Code On Time web app generator automatically creates controllers for any specified tables and views from your database. In addition, you can define new controllers from any SQL query. One can also choose to display data from any data source using C# or Visual Basic business rules – you are only limited by your imagination.
In this example, let’s request a list of articles recently published on /blog. A sample application showing the blog posts can be seen below.
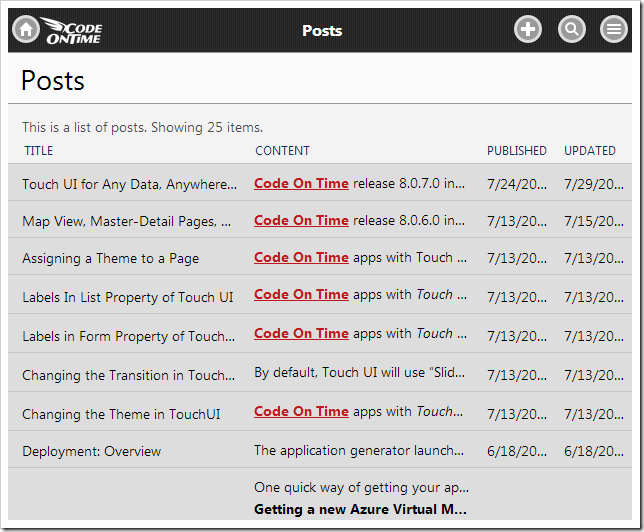
The URL that will be used to compose a REST request is the following:
http://www.blogger.com/feeds/2297698770491701674/posts/default/
You can see an example of the response with the essential items highlighted below.
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<?xml-stylesheet href="http://www.blogger.com/styles/atom.css" type="text/css"?>
<feed xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom' ...>
...
<entry>
...
<published>2014-07-13T22:25:00.000-07:00</published>
<updated>2014-07-15T00:03:46.566-07:00</updated>
...
<title type='text'>
Map View, Master-Detail Pages,
Custom Result Sets, Client-Side APIs
</title>
<content type='html'>
<p><a title="Code On Time generator creates line-of-business Web Apps ...
</content>
...
</entry>
<entry>
...
<published>2014-07-13T10:00:00.000-07:00</published>
<updated>2014-07-13T17:11:25.294-07:00</updated>
...
<title type='text'>Assigning a Theme to a Page</title>
<content type='html'>
<p><a title="Code On Time Generator is a premier web application ...
</content>
...
</entry>
...
</feed>
The code business rule will need to accept this XML, create a data table and convert each “entry” element into a data row. The data rows will have four columns – Published, Updated, Title, and Content.
Defining the Controller
The first step is to define a controller that will handle the data table. One possible way of defining the controller would be to simply create it in the Project Designer. However, let’s take advantage of the automatic field, view, data field, and action generation provided by the Define Data Controller tool.
Start the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab and press the New Controller icon.
Give the controller a name:
| Property |
Value |
| Name |
Posts |
Press OK to save the new controller. Expand the new controller in the Project Explorer, and right-click on the Fields node. Select New Field option.
Define the following properties:
| Property |
Value |
| Name |
Title |
| Type |
String |
| Length |
256 |
Press OK to save. Create another field with these properties:
| Property |
Value |
| Name |
Content |
| Type |
String |
| Html Encoding |
False |
Save the field, and add another:
| Property |
Value |
| Name |
Published |
| Type |
DateTime |
Save, and add the Updated field:
| Property |
Value |
| Name |
Updated |
| Type |
DateTime |
Save the last field. Right-click on the controller, and press Generate From Fields.
This will proceed to generate views, data fields, actions, and several code business rules to override CRUD operations. No command will be created.
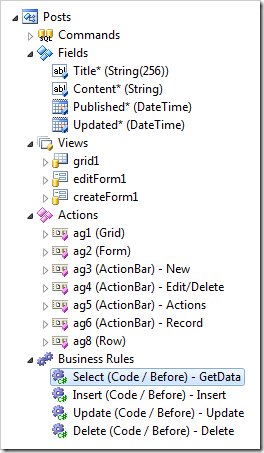
The first code business rule will provide an outline for defining the result set. The next three rules simply override the Insert, Update, and Delete actions and call PreventDefault() method. The developer must implement these rules in order for the respective actions to work.
