Commonly, multiple screens are connected and the user is required to page through these forms in order to complete their task. This pattern of presentation is called the “Wizard”. Starting with release 8.5.11.0, it is possible to create wizards in Touch UI. The picture below shows an example of a Create Employee Wizard in the Northwind sample database.
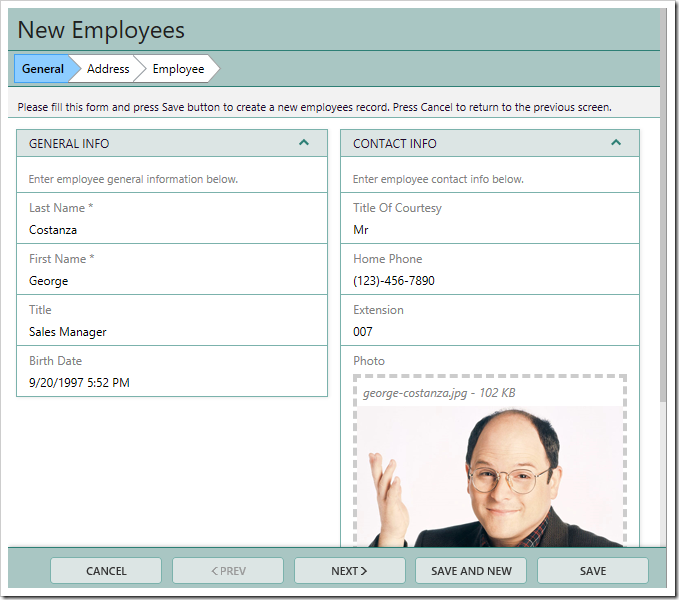
Each step of the wizard contains one or more categories. If all categories belonging to a particular step are rendered invisible via the Visible When property, then that step will be hidden.
Let’s implement the wizard shown above. Start the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer window, switch to Controllers tab. Double-click on “Employees / Views / createForm1 / c1 – New Employees” category.
Make the following changes and press OK to save:
| Property | Value |
| Header Text | General Info |
| Description | Enter employee general information below. |
| Wizard | General |
Next, let’s create several new categories. Right-click on “Employees / Views / createForm1” and press “New Category”.
The second category will display in a new column alongside the previous category in the first step of the wizard.
| Property | Value |
| Header Text | Contact Info |
| Description | Enter employee contact information below. |
| New Column | Yes |
| Wizard | General |
The next category will have the following configuration. Note the use of curly brackets wrapping field names. These will be replaced by the value of the field at runtime.
| Property | Value |
| Header Text | Address |
| Description | Enter the home address of {FirstName} {LastName} below. |
| Wizard | Address |
The last category representing the final wizard step is configured below. Notice that the Visible When property is configured to hide the category when the Title field is equal to the value “President”.
| Property | Value |
| Header Text | Employee Info |
| Description | Enter {TitleOfCourtesy} {LastName}'s employee information below. |
| Wizard | Employee |
| Visible When | $row.Title != 'President'
|
Any categories that do not have a “Wizard” property assigned will be displayed on every step, either above or below the wizard content, depending on the position of the category relative to the first wizard category.
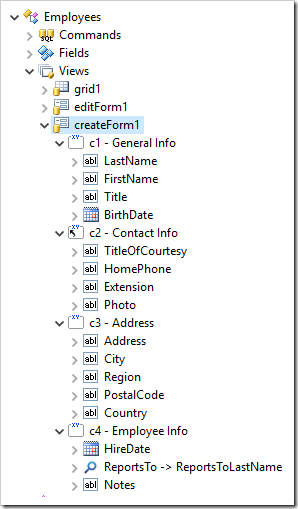
Rearrange the data fields as presented in the picture below using drag & drop.
On the toolbar, press Browse to regenerate the app. Once generation is complete, navigate to the Employees page and create a new employee.
