Code On Time generator allows creating data controllers from the result set of a stored procedure. Some stored procedures use parameters in order to perform operations on the data. In the Northwind sample database, the [Employee Sales By Country] stored procedure shows total sales amounts grouped by employee, and then by country. It accepts two parameters, @Starting_Date and @Ending_Date to determine the filter.
Let’s create a controller from this stored procedure and pass parameters to the script via properties in the BusinessRules class of the app.
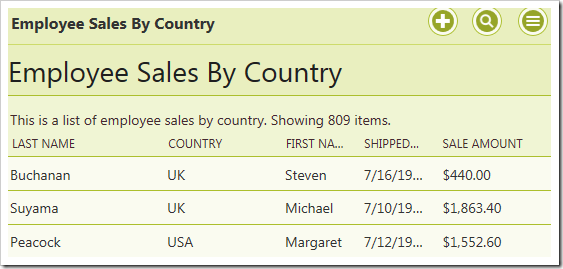
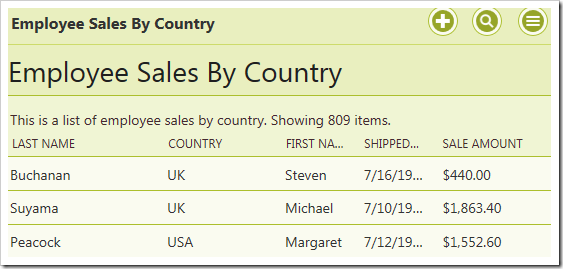
This picture shows the results of the stored procedure with @Beginning_Date and @Ending_Date parameters returned by a business rule property.
The CREATE script for the stored procedure can be seen below.
CREATE procedure [dbo].[Employee Sales by Country]
@Beginning_Date DateTime, @Ending_Date DateTime AS
SELECT Employees.Country,
Employees.LastName,
Employees.FirstName,
Orders.ShippedDate,
Orders.OrderID,
"Order Subtotals".Subtotal AS SaleAmount
FROM Employees INNER JOIN
(Orders INNER JOIN "Order Subtotals" ON Orders.OrderID = "Order Subtotals".OrderID)
ON Employees.EmployeeID = Orders.EmployeeID
WHERE Orders.ShippedDate Between @Beginning_Date And @Ending_Date
Creating the Controller
Start the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab. Click on the New Controller icon on the toolbar.
Enter a name for the controller.
| Property |
Value |
| Name |
EmployeeSalesByCountry |
Press OK to save. Right-click the new controller and press “Generate From SQL…”.
In the SQL script textbox, paste in the following script. The debug section is removed from the business rule when the application framework executes the script at runtime and declares the business rule properties as SQL parameters.
-- debug
DECLARE @BusinessRules_BeginningDate datetime,
@BusinessRules_EndingDate datetime
-- end debug
EXEC [dbo].[Employee Sales by Country]
@BusinessRules_BeginningDate,
@BusinessRules_EndingDate
Press OK to generate the controller.
Adding Controller To Page
Next, let’s add the controller to a page. Right-click on the controller and press Copy.
Switch to the Pages tab in the Project Explorer. On the toolbar, press the New Page icon.
Give a name to the page and press OK to save.
| Property |
Value |
| Name |
Employee Sales By Country |
Drop the new page to the right side of Home page node to place it second in the site menu.
Right-click on the page and press Paste to instantiate the controller as a data view on the page.
Adding Business Rule Property
Let’s create two properties in the BusinessRules class. These properties will return a DateTime value that will be picked up and used by the query to filter the results. If the user is in role “Administrators”, it will display all records between 1970 and 2000. Otherwise, no records will be displayed.
On the Project Designer toolbar, press Browse to first generate the web app. Then, press Develop to open the solution in Visual Studio.
In the Solution Explorer on the right side, right-click on App_Code folder and press Add | Class.
Assign a name of “EmployeeSalesByCountryProperties” and press OK to create the file. Replace the contents of the file with the following:
C#:
using System;
namespace MyCompany.Data
{
public partial class BusinessRules
{
public static DateTime BeginningDate
{
get
{
if (Controller.UserIsInRole("Administrators"))
return new DateTime(1970, 1, 1);
else
return DateTime.Now;
}
}
public static DateTime EndingDate
{
get
{
if (Controller.UserIsInRole("Administrators"))
return new DateTime(2000, 1, 1);
else
return DateTime.Now;
}
}
}
}
Visual Basic:
Imports Microsoft.VisualBasic
Namespace MyCompany.Data
Partial Public Class BusinessRules
Public ReadOnly Property BeginningDate As DateTime
Get
If Controller.UserIsInRole("Administrators") Then
Return New DateTime(1970, 1, 1)
Else
Return DateTime.Now
End If
End Get
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property EndingDate As DateTime
Get
If Controller.UserIsInRole("Administrators") Then
Return New DateTime(2000, 1, 1)
Else
Return DateTime.Now
End If
End Get
End Property
End Class
End Namespace
Make sure to save the file.
Viewing the Results
Press Ctrl+F5 to start the app without debugging. Log in as an administrator and navigate to the Employee Sales By Country page. Notice that all 809 records are displayed.
Log out, and log in again as a user. Notice that no records are displayed.