With the release of Windows Azure, Microsoft has provided a great cloud database, storage, and computing service platform. Windows Azure offers many benefits, such as guaranteed 99.95% uptime, automatic OS and service patching, integrated network load balancing, and easy scaling.
While the Windows Azure cloud may offer the perfect platform to deploy your next web application, you still need to build this application. This is where Code On Time’s Azure Factory comes in. All you have to do is paste in your SQL Azure database connection string, and hit Generate. In a minute, your advanced web application will start in your default browser, complete with sorting, adaptive filtering, reporting, charts, and much more. Hit Publish, and the application will be packaged. Upload the published deployment package to Windows Azure, and within minutes you’ll have your app running in the cloud.
Need to add more features and customize your app? Just use the easy to use Designer to make necessary changes to the logical definition of the application. While no coding is needed to make a great app, you can always open the source code in Visual Studio and change it to precisely fit your requirements.
The following article will explain how to generate and deploy an Azure Factory application. View our learning system if you need help setting up a Windows Azure account, creating a database server, or creating a database using SQL Azure tools.
Generating the Azure Factory Project
Launch the web application generator, and create a new project. Choose Azure Factory.
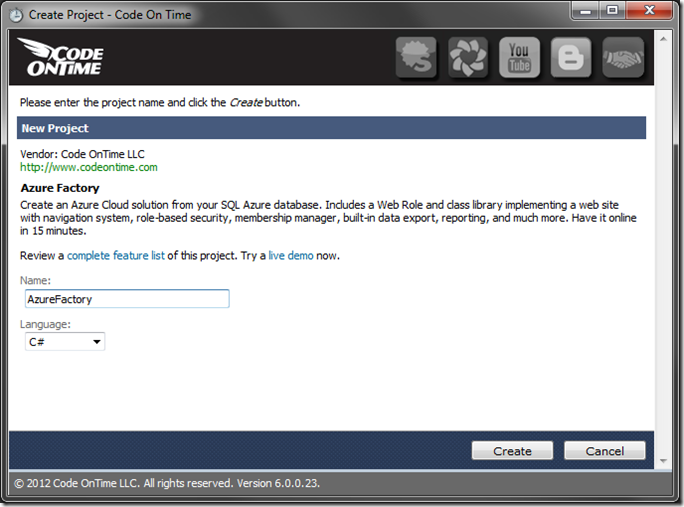
Give this project the name of “AzureFactory”. Pick the programming language of your choice. Press Create to create the project.
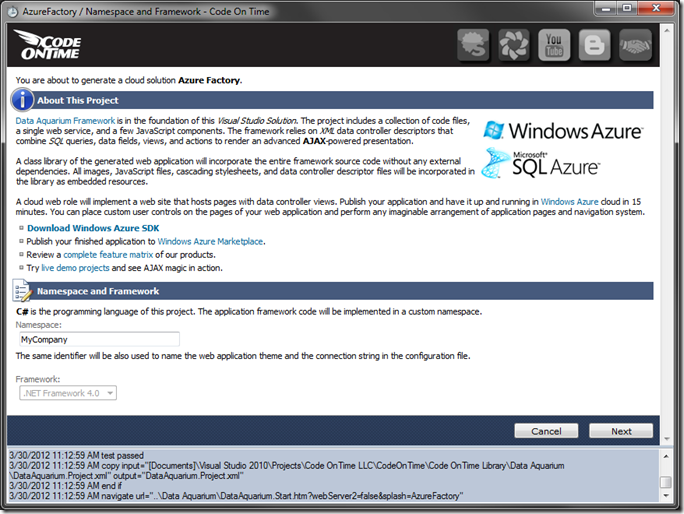
On the next page, you can specify your namespace. We’ll leave the default of “MyCompany” and continue to the next page of the wizard by pressing Next.
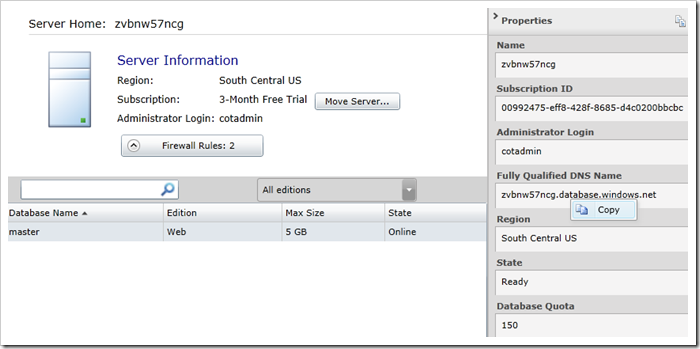
This page requires you to specify a database connection. Click on the “…” button next to the Connection String field to configure the string.
