Code On Time release 8.5.6.0 introduces Model Builder – a new way to build the app you want.
In the past, applications created with Code On Time created a baseline for every entity in the database, and tried to estimate the best configuration for every page, controller, and application component. A frequent complaint about the previous versions about the app generator is the lack of ability to control this automatic process. In response to these complaints, we have included a new feature, designed to give Code On Time users more control over the application development process.
The Model Builder allows developers to design a data model for each and every database entity used by the app generator. They can pick and choose fields to include in the model, define or create foreign key relationships, and even import fields from several levels away easily. Names and labels can be easily changed, formatting can be applied globally, and sorting and filtering can be applied to form a business entity.
The Model Builder is now the first step for the creation of any Code On Time premium database app.
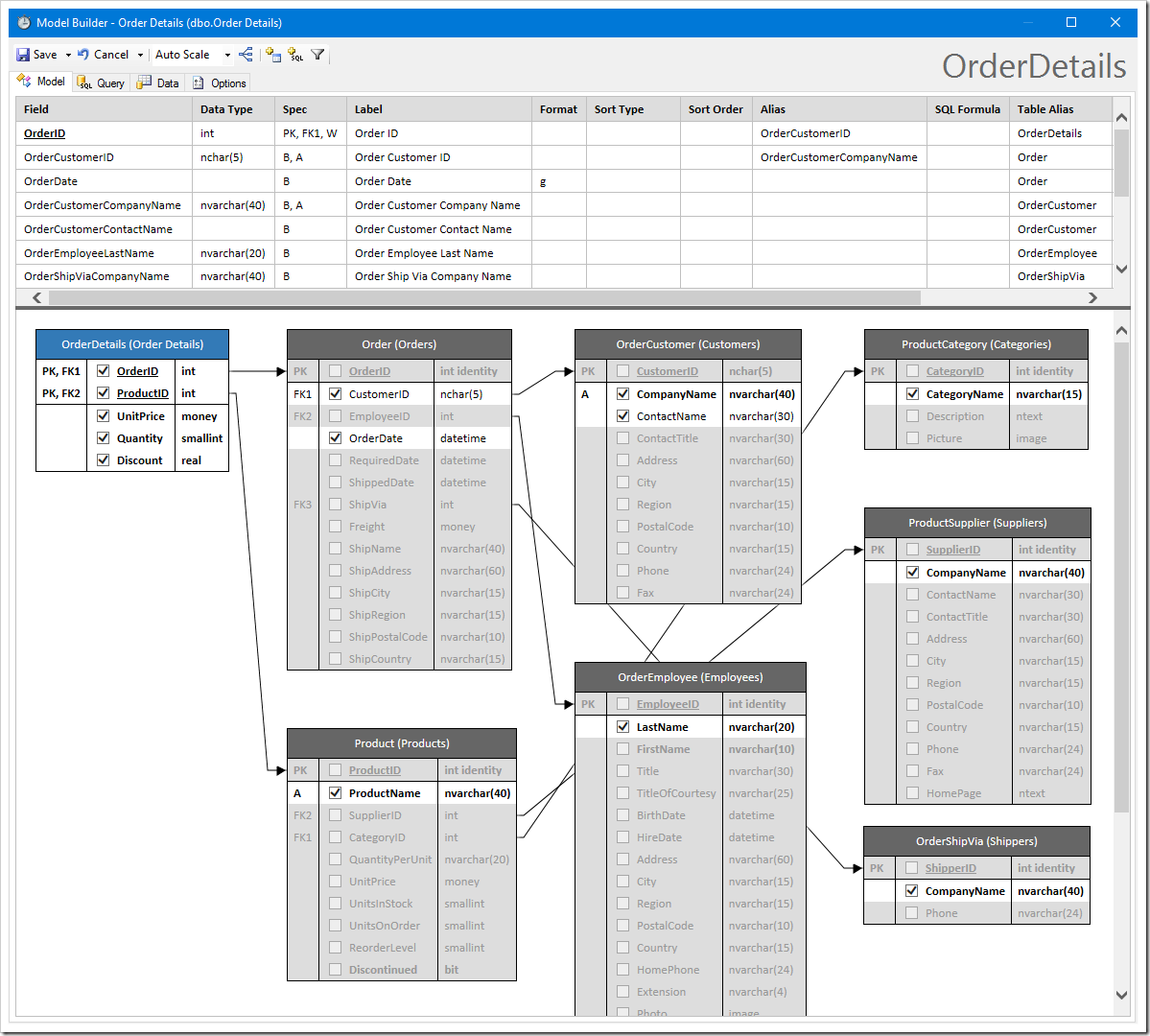
See an example of the default data model for Order Details table of Northwind database.
In addition to Model Builder, the following noteworthy bug fixes and improvements have been added to release 8.5.6.0:
- Support for Visual Studio 2015
- Support for Azure 2.7 and 2.8
- Support for .NET 4.6
- CodeMirror integration in Model Builder and Project Designer
- Charts in Touch UI now support color tags. Specify a list of colors, like so: "pivot1-row1-colors:'red, green, blue'".
- Added tag “calendar-mini-disabled” to disable the mini calendar on the sidebar
- Controller XML files ending with “.baseline.xml” in the Controllers folder will be used as a baseline controller, ignoring the data model.
- Fixed scaling problem on high DPI devices.
- Touch UI inputs now show a single line below the input.
- Neutral cultures are now included in the list supported by app generator
- Boolean fields will show check glyphicon in Touch UI when in read-only mode
- Many more minor bug fixes
Working with the Model Builder
After entering the database connection string, a list of database entities will be listed. Select an entity to start building a data model.
The Model Builder will open.
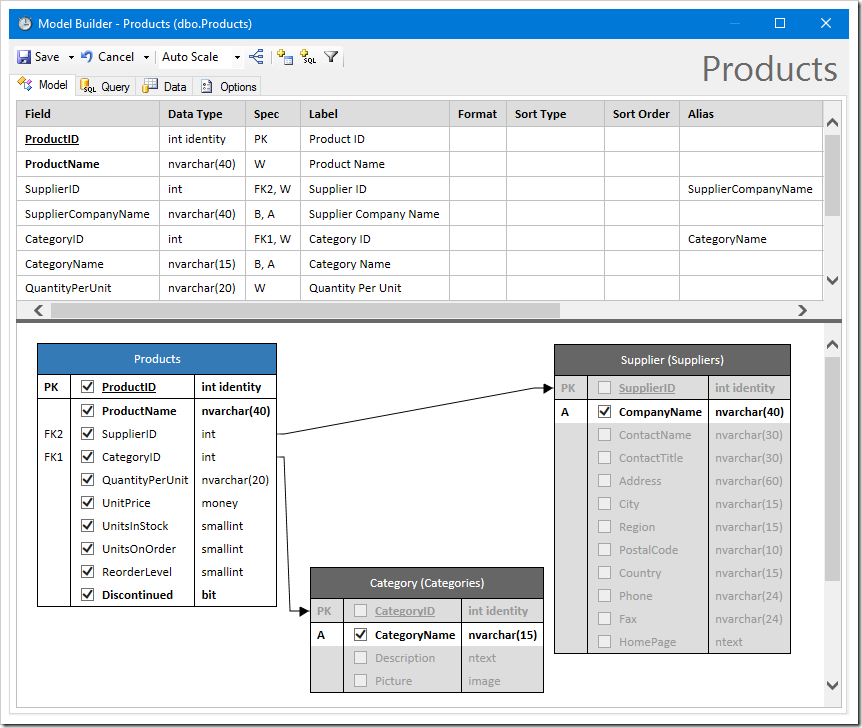
Adding additional fields to the data model is simple. Check the box next to a column to include the field.
