The state of real world business objects modeled in the application database is frequently determined by the values of multiple object attributes.
For example, an order status may depend on the Order Date and Shipped Date. It would take some time for an end user to analyze the values to understand the status of an order. It would be beneficial for an application to provide a graphical representation of the order status.
Let’s implement a graphical representation of the internal object state using the Orders table of the Northwind sample. Most records have Shipped Date before Required Date. Some records do not have a value in the Shipped Date column. Other records have a Shipped Date past the Required Date.
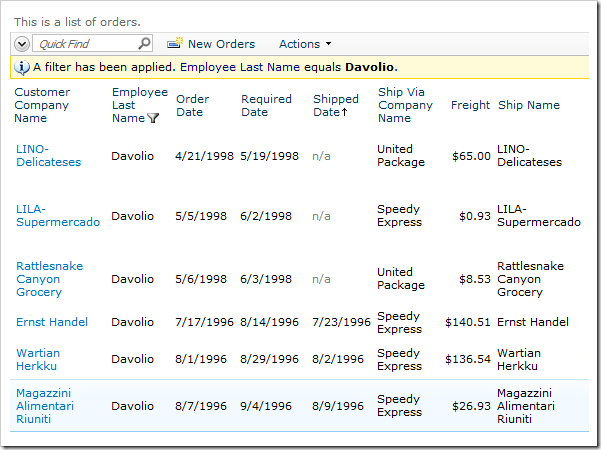
It would be reasonable to assume that records without a Shipped Date have not been shipped yet, records that have a Shipped Date past the Required Date have been shipped late, and that the order is on time when the Shipped Date is before Required Date.
Start the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab. Right-click on Orders / Fields node, and select New Field option.
Give this field the following settings:
| Property | Value |
| Name | Status |
| Type | String |
| Length | 50 |
| The value of this field is computed at run-time by SQL expression. | True |
| SQL Formula | case
when ShippedDate is null
then 'Waiting To Ship'
when ShippedDate < RequiredDate
then 'Shipped'
when ShippedDate > RequiredDate
then 'Shipped Late'
end
|
| Label |
Status |
| Values of this field cannot be edited |
True |
Press OK to save the field. Right-click on Orders / Views / editForm1 / c1 – Orders node, and select New Data Field.
Give this data field the following settings:
| Property |
Value |
| Field Name |
Status |
| The field is hidden |
True |
Double-click on Orders controller node.
Change the Status Bar property:
| Property |
New Value |
| Status Bar |
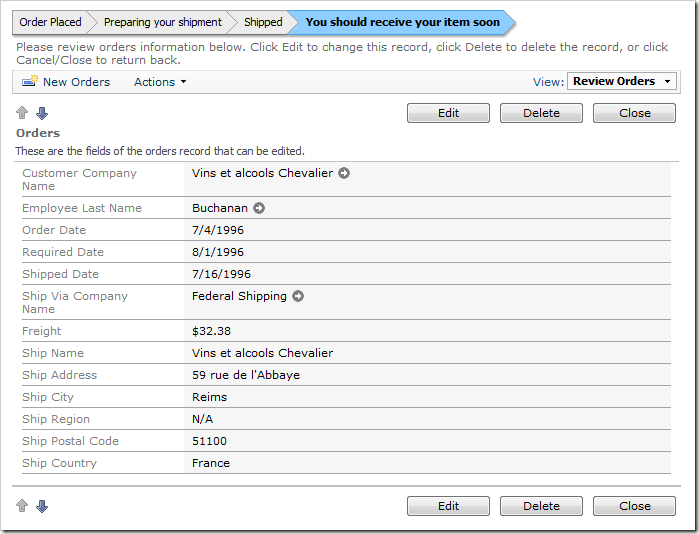
Orders.editForm1.Status: Shipped
Order Placed > Preparing your shipment > Shipped > [You should receive your item soon] >
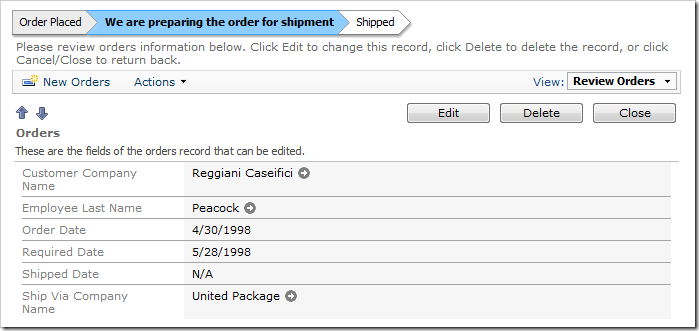
Orders.editForm1.Status: Waiting To Ship
Order Placed > [We are preparing the order for shipment] > Shipped >
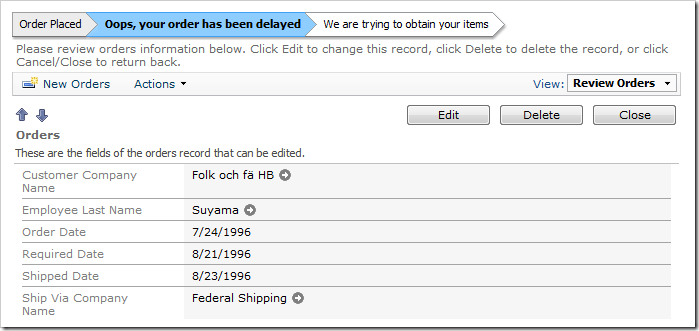
Orders.editForm1.Status: Shipped Late
Order Placed > [Oops, your order has been delayed] > We are trying to obtain your items >
|
Press OK to save the controller. On the toolbar, press Browse.