In the Server field, enter the database’s Fully Qualified DNS Name. This can be found in the Properties of the server when using Windows Azure Management Portal.
Enter your server username and password.
If you already have an SQL Azure database, then enter it’s name in the Database field. If you don’t have a database, you can quickly create one using the web application generator. The next few steps explain how to create a sample Northwind database.
In the Database field, write “Northwind”. Press the Create button to create the database. Press Yes to confirm creation of the database.
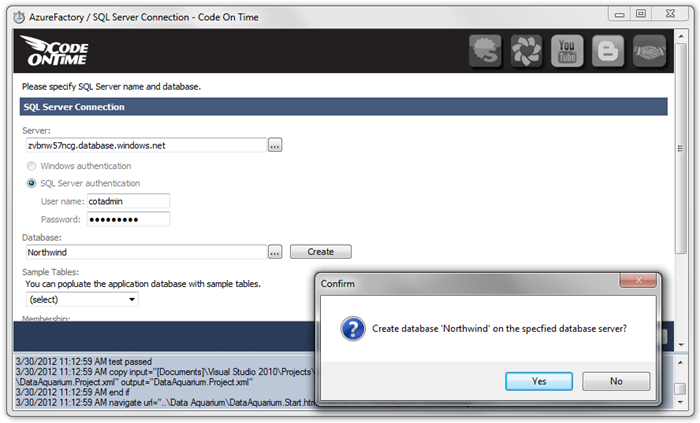
You will be notified that the database has been created. Press OK to close the notification, and select Northwind from the Sample Tables dropdown. Press Install to install the Northwind sample into the database, and press Yes to confirm.
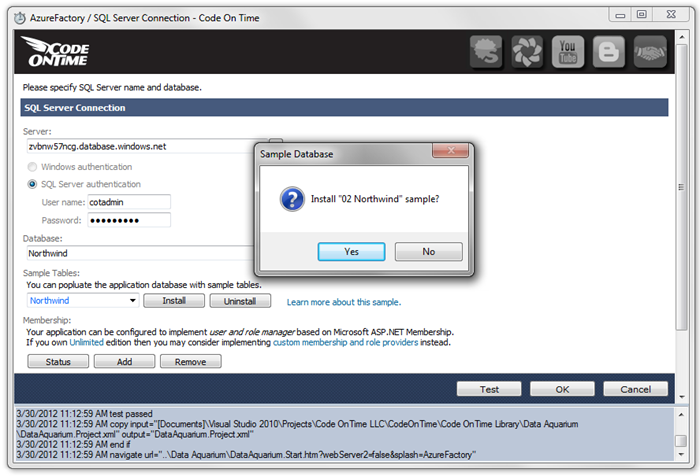
Once complete, you will be notified. Press OK to close the notification.
The next steps explain configuration of ASP.NET Membership and Session State management that apply to any database.
Let’s add ASP.NET Membership to this database. Under Membership, press Add. Press OK to confirm installation.
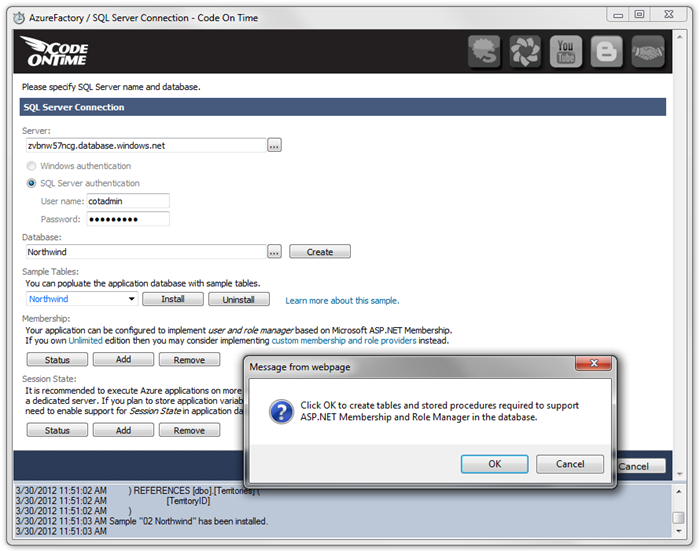
Once complete, press OK to close the notification.