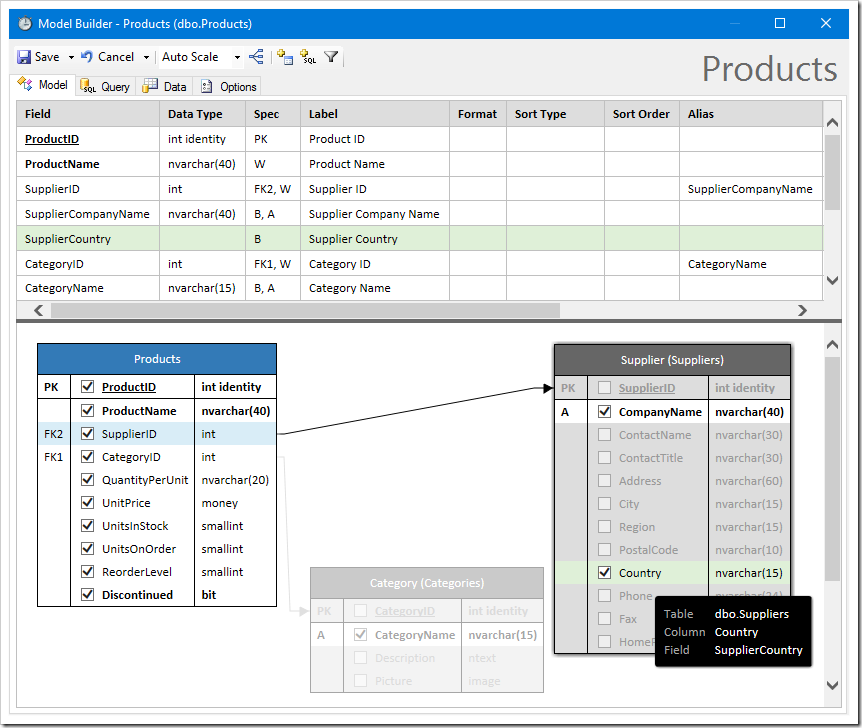
Fields defined with a custom SQL formula are also simple to add. Click the “Add Formula Field” button on the toolbar to get started.
Enter a name for the field in the first textbox. Enter the formula in the text area.
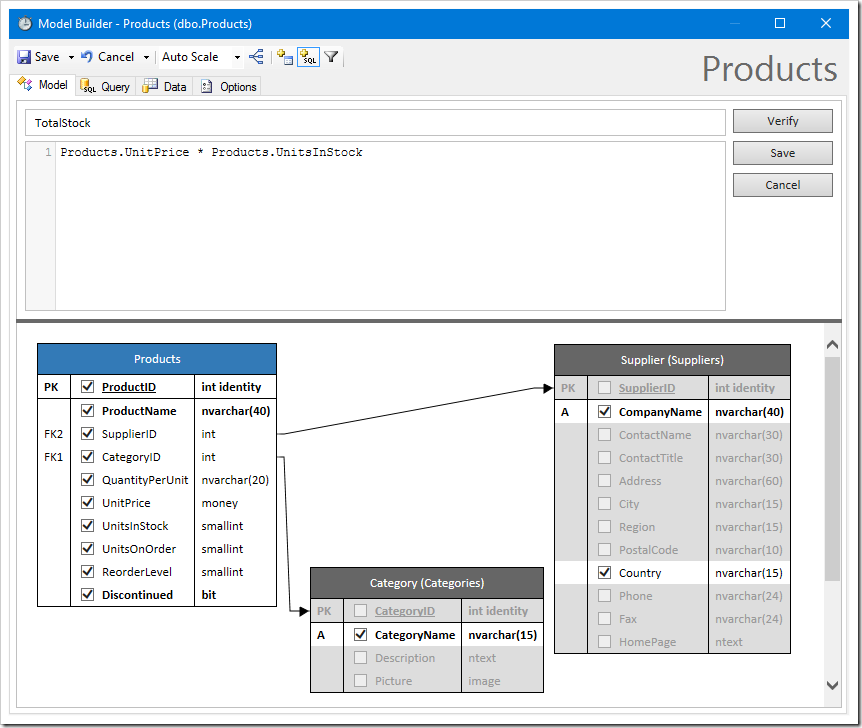
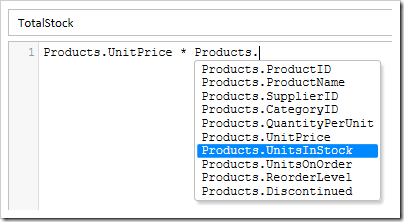
Use “Ctrl+Space” to see a list of columns. Fields can also be dragged from the diagram to be added to the formula.
Reorder fields in the model by dragging the Field column to the correct position.
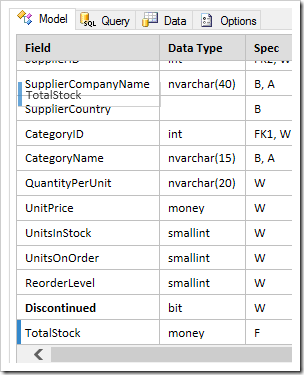
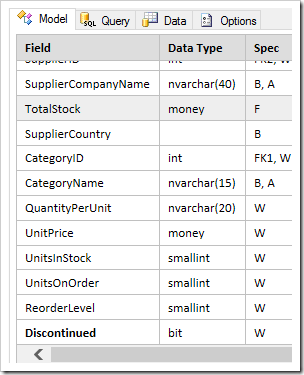
Field labels and options can be changed by clicking in the cell. The following shortcuts can be used to quickly and easily navigate between the different cells:
- If mouse cursor shows text, click to change
- F2 to Select All/End
- Left/Right moves between cells in row
- Tab/Shift+Tab to move between cells
- Up/Down to move up down
- Enter/Shift+Enter to move up down
- Esc once will restore original if changed, Esc twice will exit edit mode
- Ctrl+Enter will save, stay editing
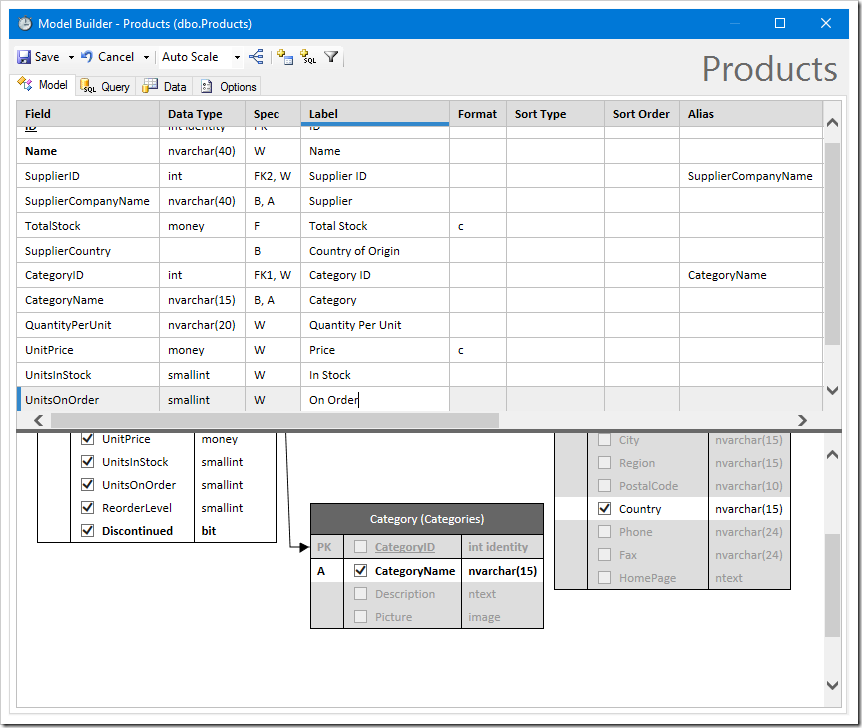
Sorting can be added to the data model by entering the Sort Type and Sort Order.
