Commands are used by the controller to select data.
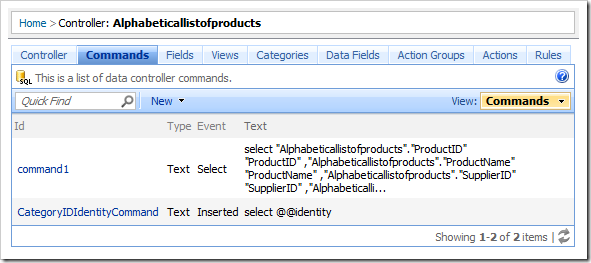
Commands can be accessed by selecting a controller and switching to the Commands tab.
The context menu option List on the Commands node in the Project Explorer will also navigate to the list of commands.
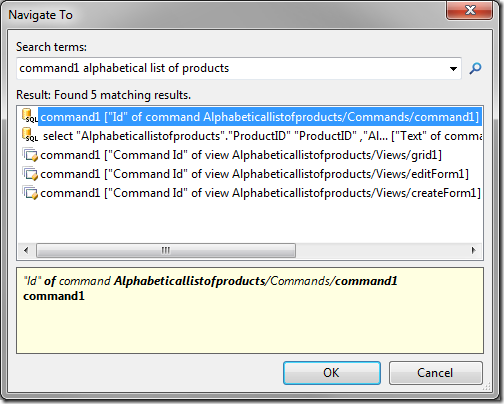
A command can be located by entering the command Id and controller Name in the configuration navigator.
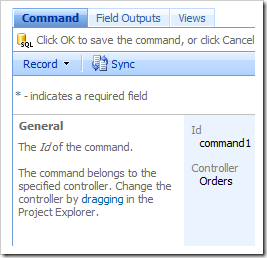
Clicking on the Id or using the context menu option View in the list of commands will navigate to the properties page of the command.
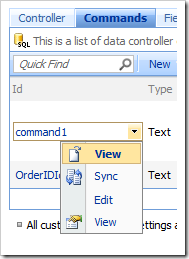
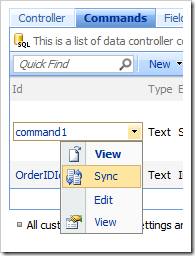
The Sync context menu option will select the relevant project configuration node in the Project Explorer.
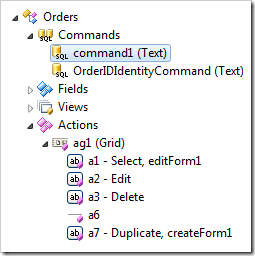
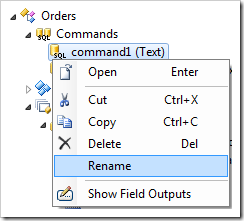
The command Id can be changed using the Rename context menu option in the Project Explorer.
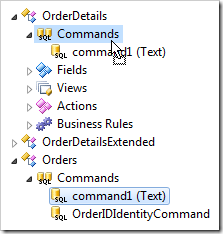
The Controller of the command can be changed by dragging the command node.
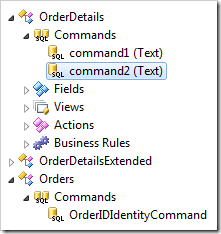
Commands are recreated by the web application generator every time the baseline is refreshed. If the developer modifies the command, automatic recreation will no longer occur, and the developer must update the command by hand.
The “Reset to Baseline” context menu option will restore the command to baseline state.