Navigate to the Orders page. Select an order in which the Shipped Date is before the Required Date. A status bar above the form provides a quick status update on the status of the order.
Select an order where Shipped Date is after Required Date. The status bar shows that the order has been delayed.
Finally, select an order without a value in Shipped Date field. The status bar will show that the order has not yet been shipped.
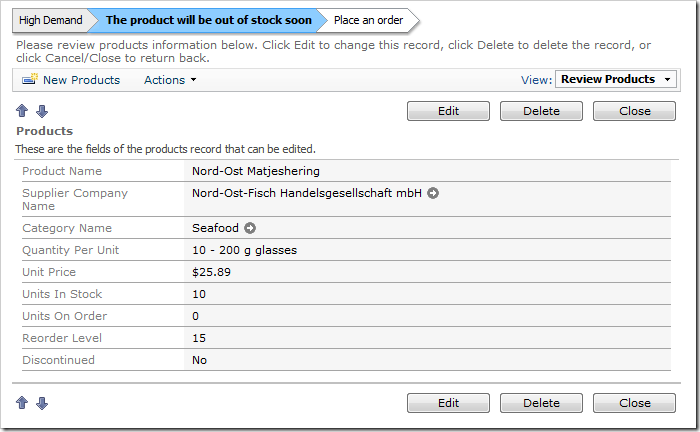
Status can be figured with complex calculations. For example, we configured the following SQL Formula for a new Status field in Products controller:
case
when Discontinued = 1
then 'Discontinued'
when UnitsInStock + UnitsOnOrder < ReorderLevel
then 'Low On Stock'
when UnitsOnOrder > 0
then 'On Order'
when UnitsOnOrder = 0
then 'In Stock'
end
The Status Bar configuration for Products controller looks like this:
Products.Status: Discontinued
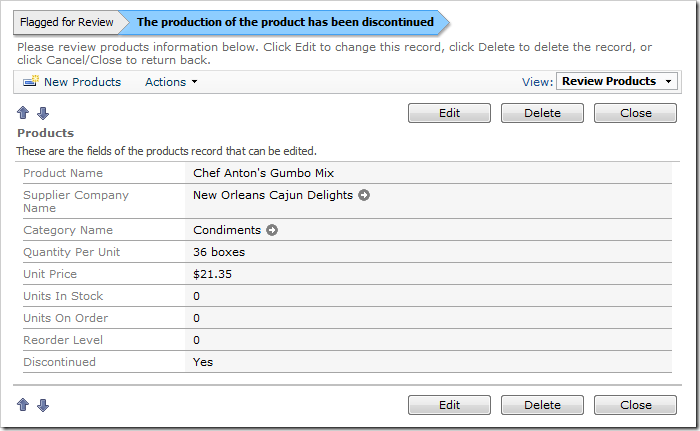
Flagged for Review > [ The production of the product has been discontinued] >
Products.Status: Low On Stock
High Demand > [The product will be out of stock soon] > Place an order >
Products.Status: On Order
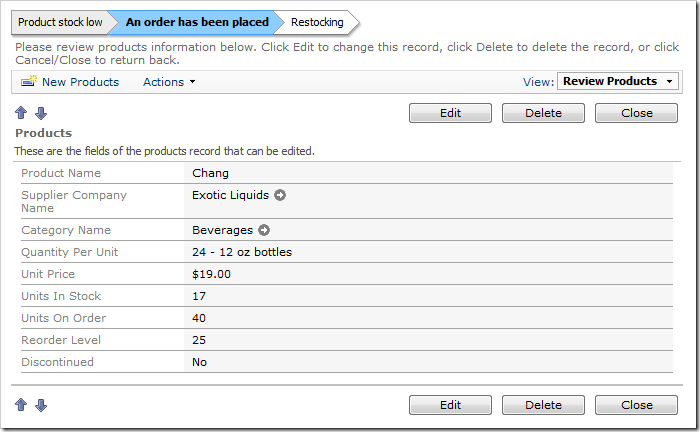
Product stock low > [An order has been placed] > Restocking >
Products.Status: In Stock
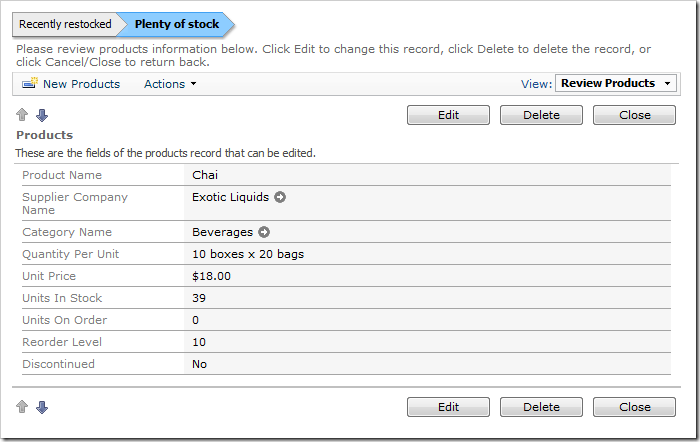
Recently restocked > [Plenty of stock] >
A product that has a large amount of Units In Stock will display the following status bar.
When there are a large amount of Units On Order, the status bar will notify that there is sufficient items ordered.
Discontinued products will be displayed like the picture below.
When the stock is low, the status bar will warn the user.