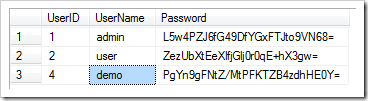
Create “Users” table in the application database using one of the scripts of a minimal membership and roles provider . Configure custom membership and generate the project.
Minimal Membership Provider in Action
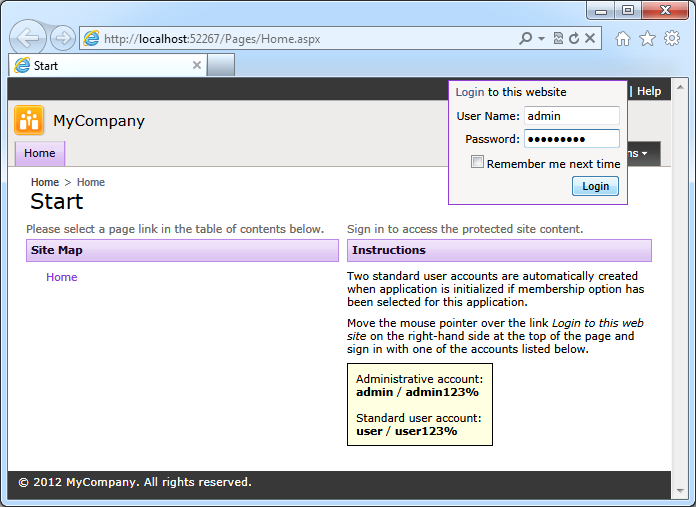
The application will open in a default web browser. Move mouse pointer over the “Login” link and sign in using one of the two accounts automatically created by the app.
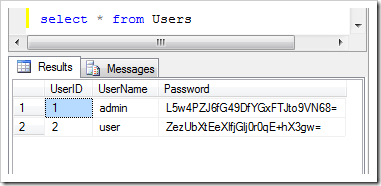
Optional standard user accounts are created when the application starts. Use SQL Management Studio to select records from “Users” table. Passwords “admin123%” and “user123%” of the corresponding user accounts are hashed by the membership provider.
User Manager
Management of users can be seamlessly integrated in an application.
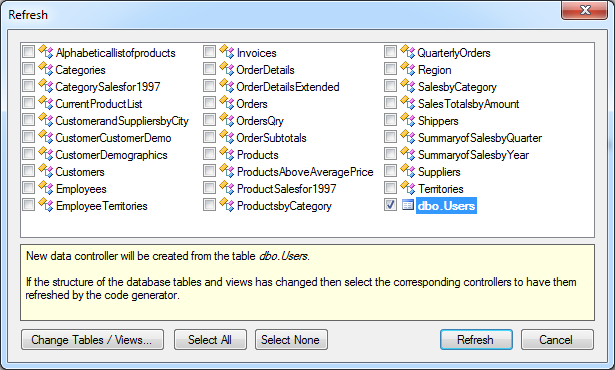
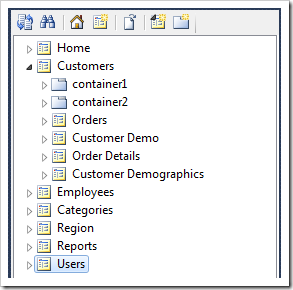
Select the project name on the start page of generator and choose Refresh. The Refresh window of Northwind project with selected Users table is shown next.
Click Refresh button to create Users data controller in the application.
Select Design to activate the Project Designer.
Press “Ctrl” and “comma” keys simultaneously (Ctrl+,) to active the Navigate To window. Enter “users” in Search terms and click on the first match.
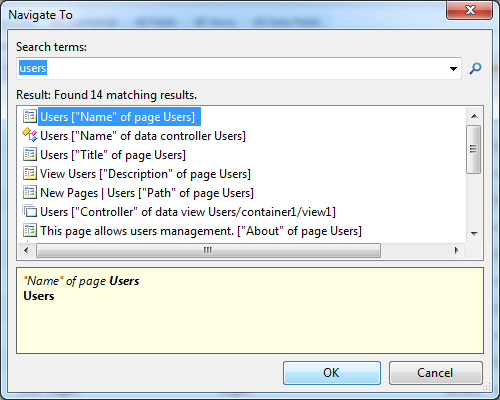
The corresponding page node will be displayed in Project Explorer. Drag the the page node to the desired location in the navigation menu.
In the page properties enter Administrators to restrict access to the page. Only a user in Administrators role will be authorized to access the page. This snippet form the provider configuration does the job.