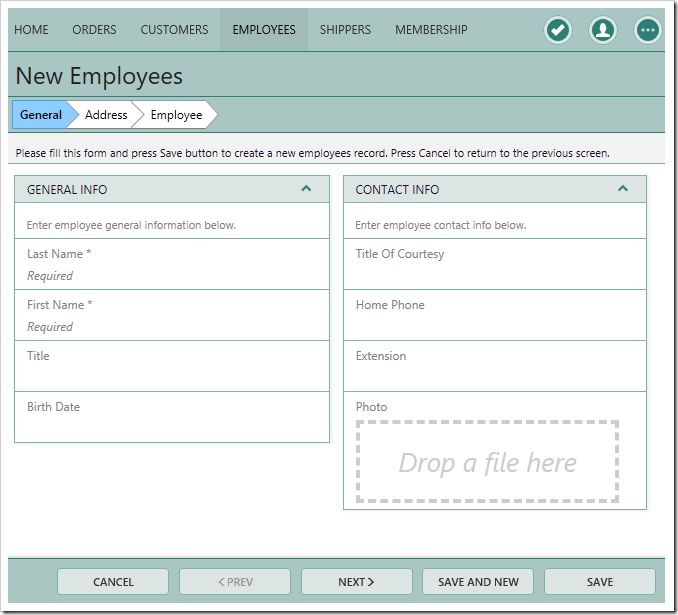
Notice that a Status Bar has automatically been defined. The “Prev” and “Next” actions have been automatically injected into the form action group. Enter some values for the fields, including specifying “President” in the Title field.
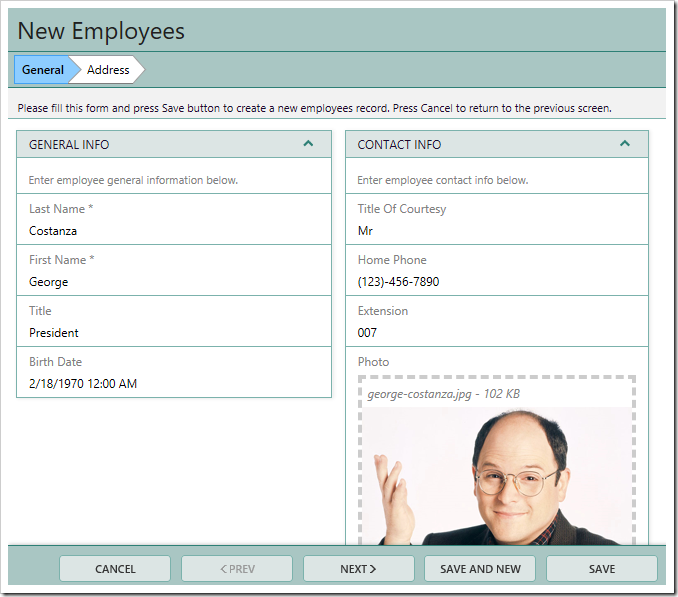
Notice that the “Employee” tab has been removed from the Status Bar. By pressing “Next”, the Address wizard step will be displayed. The field names surrounded by curly brackets have been replaced with the field values defined by the user.
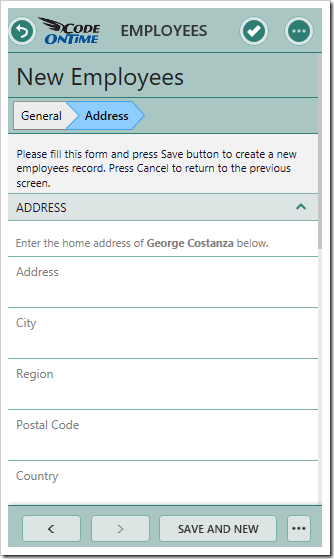
Note that when using custom form templates, wizards can be defined by encapsulating each step by a container of type “wizard”, containing the attribute “data-wizard-step”. The value of the attribute will be displayed in the status bar. See a simplified example below:
<div data-container="wizard" data-wizard-step="General">
<div data-container="collapsible" data-header-text="General Info">
...
</div>
...
</div>
<div data-container="wizard" data-wizard-step="Address">
...
</div>