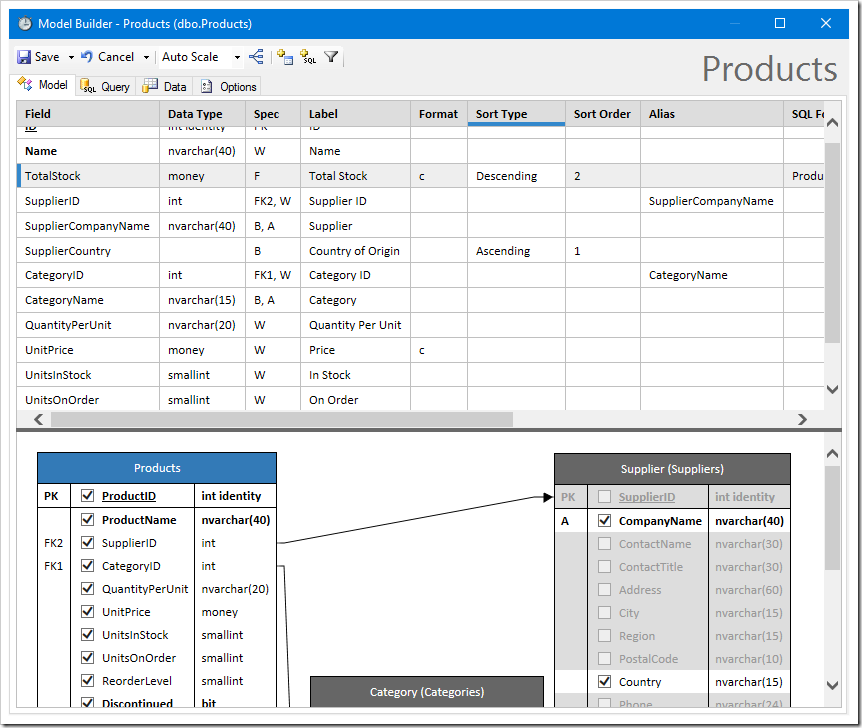
The Query tab shows the command for the data model.
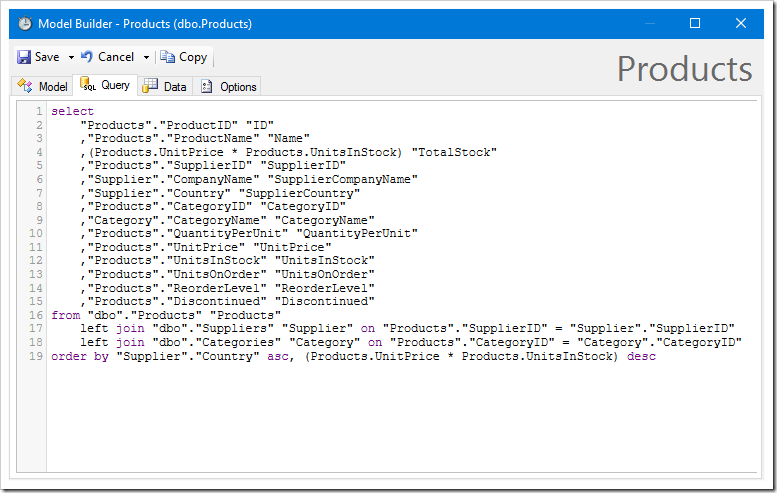
The Data tab shows the output of the command. By default, Raw Data mode is on. This will show all primary and foreign key fields, and show native value formatting from the database.
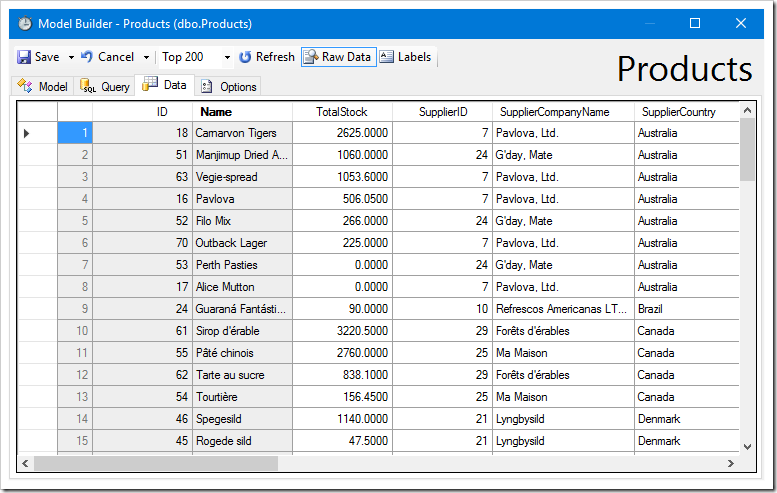
Disabling Raw Data will hide primary and foreign keys, and apply formatting.
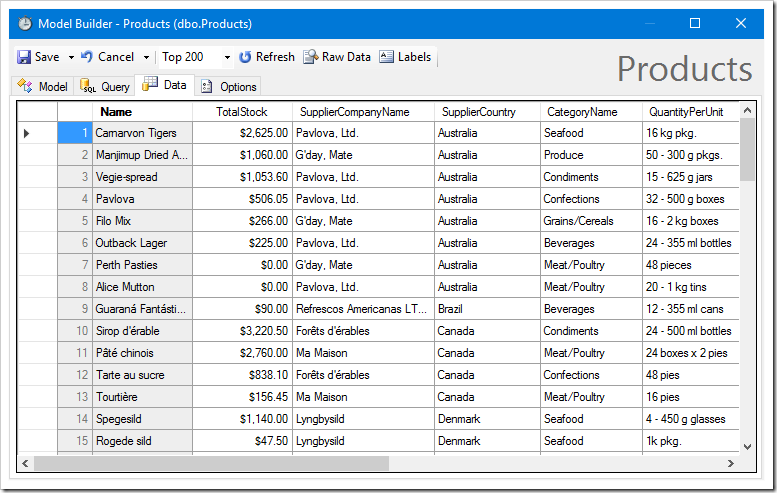
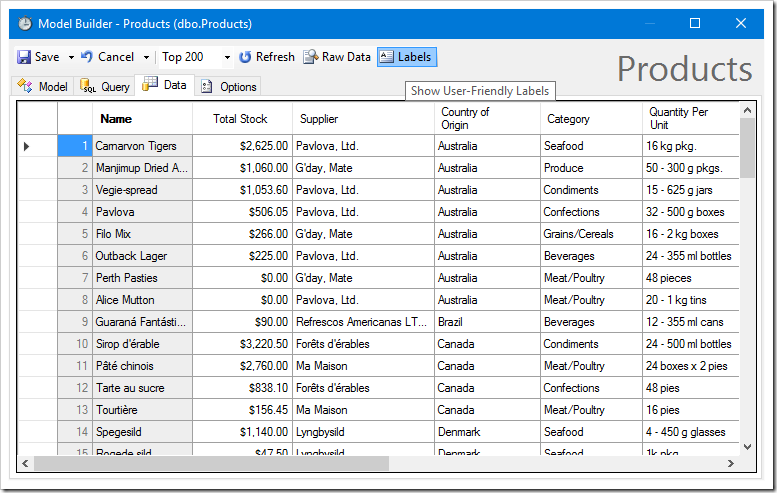
The Labels button will replace field names with labels.