By default, Azure Factory applications are configured to use two extra-small server instances in the cloud. If you use multiple instances, then Session State management must be included in the application. Under Session State, press Add. Press OK to confirm the installation.
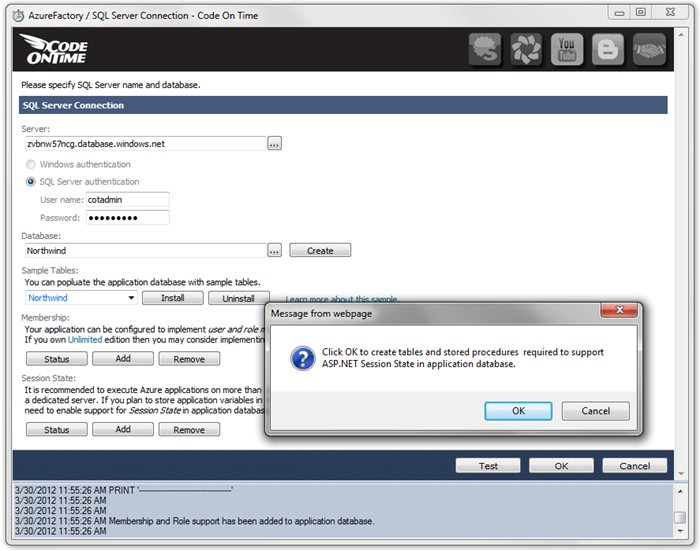
Press OK to close the notification, and press OK one more time to save the connection string. Press Next twice to get to the Reporting page.
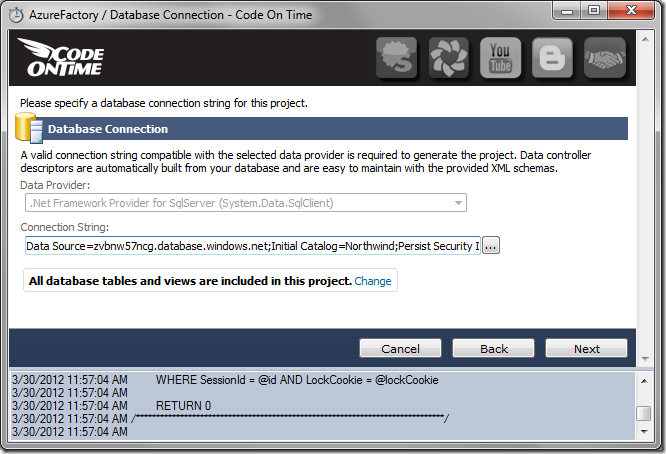
Check the box to enable reporting, and keep pressing Next to reach the Theme page.
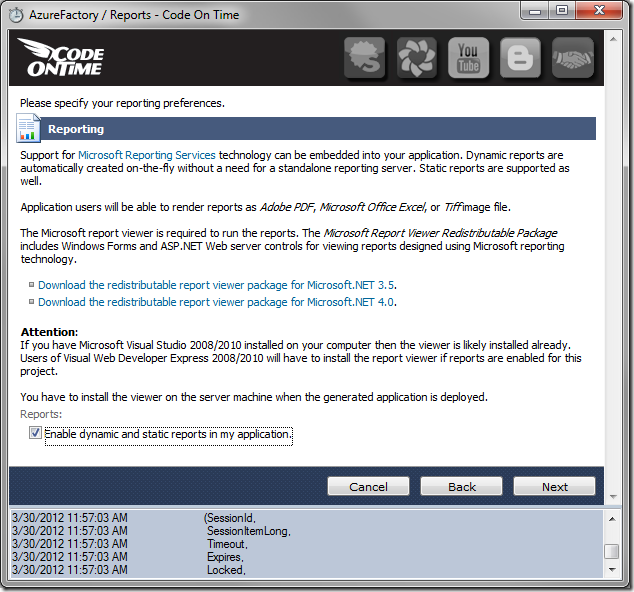
Let’s choose the Azure theme. Select Azure from the list.
