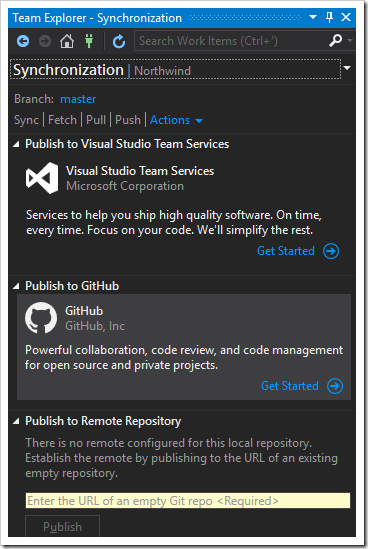
Select your account, enter a repository name, and add a description (optional). Please note that private repositories require a subscription on GitHub. If the repository is public, then anyone can find the source code on the Internet. Choose accordingly.
Press Publish to push your repo to GitHub.
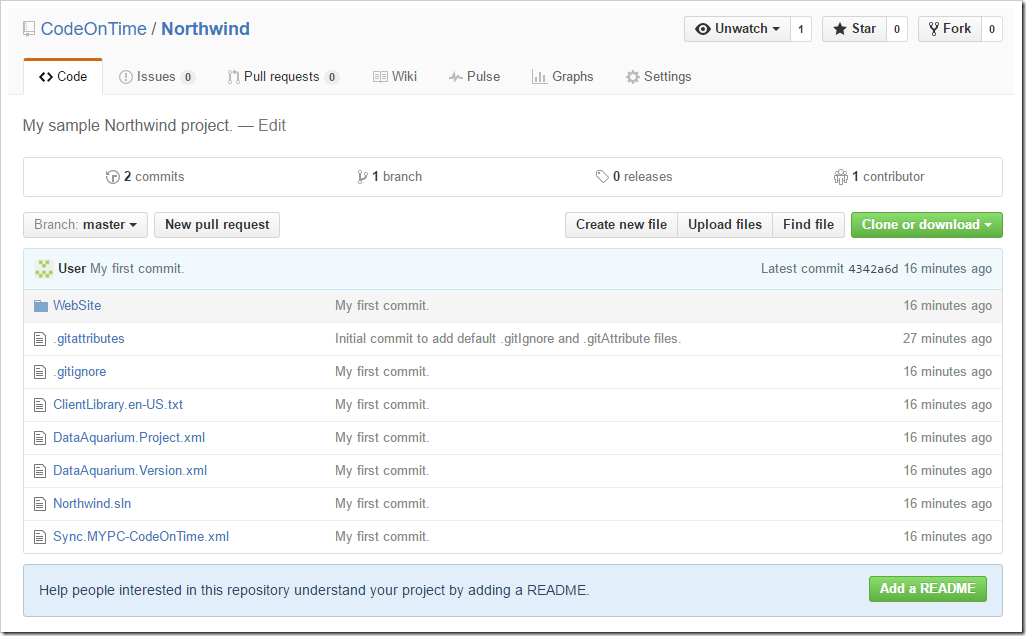
Once the upload process is complete, you will be able to access your repository online.
Synchronizing Changes
Now that the repository is online, you will need to synchronize it. Suppose that several changes have been made to the web app. Pages have been shuffled around, data fields customized, models added, business rules changed. Make sure to generate the application before synchronizing any changes.
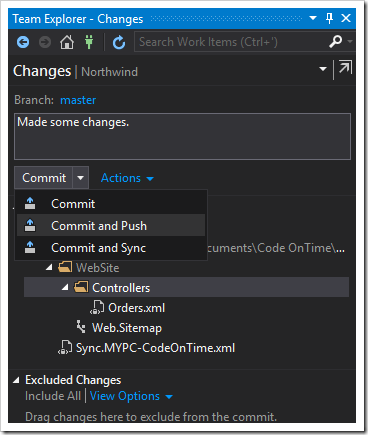
Open the project in Visual Studio, open the Team Explorer, and select “Changes”. You can also right-click on the solution and press “Commit”.
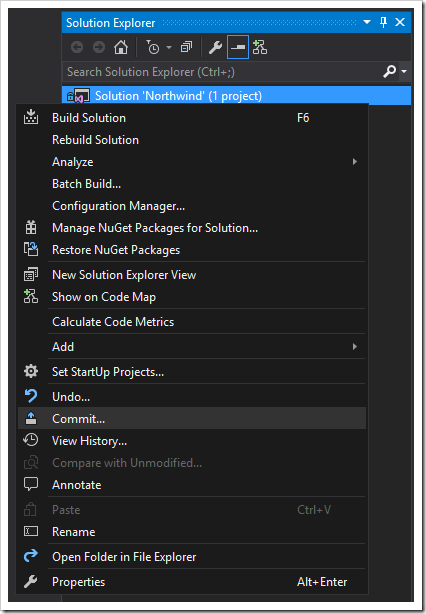
Enter a commit message, and click the dropdown next to “Commit”.
Press the “Commit” button if you wish to create a local commit, but not upload your changes to the server.