role Administrators = admin
role Users = admin, user
role Everybody = *
Right-click Users page node and choose View in Browser, sign in as admin / admin123% and click on user account. The form view editForm1 of data controller Users is shown in the screen shot
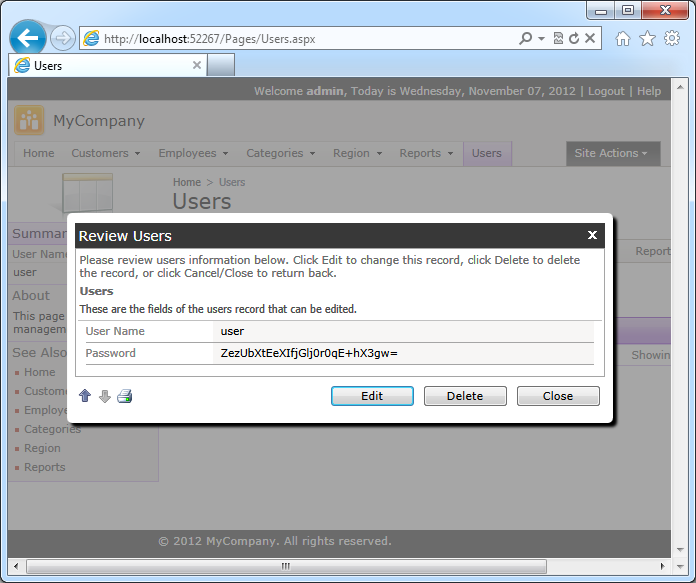
The user manager will require some work:
- The Password field is displayed as plain text. The value of the field must not be revealed to the users.
- If a password is changed by administrator then the value must be hashed before it is stored in the database.
- A new password must be validated according to the membership provider configuration.
Switch to Project Designer and navigate to Users data controller.
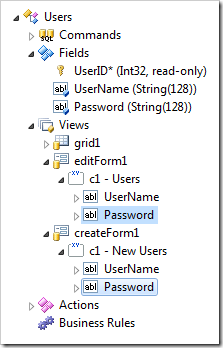
Change Text Mode property of data field nodes Users / Views / editForm1 / c1 – Users and Users / Views / createForm1 / c1 – New Users to “Password”.
The password encryption and validation will require writing some code. Right-click Users / Business Rules node and choose “New Business Rule” option.
Configure the following properties:
| Property | Value |
| Type | C# / Visual Basic |
| Command Name | Update|Insert |
| Phase | Before |
Click “Generate” button on the designer tool bar. Wait for the app to display in the Preview Window and switch back to Project Designer. The placeholder file for the implementation of the business rule has been created. Right-click the business rule in Project Explorer and choose Edit in Visual Studio.
Visual Studio will start with business rule code file ready for modification. Replace the contents with the following.
C#:
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Security;
using MyCompany.Data;
using MyCompany.Security;
namespace MyCompany.Rules
{
public partial class UsersBusinessRules : MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
{
/// <summary>
/// This method will execute in any view before an action
/// with a command name that matches "Insert|New".
/// </summary>
[Rule("r100")]
public void r100Implementation(System.Guid? userID, string userName,
FieldValue password)
{
if (password != null && password.Modified)
{
ApplicationMembershipProvider.ValidateUserPassword(userName,
(string)password.NewValue);
password.NewValue =
ApplicationMembershipProvider.EncodeUserPassword((string)password.NewValue);
}
}
}
}
Visual Basic:
Imports MyCompany.Data
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.Data
Imports System.Linq
Imports System.Text.RegularExpressions
Imports System.Web
Imports System.Web.Security
Imports MyCompany.Security
Namespace Rules
Partial Public Class UsersBusinessRules
Inherits MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
''' <summary>
''' This method will execute in any view before an action
''' with a command name that matches "Update|Insert".
''' </summary>
<Rule("r100")> _
Public Sub r100Implementation(ByVal userID As Nullable(Of Integer),
ByVal userName As String, ByVal password As FieldValue)
If Not password Is Nothing And password.Modified Then
ApplicationMembershipProvider.ValidateUserPassword(userName, password.NewValue)
password.NewValue =
ApplicationMembershipProvider.EncodeUserPassword(password.NewValue)
End If
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
The highlighted namespace MyCompany.Security links the namespace with the membership provider implementation to the code file.
The original type of the argument password has been changed from “String” to “FieldValue” to allow access to Modified and NewValue properties describing the password value submitted by the client application.
A call to the static method ValidateUserPassword checks conformance of a password with the membership provider configuration requirements. By default, a password must be at least seven characters long, and have at least one non-alphanumeric character. Use provider configuration options Min Requires Password Length and Min Required Non Alpha Numeric Characters to change that.
Next, the business rule will encode the password value according to the membership provider configuration. The default option requires password hashing.
Save the code file and refresh the Users page. Try creating a new user.
Password validation exceptions will be displayed to users.
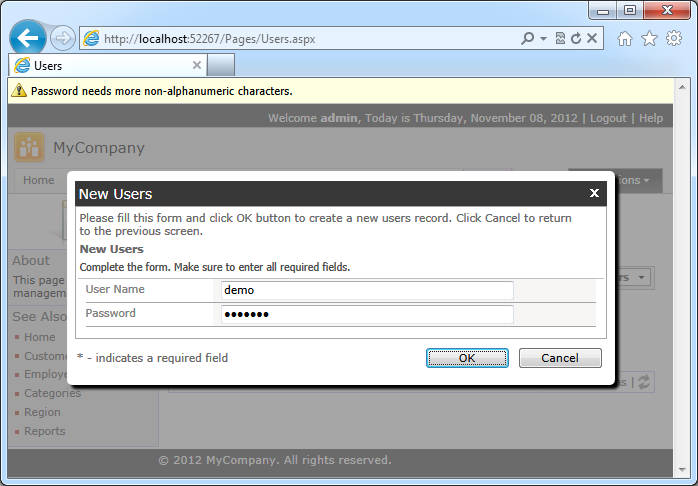
A successfully created user account will have its password “hashed”.