Click Save to persist the new data model. Proceed to generate the application. A page has been added, showing a grid of products, as defined by the data model.
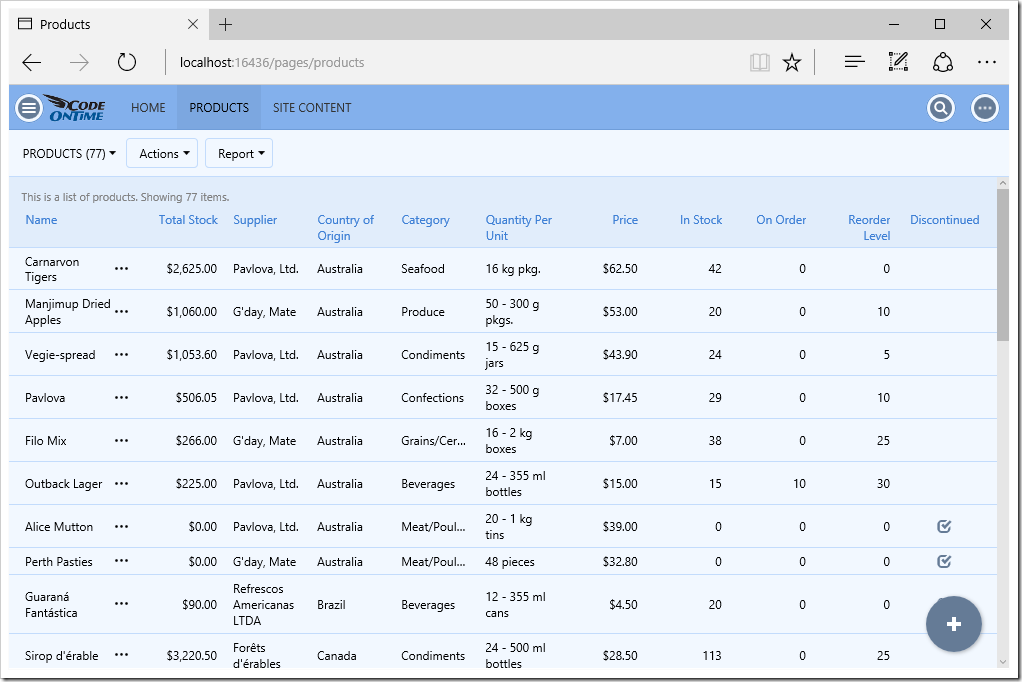
The user can also switch to list view.
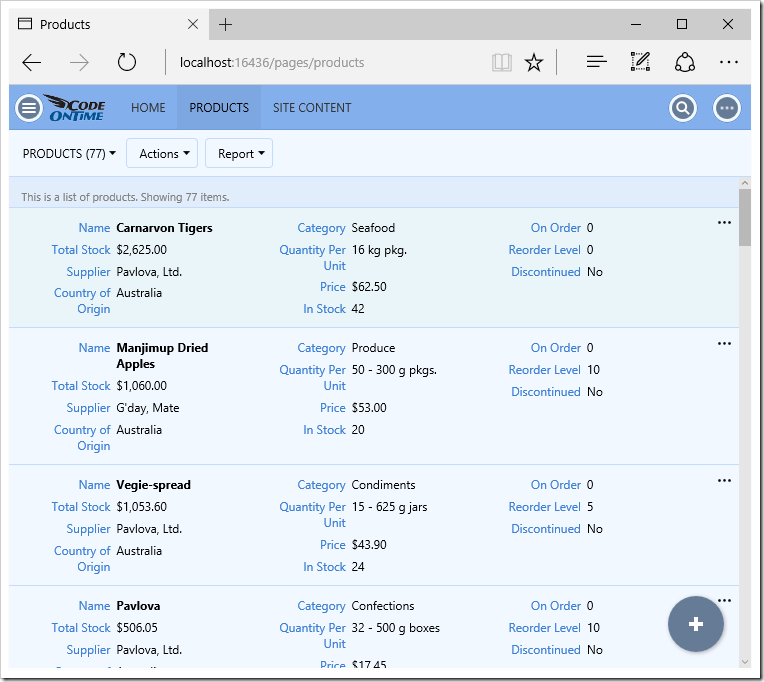
Automatic charts have also been created.
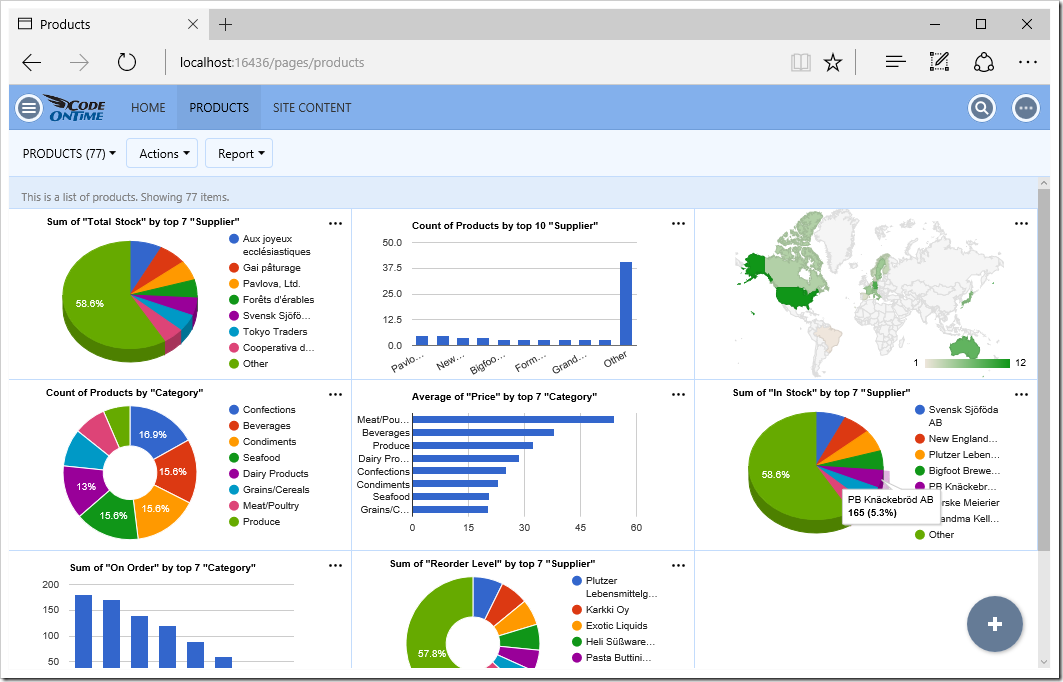
You can edit existing products or create new ones. Notice, however, that the Supplier ID and Category ID have not been configured as lookups.