Press “Commit and Push” to upload your commit to the server.
Press “Commit and Sync” to upload your commit, and download any changes that may have been pushed to the server previously.
At this point in time, press “Commit and Push”.
When the process is complete, a message will be displayed.
Downloading a Web App From Source Control
Suppose a team member has joined your team. You will need to give your teammate access to your repository. Log into your repository server and give your team member’s account access to the repo.
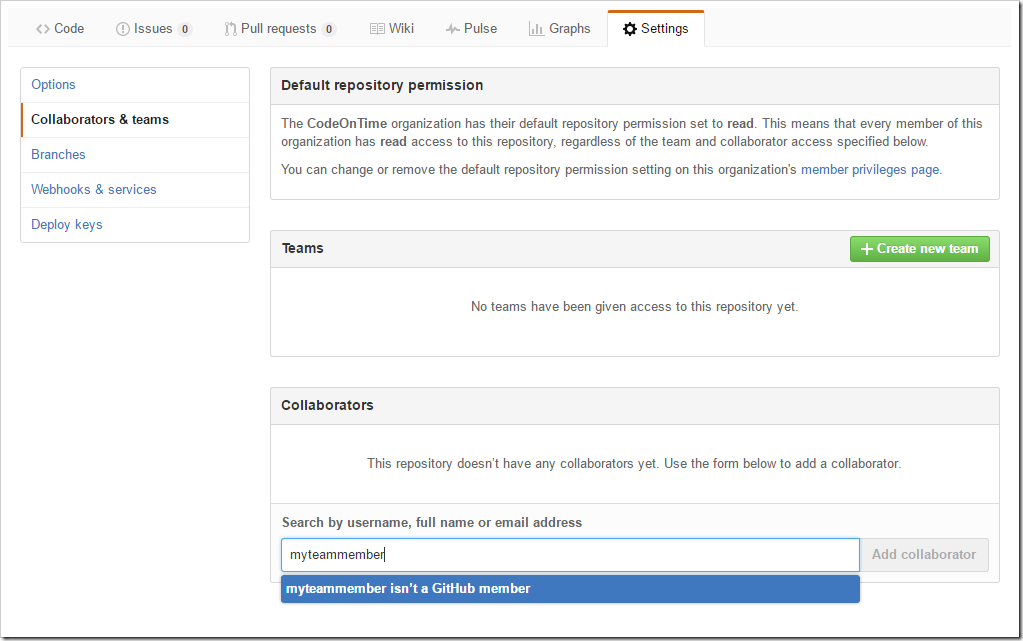
For a GitHub repo, you will need to navigate to the correct webpage on the GitHub website. Select the Settings tab near the top of the screen, and switch to the “Collaborators & Teams” section. Enter your member’s screen name in the Search bar and press “Add collaborator”.
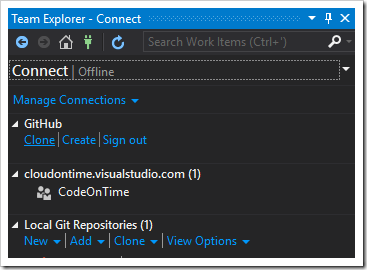
On your team member’s computer, start Visual Studio. Press “Open From Source Control…” on the Start Page if visible. Otherwise, press the green Connections icon on the Team Explorer.
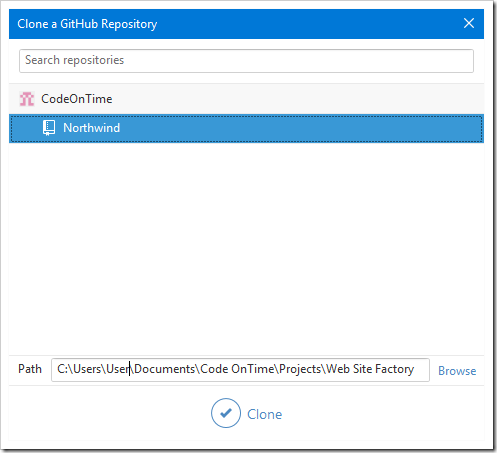
Select the “Clone” link under GitHub section. Click the repository you shared with the team member, and enter the correct path. In this case, the path is “~/Documents/Code OnTime/Projects/Web Site Factory”.
Restart the app generator. If the repository has been placed in the correct location, a new project will appear in the project list.
Pulling Changes From The Server
Suppose that your team member has made some changes, and you wish to pull these changes down to your computer.
Open the project in Visual Studio. In the Team Explorer, select “Sync” button.
The Synchronization pane offers several options.
The “Fetch” button will download pending commits, but will not integrate changes.
The “Pull” button will download pending commits and perform merge operations if necessary to bring your repository in line with the server.
The “Sync” button will uploading pending commits, downloads commits from the server, and performs merge operations to integrate remote changes with your local changes.
At this time, press “Sync”. The commits made by your coworker will be downloaded and integrated.
One last step is needed. Switch back to Code OnTime app generator. Select the project name, and press “Refresh”. This will integrate synced changes into the current project.