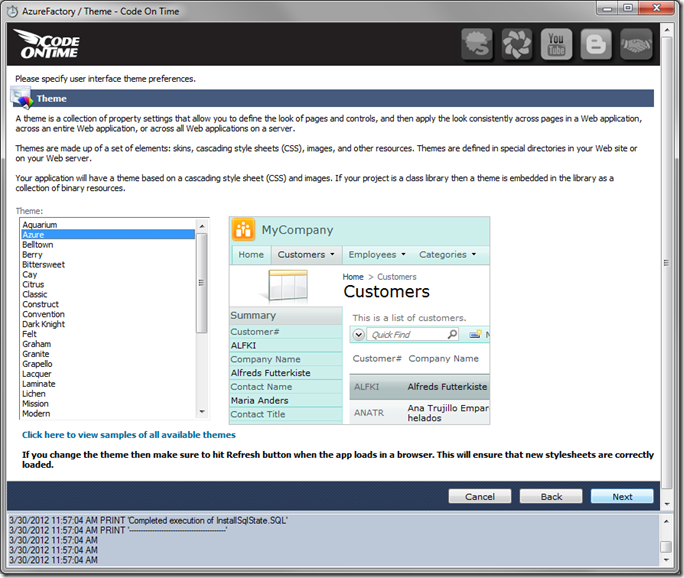
Hold down Shift key, and press Next. This shortcut will take you to the Summary page. Press the Generate button.
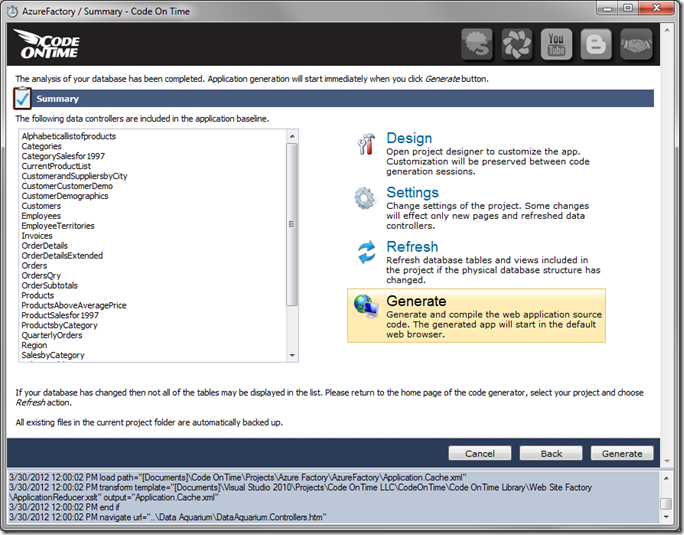
Wait until the generator finishes, and your default browser will open with your new web application. While the application is running on your computer, the database is located in the cloud. You can log in and start using the app immediately.
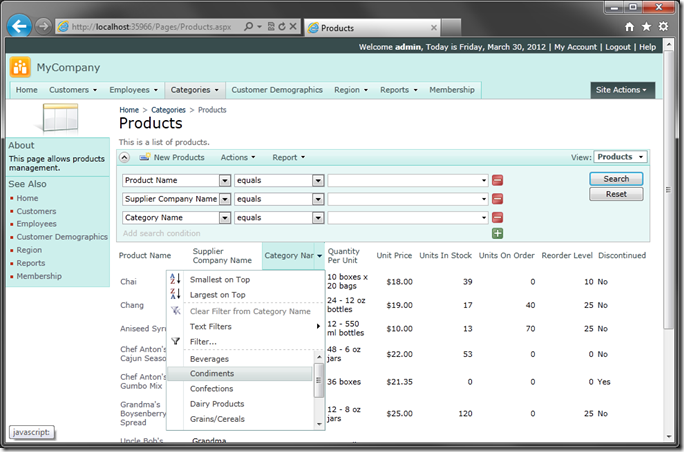
Deploying the Web App
It’s time to deploy the app to Azure. Go back to the generator, and click on the project name. Press Publish.