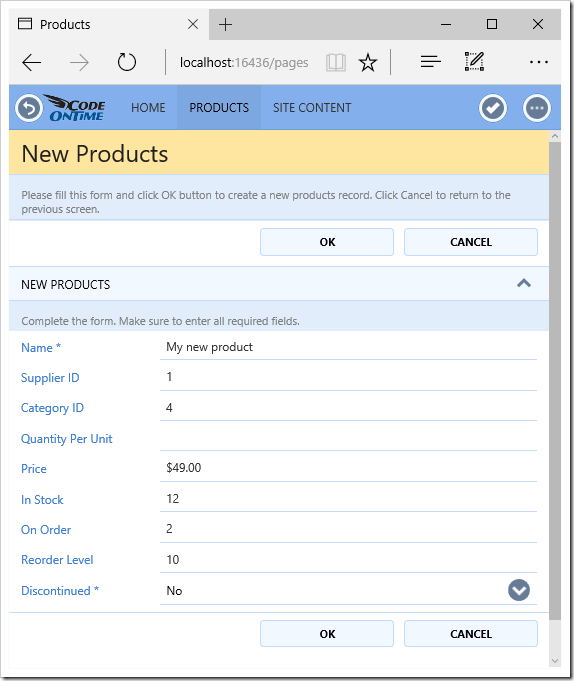
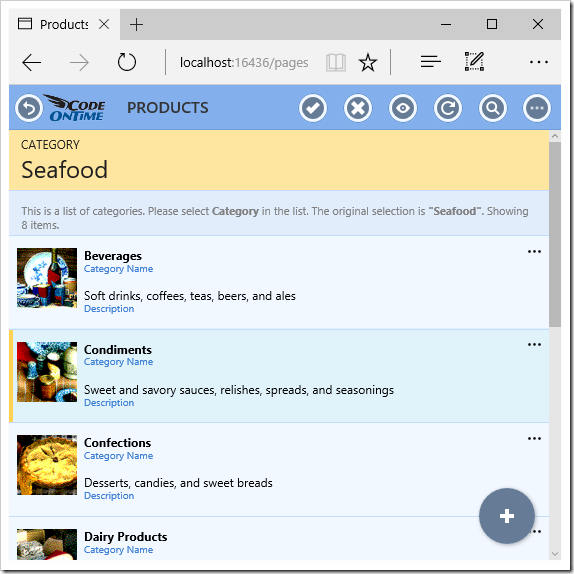
Let’s add Categories and Suppliers data models. Go back to the generator and create a data model for Categories. Notice that these two tables that are referred to are already suggested.
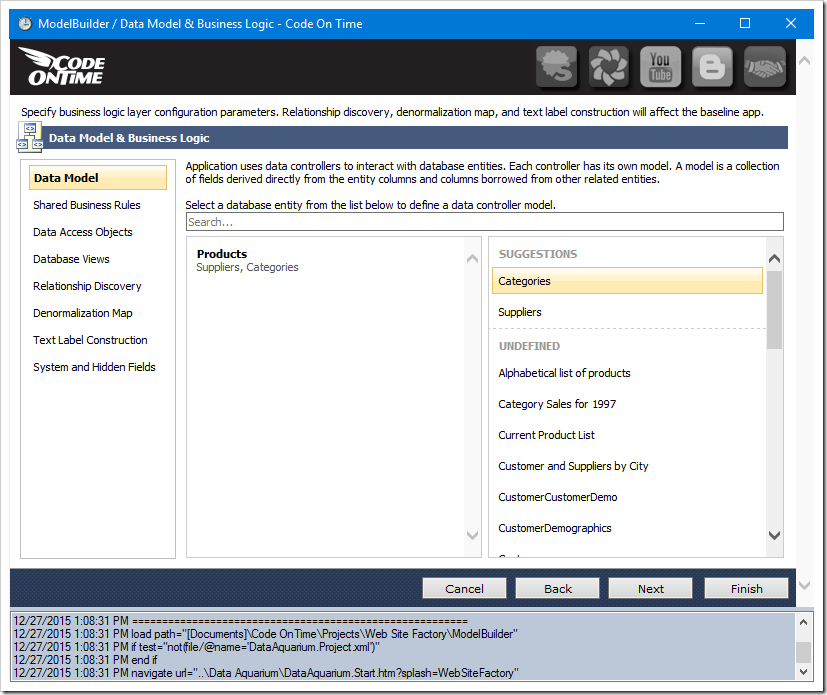
Create the data model for Categories.
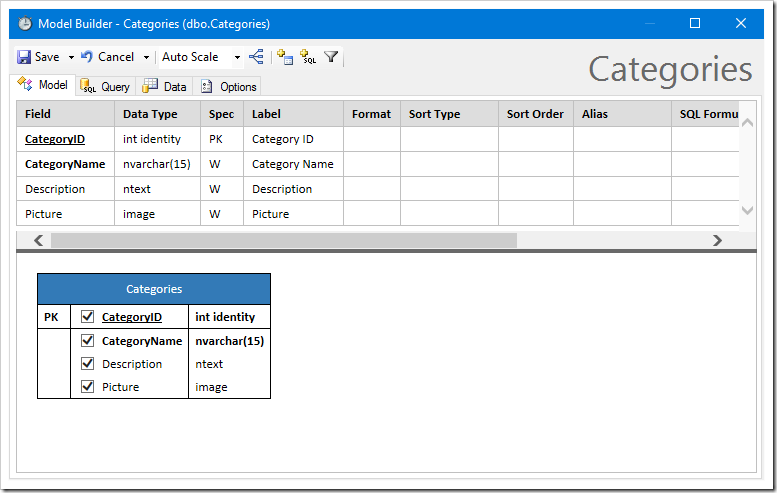
Create a data model for Suppliers. Be sure to sort by CompanyName and disable the HomePage field.
Regenerate the project. Be sure to refresh when prompted. Notice that Supplier and Category are now rendered as lookups.
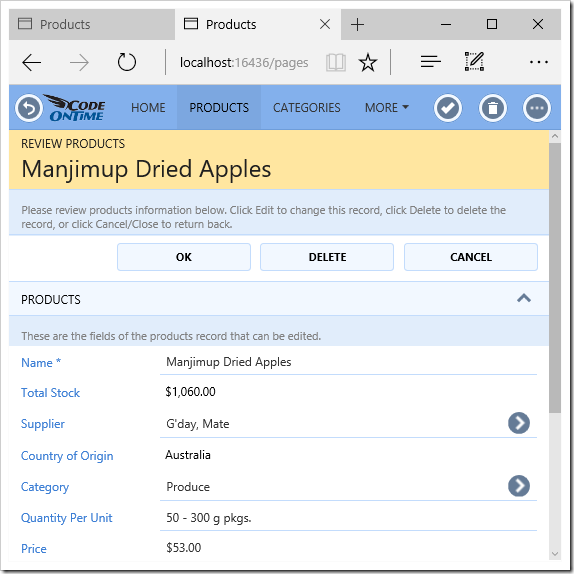
Activating the Supplier lookup will open a list of suppliers.
