Code On Time applications offer powerful methods of converting and validating field values entered by user. The unique business rules model allows elegant abstraction of the business logic required to validate and convert user values from the user interface elements responsible for presentation.
Conversion
Let’s consider a simple conversion scenario that requires automatic conversion of a customer contact name to upper case as soon as user has finished typing. We will use Northwind database for this sample.
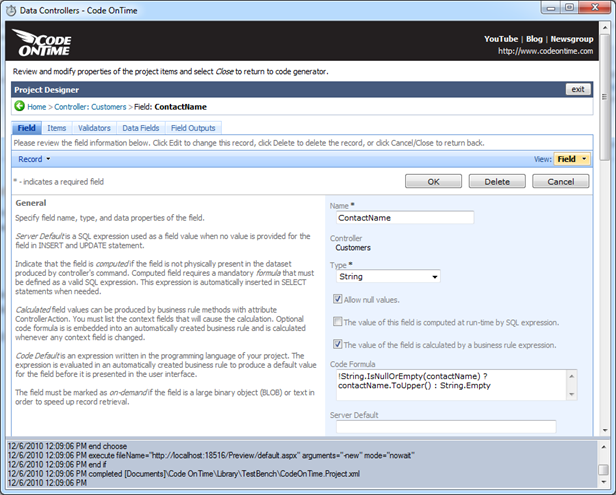
Generate your project, activate designer and select All Controllers tab. Select Customers data controller, switch to Fields tab and select the ContactName field. Select the check box “The value of the field is calculated by a business rule expression”.
Enter the following Code Formula if your programming language is C#:
!String.IsNullOrEmpty(contactName) ? contactName.ToUpper() : String.Empty
Visual Basic programmers should use the following instead:
IIf(Not (String.IsNullOrEmpty(contactName)), contactName.ToUpper(), String.Empty)
Next scroll the designer page down and enter ContactName in the Context Fields property. This is very important step that will ensure that the business rules formula is executed as soon as user leaves the field.
Here is the screen short of Designer that shows the partial configuration of the ContactName field.
Try running the program and observe the contact name convert to upper case as soon as you enter a value.
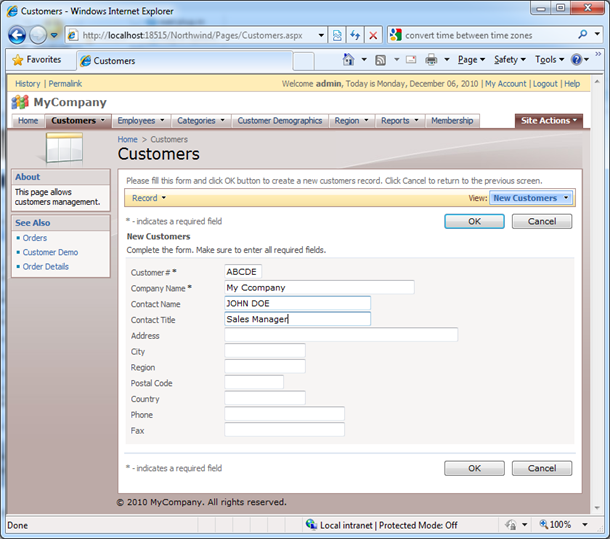
Note that this works in all views without you doing anything about it. You change the model and all views automatically engage the business rules.
Here is the actual file that is automatically produced to implement this calculation. This code is placed into ~/App_Code/Rules/Customers.Generated.cs file
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
using System.Web;
using MyCompany.Data;
namespace MyCompany.Rules
{
public partial class CustomersBusinessRules :
MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
{
[ControllerAction("Customers", "Calculate", "ContactName")]
public void CalculateCustomers(string customerID,
string companyName, string contactName, string contactTitle,
string address, string city, string region,
string postalCode, string country, string phone, string fax)
{
UpdateFieldValue("ContactName",
!String.IsNullOrEmpty(contactName) ?
contactName.ToUpper() :
String.Empty);
}
}
}
Note that the class is partial. You can implement you own class with the same name and offer a method that performs a more complex conversion using database or any other resources required for successful conversion calculation. Make sure not to change the file directly since the changes will be lost during next code generation. Instead use Designer to change the Code Formula of the corresponding field.