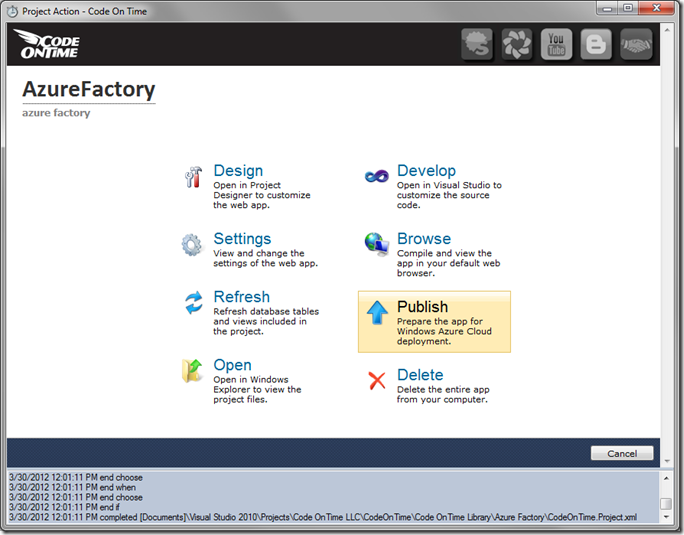
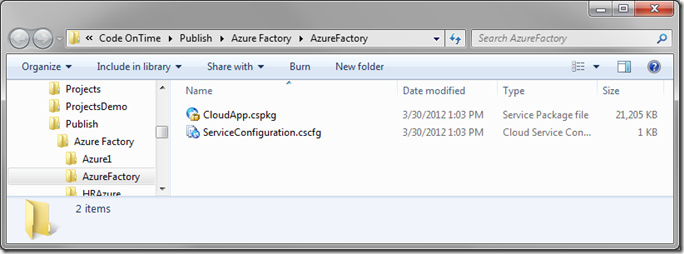
The generator will package the web application and create the files necessary for deployment. A Windows Explorer screen will open and display the location of the files.
Log in to your Windows Azure Management Portal, and switch to Hosted Services, Storage Accounts & CDN section in the bottom left corner. In the folders, click on Hosted Services. Select your subscription, and press New Hosted Service on the ribbon.
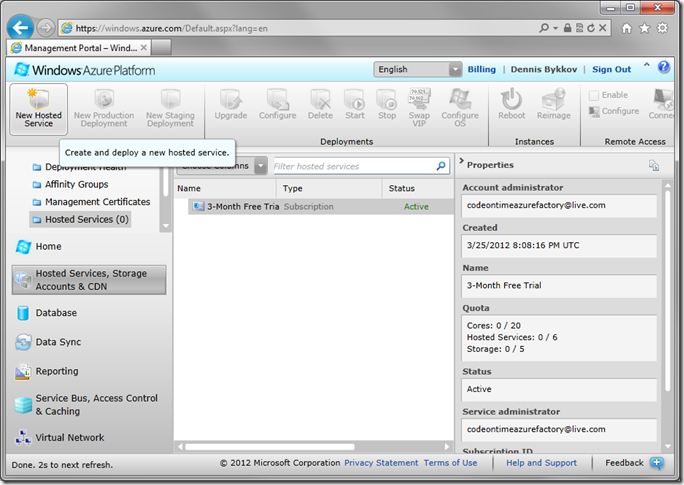
Use the following settings for your new hosted service:
| Choose a subscription | 3-Month Free Trial |
| Enter a name for your service | AzureFactory |
| Enter a URL Prefix for your service | AzureFactory (if not available, use something else) |
| Choose a region or affinity group | Anywhere US (or your closest region) |
| Deployment options | Deploy to stage environment |
| Deployment name | AzureFactory |
| Package location | ~\MyDocuments\CodeOnTime\Publish\Azure Factory\AzureFactory\CloudApp.cspkg |
| Configuration file | ~\MyDocuments\CodeOnTime\Publish\Azure Factory\AzureFactory\ServiceConfiguration.cscfg |
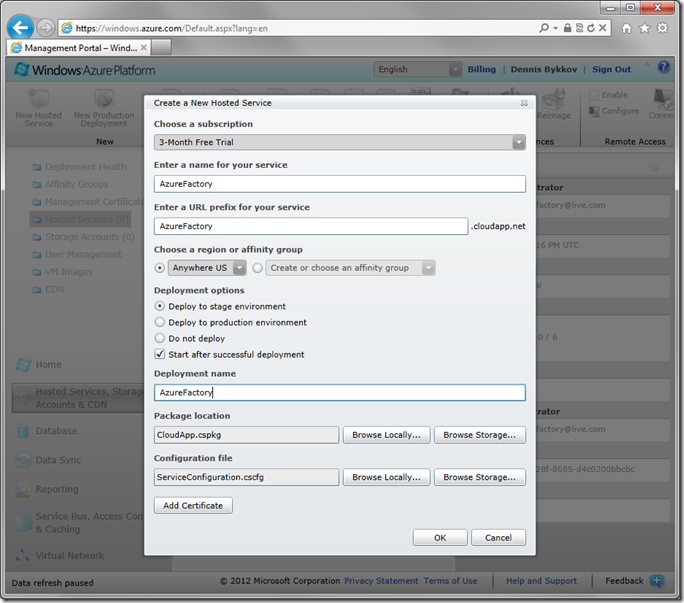