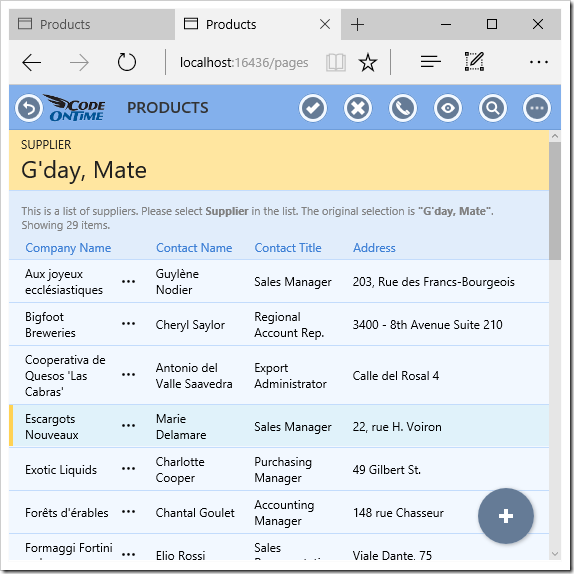
Activating the Categories lookup will show a list of categories to select.
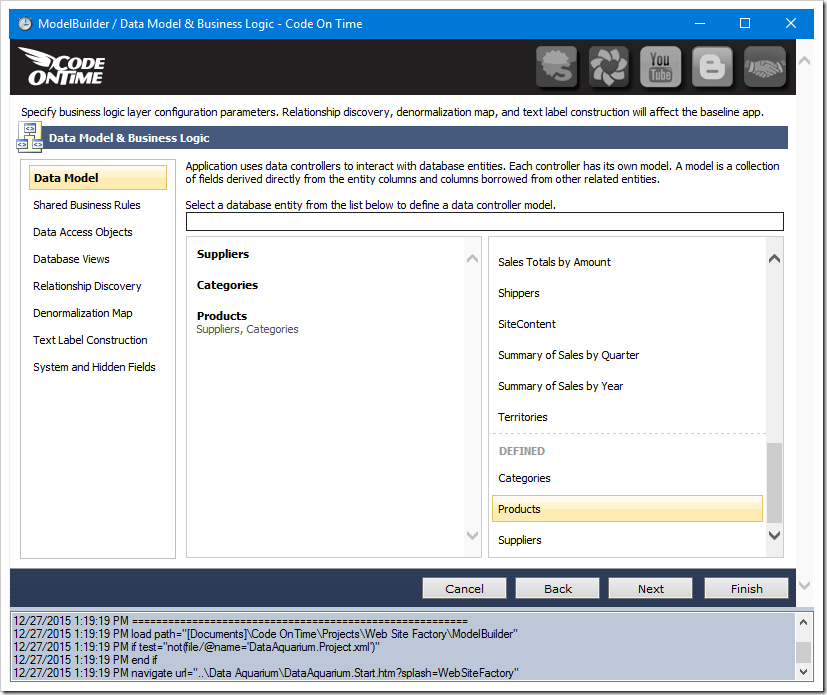
Let’s create a second data model for Products, that only shows products from North America. There are two ways of creating a copy of a data model – saving a copy of an existing model, or creating a new model, listed under “Defined” section.
Let’s create a copy. Open the Products data model, and change the name to “NorthAmericanProducts” by typing in the name in the top-right corner.
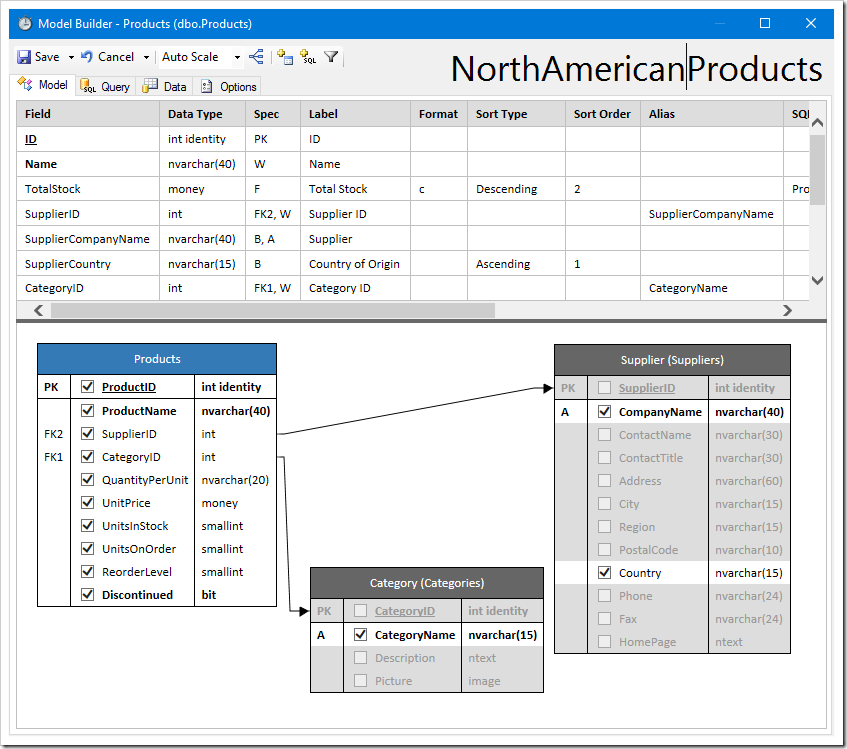
Let’s add a filter to the new model. Click the “Add Filter…” button on the toolbar.
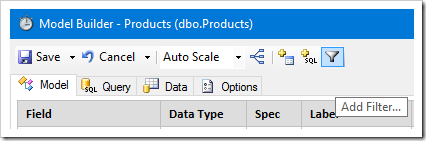
Enter the filter in the text area.
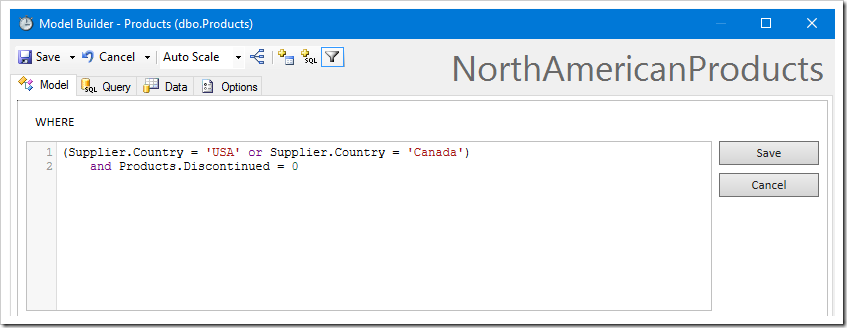
In addition, sort the ProductName in descending order.
The Query tab will show the new command.