Here is the Visual Basic version of the same automatically generated method.
Imports MyCompany.Data
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.Data
Imports System.Linq
Imports System.Text.RegularExpressions
Imports System.Web
Namespace MyCompany.Rules
Partial Public Class CustomersBusinessRules
Inherits MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
<ControllerAction("Customers", "Calculate", "ContactName")> _
Public Sub CalculateCustomers(ByVal customerID As String, _
ByVal companyName As String, _
ByVal contactName As String, _
ByVal contactTitle As String, _
ByVal address As String, _
ByVal city As String, _
ByVal region As String, _
ByVal postalCode As String, _
ByVal country As String, _
ByVal phone As String, _
ByVal fax As String)
UpdateFieldValue("ContactName", _
IIf(Not (String.IsNullOrEmpty(contactName)), _
contactName.ToUpper(), _
String.Empty))
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Accessing field values
Many scenarios of validation may be narrowed performed as silent conversion using the method described above. The business rules methods offer every single field of the field dictionary of the data controller and you can use values of all fields to produce the value.
You can also use methods SelectFieldValue and SelectFieldValueObject and retrieve a field value required for conversion/validation.
The first method will return the untyped object representing the value of the field or external URL parameter. It is your responsibility to convert the value to use it in a calculation. For example,
Convert.ToString(SelectFieldValue("ContactName")).ToUpper()
The second method returns only the value objects that correspond to the fields of the data controller. The advantage of using SelectFieldValueObject is the ability to access the “Old” and “New” values and availablility of Modified property that tells if the field value has changed.
Convert.ToString(SelectFieldValueObject("ContactName").NewValue).ToUpper())
Validation
Validation is usually performed just before the standard logic of Code On Time application is about to be executed. User has completed input and initiated a command that will result in INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement execution.
Let’s consider another example. Let’s prevent posting of invalid values to the Order Details table.
Select your project on the start page of the code generator, activate designer, find Order Details data controller, select the data controller and edit the controller to have OrderDetailsBusinessRules as business rules Handler. See the screen shot below.
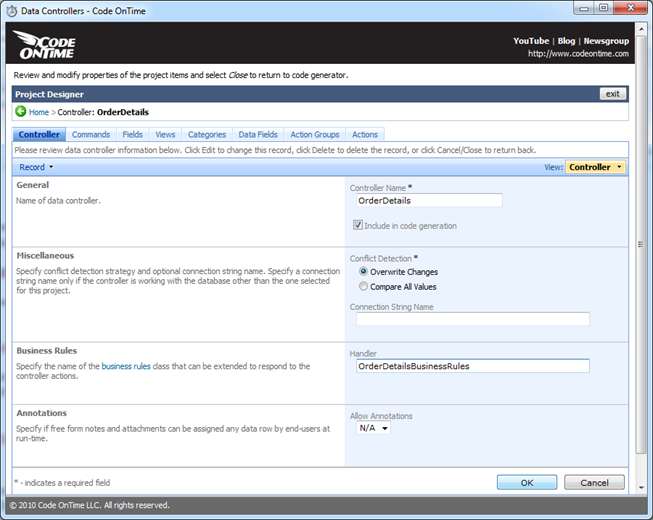
Save the changes, exit the designer and generate the project.
Open the project in Visual Studio using File | Open Web Site option and double click the ~/App_Code/Rules/OrderDetaulsBusinessRules.cs file to open it in the editor. Enter the following method if your project language is C#.
