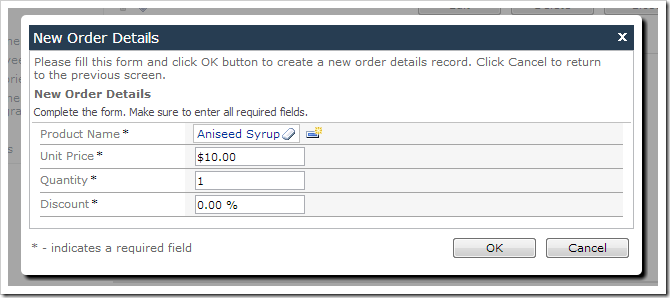
Let’s assign default values to fields Quantity and Discount of a new order detail record. These fields already have server defaults that are added when the order detail is saved to the database. It would be better to have these defaults displayed to the user before insertion, and have Discount formatted as percentage.
There are multiple ways of assigning a default value to the field. The following sections will describe each method.
SQL Business Rule
Switch to the Project Designer, and right-click on OrderDetails / Business Rules node. Select New Business Rule option.
Assign the following values:
| Property | Value |
| Type | SQL |
| Command Name | New |
| Phase | Execute |
| Script | set @Quantity = 1
set @Discount = 0
|
Press OK to save. On the toolbar, press Browse.
Navigate to the Order Form page, and select an order. Create a new order detail, and select a product. The Quantity and Discount fields will be populated with default values.
Code Business Rule
The Quantity and Discount fields can also be assigned defaults using C#or Visual Basic.
If you have created the SQL business rule in the previous section, delete it now.
Right-click on OrderDetails / Business Rules node, and press New Business Rule.
Assign the following values:
| Property |
Value |
| Type |
C# / Visual Basic |
| Command Name |
New |
| Phase |
Execute |
Press OK to save the business rule. On the toolbar, press Browse to regenerate the web application and create the business rule file.
When complete, right-click on OrderDetails / Business Rules / New (Code / Execute) – r100 node, and press Edit Rule in Visual Studio.
The file will open in Visual Studio. Replace the body of the predefined business rule method with the following:
C#:
using System;
using MyCompany.Data;
namespace MyCompany.Rules
{
public partial class OrderDetailsBusinessRules : MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
{
[Rule("r100")]
public void r100Implementation(int? orderID,
string orderCustomerID,
string orderCustomerCompanyName,
string orderEmployeeLastName,
string orderShipViaCompanyName,
int? productID,
string productProductName,
string productCategoryCategoryName,
string productSupplierCompanyName,
decimal? unitPrice,
short? quantity,
float? discount)
{
UpdateFieldValue("Quantity", 1);
UpdateFieldValue("Discount", 0);
}
}
}
Visual Basic:
Imports MyCompany.Data
Imports System
Namespace MyCompany.Rules
Partial Public Class OrderDetailsBusinessRules
Inherits MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
<Rule("r100")> _
Public Sub r100Implementation(ByVal orderID As Nullable(Of Integer),
ByVal orderCustomerID As String,
ByVal orderCustomerCompanyName As String,
ByVal orderEmployeeLastName As String,
ByVal orderShipViaCompanyName As String,
ByVal productID As Nullable(Of Integer),
ByVal productProductName As String,
ByVal productCategoryCategoryName As String,
ByVal productSupplierCompanyName As String,
ByVal unitPrice As Nullable(Of Decimal),
ByVal quantity As Nullable(Of Short),
ByVal discount As Nullable(Of Single))
UpdateFieldValue("Quantity", 1)
UpdateFieldValue("Discount", 0)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Save the file. The default values will function as described earlier when an order detail record is created.
JavaScript Business Rule
The third method of implementation is by using JavaScript.
If you have created the SQL or Code business rules described above, delete them now.
Right-click on OrderDetails / Business Rules node, and press New Business Rule.
Assign the following values:
| Property |
Value |
| Type |
JavaScript |
| Command Name |
New |
| Phase |
After |
| Script |
[Quantity] = 0;
[Discount] = 1;
|
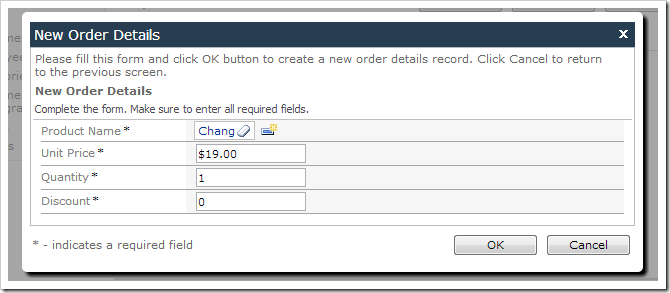
Press OK to save. If you browse the application and create a new order detail record, the Quantity and Discount fields will be assigned default values as described earlier.
Formatting Discount as Percentage
In the Project Explorer, double-click on OrderDetails / Fields / Discount node.
Change the Data Format String property:
Press OK to save the field, and regenerate the project. Navigate to the Order Form page. Select an order, and create a new order detail. Select a product for the order detail. Discount field is now formatted as a percentage (0.00%).