Code On Time generator offers the ability to compose controllers from the results of custom SQL scripts.
If a stored procedure is the data source, business rules must be used to compose a result set. This allows the application framework to perform sorting and filtering operations that would otherwise be performed by the database server.
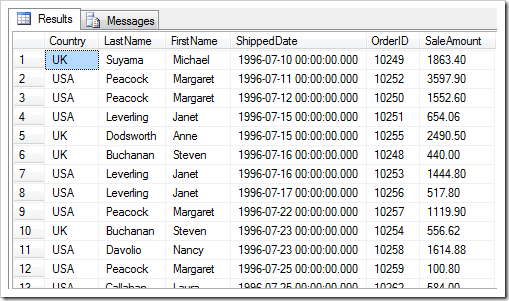
Here is an example of a result set produced by a stored procedure called from an SQL business rule.
In this example, we will be using the “Employee Sales by Country” stored procedure, available with the Northwind sample database. The procedure combines data from Employees, Orders, and gets the total price (from Order Details) for each order in between the Beginning Date and Ending Date parameters. The CREATE script for the stored procedure can be seen below.
CREATE procedure dbo.[Employee Sales by Country]
@Beginning_Date DateTime, @Ending_Date DateTime AS
SELECT Employees.Country,
Employees.LastName,
Employees.FirstName,
Orders.ShippedDate,
Orders.OrderID,
"Order Subtotals".Subtotal AS SaleAmount
FROM Employees INNER JOIN
(Orders INNER JOIN "Order Subtotals" ON Orders.OrderID = "Order Subtotals".OrderID)
ON Employees.EmployeeID = Orders.EmployeeID
WHERE Orders.ShippedDate Between @Beginning_Date And @Ending_Date
Example output can be seen in the following picture.
Let’s generate this data controller.
Start the web app generator and activate the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab. Click on the New Controller icon on the toolbar.
Give the controller a name:
| Property |
Value |
| Name |
EmployeeSalesByCountry |
Press OK to save the new controller. In the Project Explorer, right-click on the new controller and press “Generate From SQL…”.
The Define Data Controller window will open. Paste in the following script:
EXEC dbo.[Employee Sales by Country]
@Beginning_Date = '1970-01-01',
@Ending_Date = '2000-01-01'
Press Verify and the result will be seen in the data grid, as in the picture below:
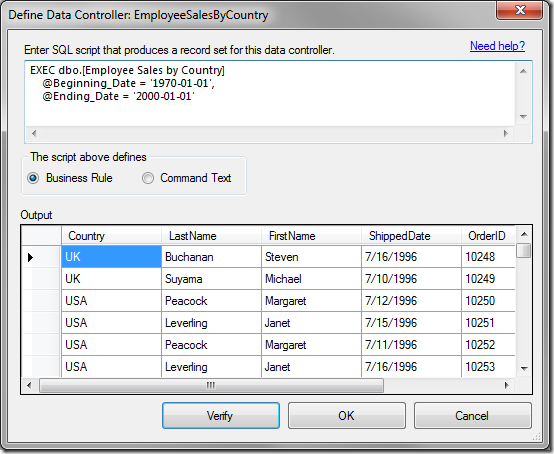
The Define Data Controller window also offers the option to define a Business Rule or the Command Text for the controller.
When “Command Text” is selected, the controller will have a command defined from the SQL script and will take advantage of the application framework’s ability to compose SQL statements on the fly. SQL formulas will be defined for each field. If specified, the “Base Table Name” property will be used in any dynamically created Insert and Update statements.
The “Business Rule” option will not generate a command for the controller. Instead, two SQL business rules will be created that prevent the default Select action from occurring and define a custom result set. In addition, three more business rules will be created to override the insert, update, and delete actions from occurring.
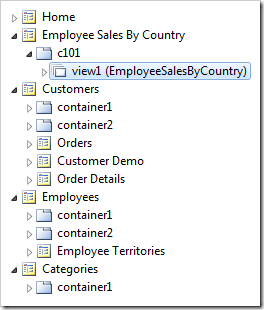
Keep default settings and press OK to define the data controller. The window will close and the Project Explorer will refresh with added fields, views, data fields, actions, as well as the command or business rules.
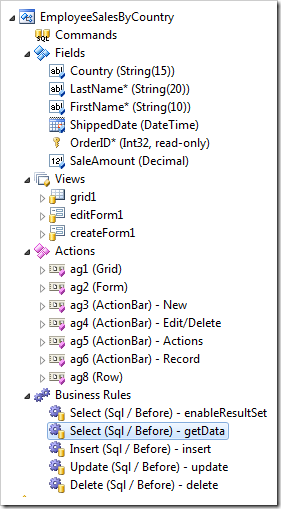
Next, we will need to create a page and bind the controller to the page with a data view. Right-click on the controller and press Copy.
Switch to the Pages tab in the Project Explorer. Click on the New Page icon.
Assign a name.
| Property |
Value |
| Name |
EmployeeSalesByCountry |
Press OK to save the page. Drag the new page in the Project Explorer to the right of Home page node to place it second in the site menu.
Right-click on the new page and press Paste to bind the controller to the page.
On the toolbar, press Browse to generate the app and open it in the default browser.
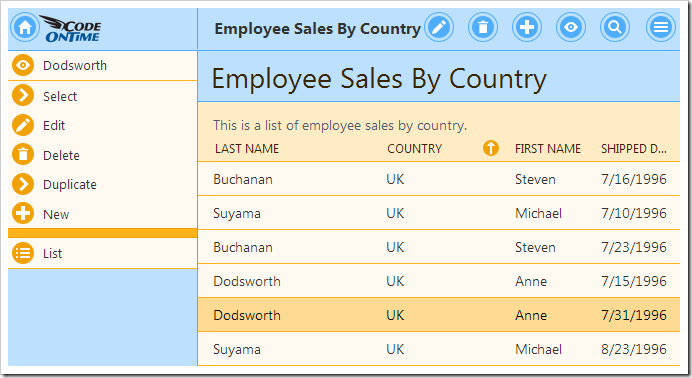
The result set will be visible on the page. The user can sort, filter, and view data. Note that additional programming will be required to allow the user to update, insert, or delete records.