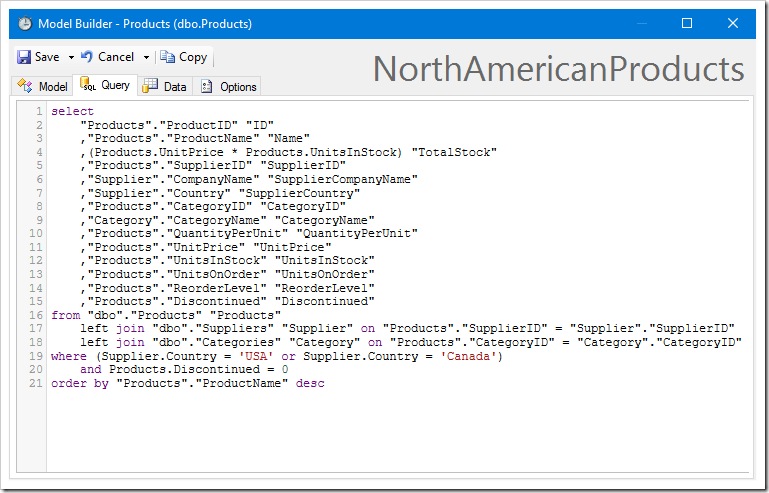
The Data tab shows that the sorting and filtering was a success.
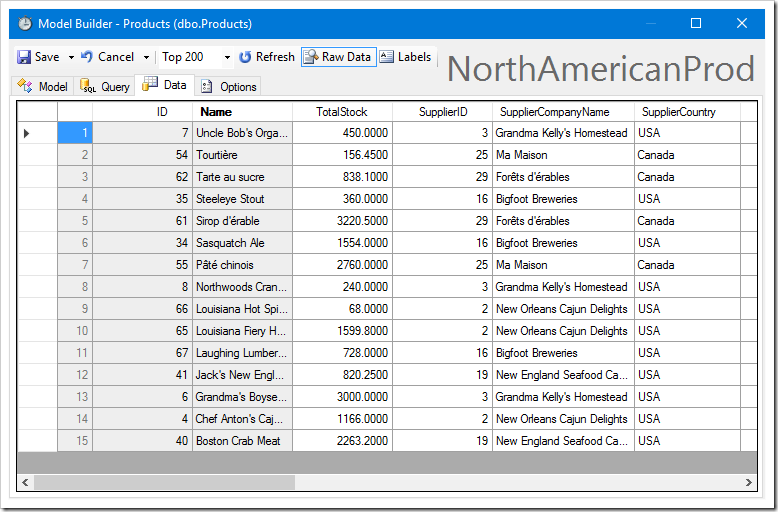
To save the data model as a copy, activate the dropdown next to “Save”, and press “Save a Copy”.
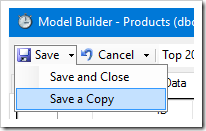
Proceed to generate the application. Notice that another page has been added to the sitemap. This page is a Single Page Application created to handle products from North America.
Virtual Connections
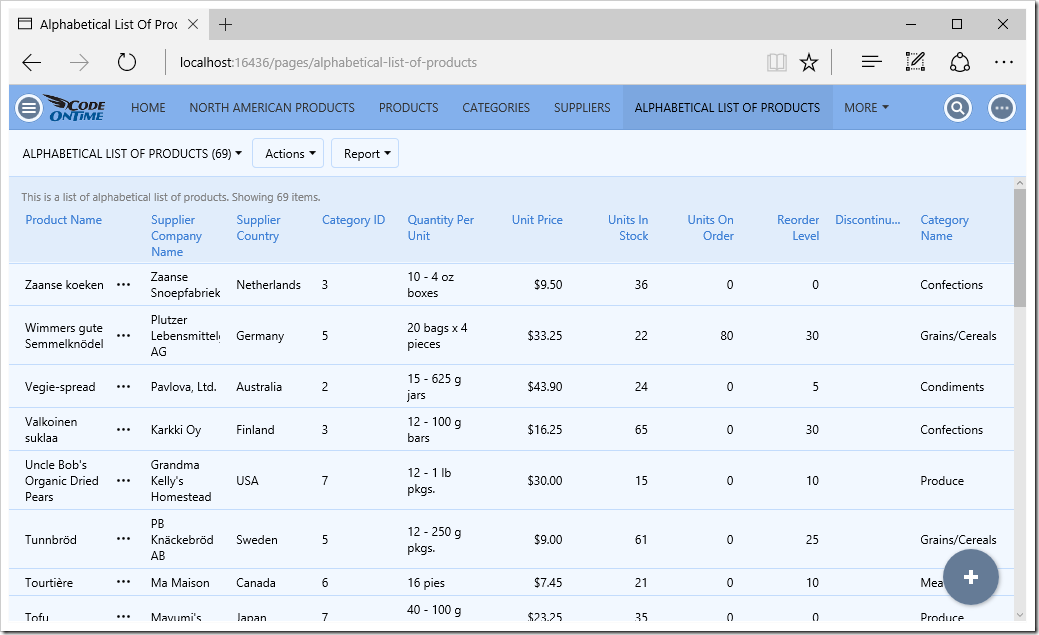
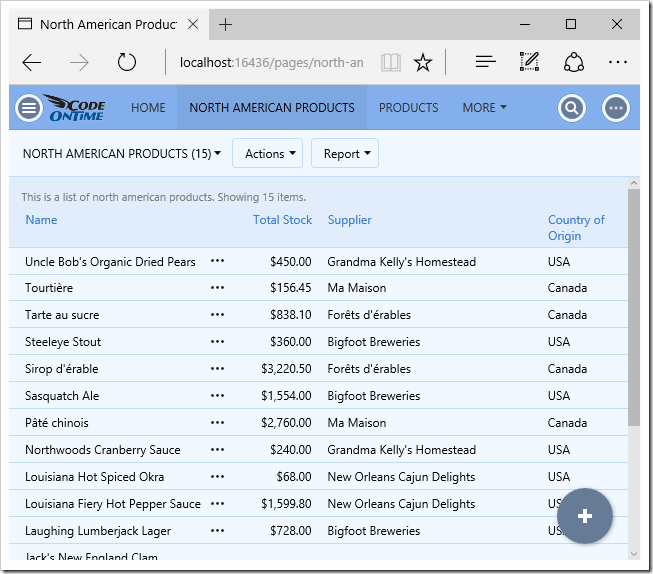
One of the most powerful aspects of the Model Builder is the ability to define virtual primary and foreign keys. Let’s create a data model using the view Alphabetical List Of Products.
The application framework is unable to perform any CRUD operations on a business entity until a primary key is defined. Let’s create a virtual primary key by right-clicking ProductID and pressing Set Primary Key.
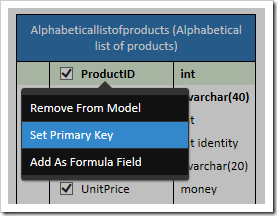
The spec “VPK” will be added to the first column of the diagram.
