Requirements for high-security web applications may require the logging of user credentials when data is accessed. Let’s create two fields, AccessedBy and AccessedOn, and use SQL Business Rules to automatically update these fields.
Adding AccessedBy and AccessedOn Columns
Start SQL Server Management Studio. Connect to your database. In the Object Explorer, right-click on Databases / Northwind / Tables / dbo.Customers node, and press Design.
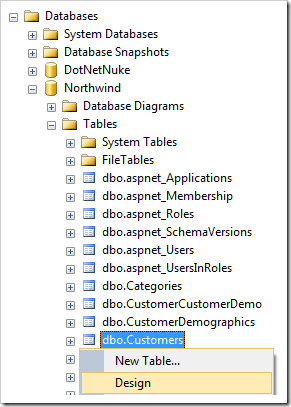
Add two columns to the table:
| Column Name | Data Type | Allow Nulls |
| AccessedOn | datetime | true |
| AccessedBy | nvarchar(50) | true |
Save the table.
Switch back to Code On Time web application generator. Refresh the project.
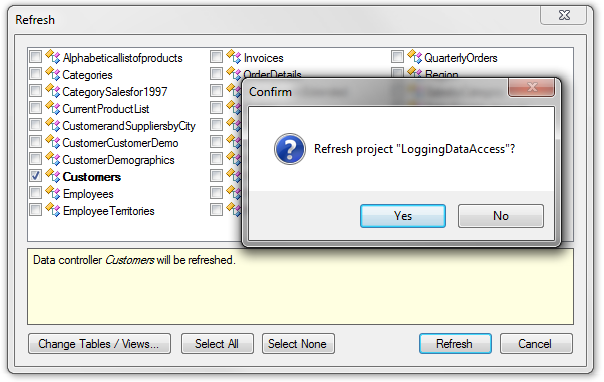
Configuring the Fields
Start the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab and double-click on Customers / Fields / AccessedOn node.
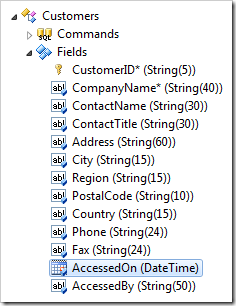
Change the following properties:
Press OK to save the field. Double-click on Customers / Fields / AccessedBy node.
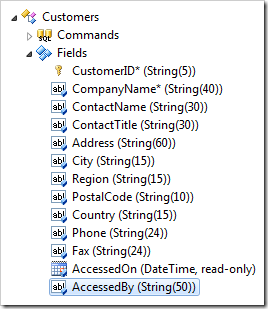
Mark the field as read-only:
| Property | Value |
| Values of this field cannot be edited | true |
Press OK to save the field. Right-click on Customers / Business Rules node, and press New Business Rule.
Give this rule the following properties:
| Property | Value |
| Type | SQL |
| Command Name | Select |
| View | editForm1 |
| Phase | Execute |
| Script | set @AccessedOn = getdate()
set @AccessedBy = @BusinessRules_UserName
|
Seeing the Results
On the toolbar, press Browse. Navigate to the Customers page, and select a customer. The Accessed On and Accessed By fields will be appear on the form with updated values.
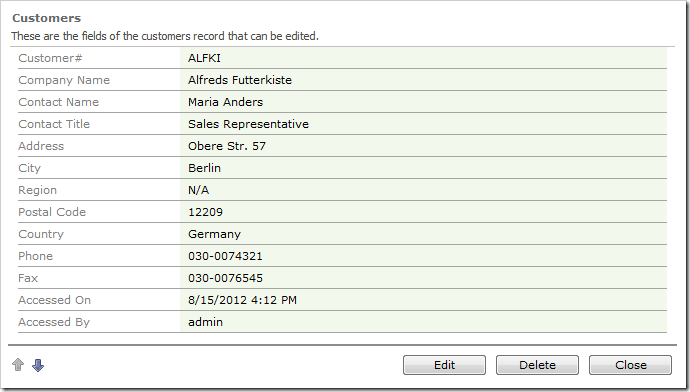
However, if you check the records in the database, the columns will not be updated.
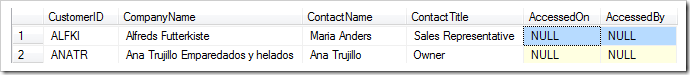
This is due to the way that the client library works – when data is selected from the database, the business rule adds the values to AccessedOn and AccessedBy before they are displayed in the user interface. If the user tries to save the values, the client library will compare the data requested from the server (with appended values) and any new values. Because the user has not changed these fields, the client library assumes that the values are unchanged and does not update the record.
There are two methods of updating the field value:
- Update the field value when the user selects the record.
- Update the field value after the user updates the record.
Method 1: Update When User Selects
Switch back to the Project Designer. The business rule will still be open in the Browser window. Change the Script property as follows:
| Property |
New Value |
| Script |
set @AccessedOn = getdate()
set @AccessedBy = @BusinessRules_UserName
update Customers
set AccessedOn=@AccessedOn, AccessedBy=@AccessedBy
where CustomerID=@CustomerID
|
Press OK to save the business rule. On the toolbar, press Browse.
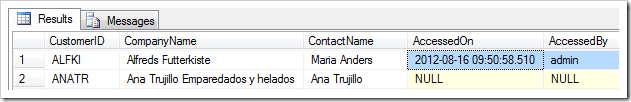
Navigate to the Customers page, and select a record. The Accessed On and Accessed By fields will be populated in the user interface.
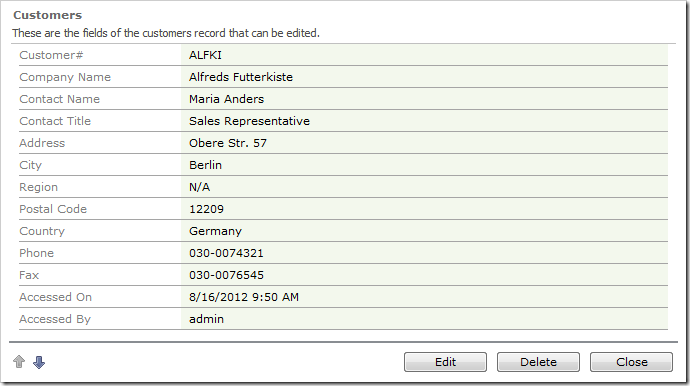
The database record will be updated as well.
Method 2: Update When User Updates
Make sure you are not using the business rule from Method 1. Switch back to the Project Designer. Right-click on Customers / Business Rules and press New Business Rule.
Give this business rule the following properties:
| Property |
Value |
| Type |
SQL |
| Command Name |
Update |
| Phase |
Execute |
| Script |
update Customers
set AccessedOn=@AccessedOn, AccessedBy=@AccessedBy
where CustomerID=@CustomerID
|
Press OK to save. On the toolbar, press Browse.
Navigate to the Customers page. Select a customer, and the fields will be populated in the user interface.
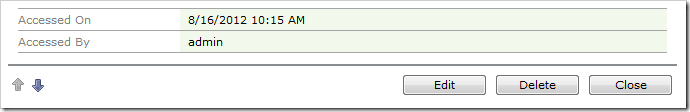
However, the database will not be updated.

Press Edit, change a field value, and press OK to save.
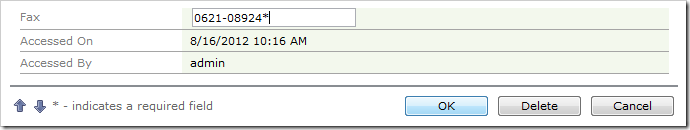
The column values will be updated only when the record is updated.