On the toolbar, press Browse to regenerate the app and create the code files. When complete, right-click on Posts / Business Rules / Select (Code / Before) – GetData business rule, and press Edit Rule In Visual Studio.
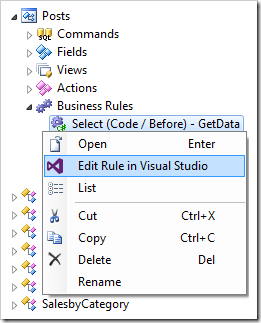
The file will open in Visual Studio. The business rule will create a DataTable object by calling to CreatePostsDataTable() method. The default implementation of this method will simply return a data table with no data.
[Rule("GetData")]
public void GetDataImplementation(
string title,
string content,
DateTime? published,
DateTime? updated)
{
ResultSet = CreatePostsDataTable();
}
private DataTable CreatePostsDataTable()
{
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
dt.Columns.Add("Title", typeof(String));
dt.Columns.Add("Content", typeof(String));
dt.Columns.Add("Published", typeof(DateTime));
dt.Columns.Add("Updated", typeof(DateTime));
//
// Populate rows of table "dt" with data from any source
// (web service, file system, database, etc.)
//
return dt;
}
Let’s complete the implementation by providing the data for the data table. At the top of the file, add the following using/import directive:
C#:
using System.Xml;
Visual Basic:
Imports System.Xml
Then, replace the “Populate rows of table” comment after the data table is declared with the following code. The code will make a request to Blogger, read in each “entry” element and create a new data row in the table using the values of that element.
C#:
// get data into table
XmlReader reader = XmlReader.Create(
"http://www.blogger.com/feeds/2297698770491701674/posts/default/");
reader.ReadToDescendant("entry");
while (reader.LocalName == "entry")
{
DataRow r = dt.NewRow();
XmlReader subtree = reader.ReadSubtree();
if (subtree.ReadToDescendant("published"))
{
r["Published"] = subtree.ReadElementContentAsDateTime("published",
"http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom");
r["Updated"] = subtree.ReadElementContentAsDateTime("updated",
"http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom");
while (subtree.LocalName != "title")
subtree.Read();
r["Title"] = subtree.ReadElementContentAsString("title",
"http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom");
r["Content"] = subtree.ReadElementContentAsString("content",
"http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom");
dt.Rows.Add(r);
}
if (!reader.ReadToFollowing("entry") || reader.EOF)
break;
}
Visual Basic:
Dim reader As XmlReader = XmlReader.Create(
"http://www.blogger.com/feeds/2297698770491701674/posts/default/")
reader.ReadToDescendant("entry")
While reader.LocalName = "entry"
Dim r As DataRow = dt.NewRow()
Dim subtree As XmlReader = reader.ReadSubtree()
If subtree.ReadToDescendant("published") Then
r("Published") = subtree.ReadElementContentAsDateTime("published",
"http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom")
r("Updated") = subtree.ReadElementContentAsDateTime("updated",
"http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom")
While subtree.LocalName <> "title"
subtree.Read()
End While
r("Title") = subtree.ReadElementContentAsString("title",
"http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom")
r("Content") = subtree.ReadElementContentAsString("content",
"http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom")
dt.Rows.Add(r)
End If
If Not reader.ReadToFollowing("entry") OrElse reader.EOF Then
Exit While
End If
End While
Make sure to save the file.
Adding the Page and Viewing the Results
Switch back to the Project Designer. Right-click on the Posts controller node, and press Copy.
Switch to the Pages tab in the Project Explorer. Click on the New Page icon.
Assign a name.
| Property |
Value |
| Name |
Posts |
Press OK to save the page. Drag the new page in the Project Explorer to the right of Home page node to place it second in the site menu.
Right-click on the new page and press Paste to bind the controller to the page.
On the toolbar, press Browse to generate and open the web app in the default browser. The list of posts retrieved from the web service is displayed on the page. Note that you must define a primary key before any of the items can be selected.