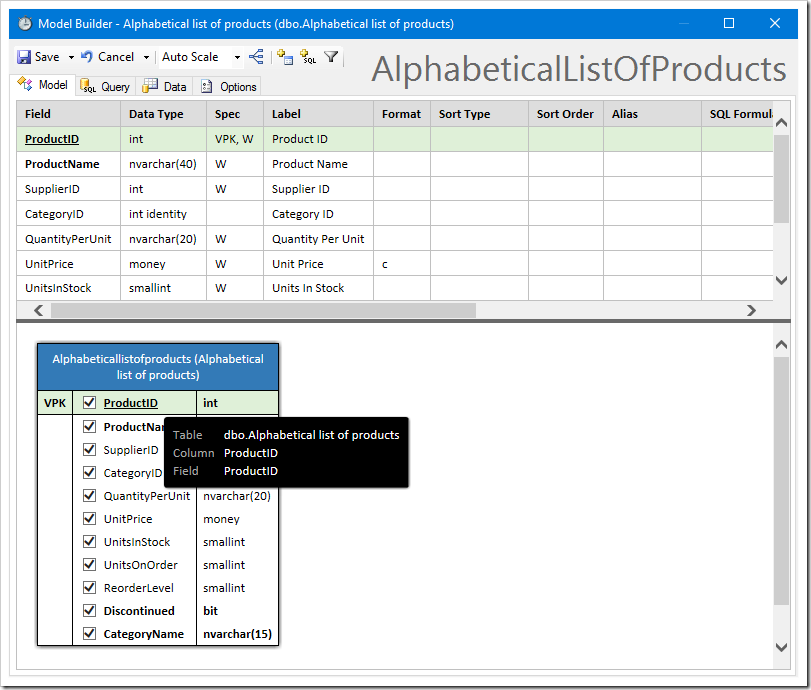
Notice that because Alphabetical List Of Products is a view, foreign keys are not known, and values from these foreign key relationships cannot be included until a virtual foreign key is defined.
On the toolbar, click the “Add Table” button.
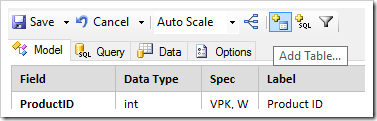
The field list at the top of the Model tab will be replaced with a list of database objects.
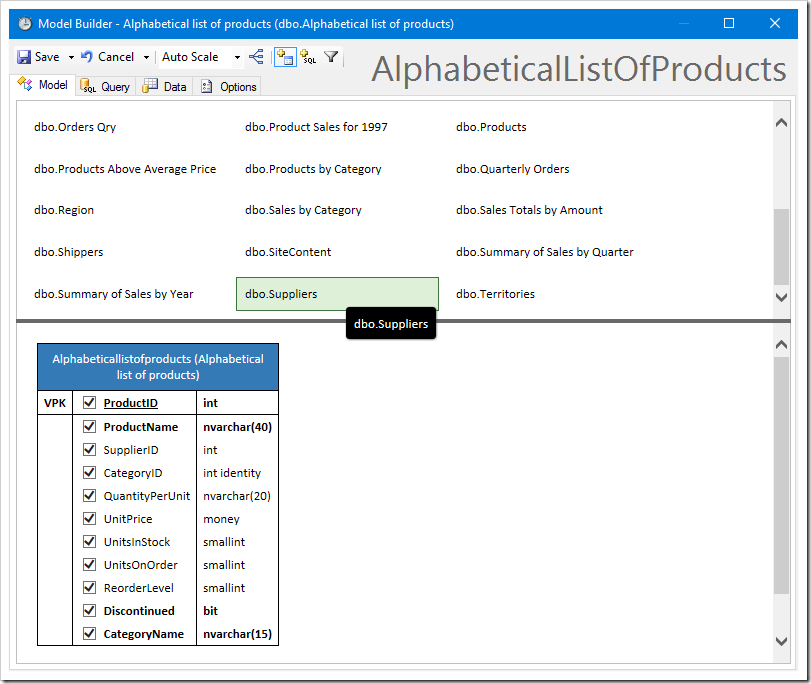
Drag the “dbo.Suppliers” table onto the diagram. Rename the alias of Suppliers to “Supplier” by clicking on the header of the new table in the diagram.
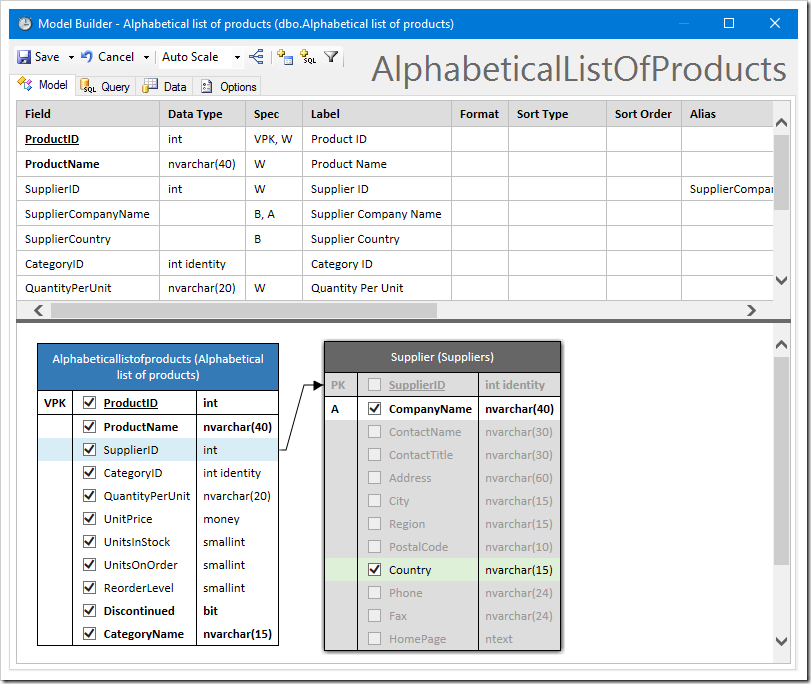
Then, drag the “SupplierID” field from Alphabeticallistofproducts onto SupplierID column of Suppliers table to form a virtual foreign key. You can now check fields from the Suppliers table to include in the data model.
Sort this data model by entering “Descending” in the Sort Type of ProductName.
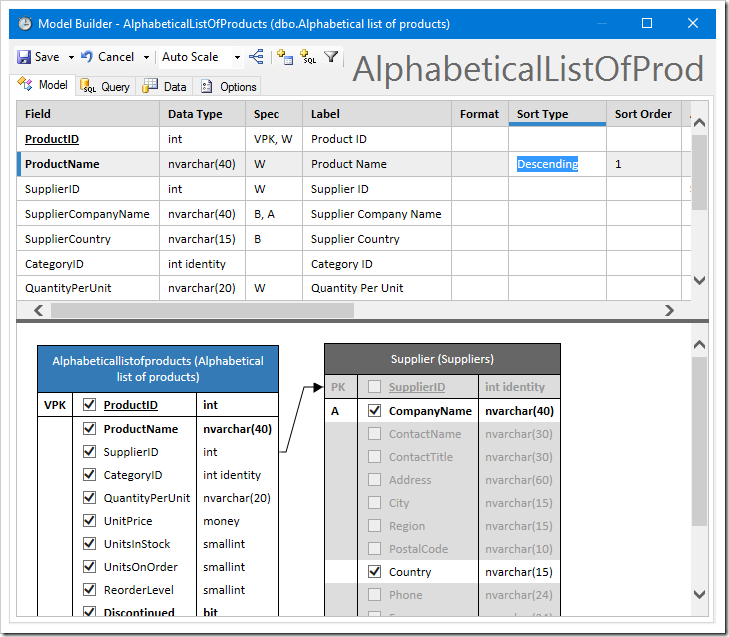
The final result will show the inclusion of Supplier fields in the grid.