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using MyCompany.Data;
namespace MyCompany.Rules
{
public partial class OrderDetailsBusinessRules : MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
{
[ControllerAction("OrderDetails", "Update", ActionPhase.Before)]
[ControllerAction("OrderDetails", "Insert", ActionPhase.Before)]
public void ValidateInput(float? discount, short? quanity, decimal? price)
{
if (quanity.HasValue && quanity > 10)
if (!Controller.UserIsInRole("Administrators"))
throw new Exception("You are not authorized to sell more then 10 items.");
if (discount.HasValue && discount.Value > 0.15)
throw new Exception("The discount cannot be more than 15%.");
if (!price.HasValue || price.Value == 0.0m)
{
Result.ExecuteOnClient("this._focus('UnitPrice', 'The price must be greater than zero.')");
throw new Exception("Please validate the entered unit price.");
}
}
}
}
Here is the Visual Basic version.
Imports MyCompany.Data
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.Data
Imports System.Linq
Namespace MyCompany.Rules
Partial Public Class OrderDetailsBusinessRules
Inherits MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
<ControllerAction("OrderDetails", "Update", ActionPhase.Before)> _
<ControllerAction("OrderDetails", "Insert", ActionPhase.Before)> _
Public Sub ValidateInput(ByVal discount As Nullable(Of Single), _
ByVal quantity As Nullable(Of Short), _
ByVal unitPrice As Nullable(Of Decimal))
If (quantity.HasValue AndAlso quantity > 10) Then
If (Not Controller.UserIsInRole("Administrators")) Then
Throw New Exception("You are not authorized to sell more then 10 items.")
End If
End If
If (discount.HasValue AndAlso discount.Value > 0.15) Then
Throw New Exception("The discount cannot be more than 15%.")
End If
If (Not (unitPrice.HasValue) Or (unitPrice.HasValue AndAlso unitPrice.Value = 0)) Then
Result.ExecuteOnClient("this._focus('UnitPrice', 'The price must be greater than zero.')")
Throw New Exception("Please validate the entered unit price.")
End If
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Notice that the order of the arguments in the validation method is absolutely irrelevant. The same method is handling both Insert and Update actions. You can implement a dedicated method to handle each situation differently. You can use a Shared Business Rules method to create a handler for multiple data controllers.
Runt he program, select Customers | Order Details page and try entering the order details records while leaving blank Discount, Unit Price, and Quantity fields. The Unit Price validation will detect the problem and will result in the following. The message bar at the top of the page indicates that there is a problem. The inline error message explains what the problem in with more details.
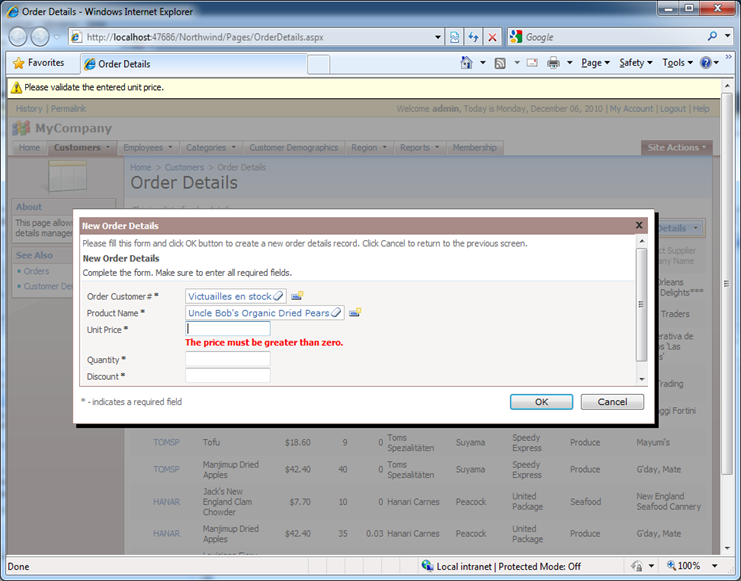
The future versions of the code generation library will offer an alternative method of indicating the error using the business rules method to eliminate the need to use a snippet of JavaScript to report the validation error.