Press OK, and Windows Azure will start the deployment process. This step may take 10-15 minutes. Once the status of the deployment changes to Ready, use the link found under Properties. You will be taken to the fully functional website running in the cloud .
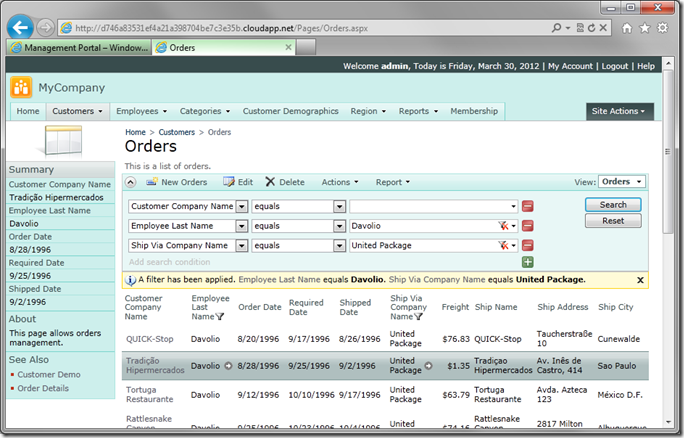
If you look at the URL, you will notice that it uses the ID of the deployment, not the requested DNS Name. This is because the deployment is a staging deployment. You can go back to the management portal, and choose Swap VIP to change it into a production deployment. Now you can use the DNS Name you specified during creation of the hosted service.
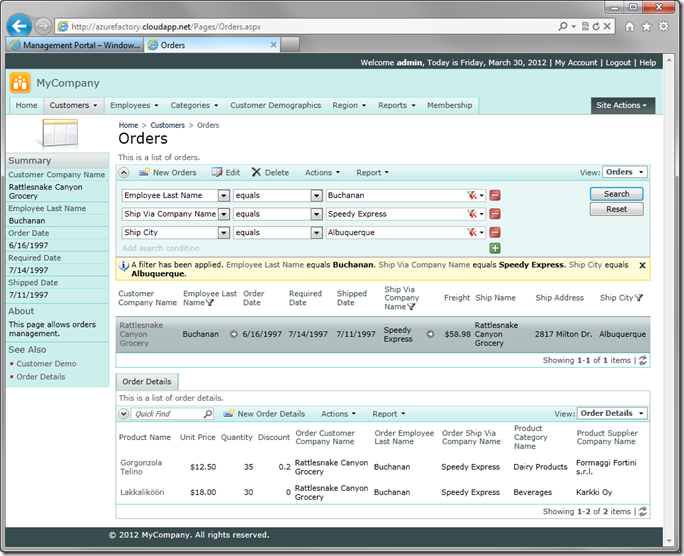
When you are ready to deploy a new project revision, create a new staging deployment. Test the new deployment in the cloud. If everything is working as expected, then swap the virtual IP address of the staging deployment with the production one. Click Swap VIP button on the Management Portal ribbon to do so.
When VIP swapping has finished, the previous application revision will become a staging deployment. Shut it down if you don’t need it. Continue upgrading staging deployment with the new revisions of the application, and swapping them later with production.