Data views in an app created with Code On Time may present users with the view style called “Charts”. This view style is either enabled automatically by application at runtime or by developers at design time. The purpose of the view style is to provide instant insight into data.
If the definitions of charts are not a part of application design, then the application framework will compose up to nine charts based on the properties of fields in the data view if possible. The app will attempt to define charts after examining the presence of lookup, date, or numeric fields in the view. First, it will try creating charts with dates as the rows, and lookups as the values. Then, it will pair a few numeric fields with a lookup.
The picture shown below displays the charts automatically created for the Orders controller of the Northwind sample application.
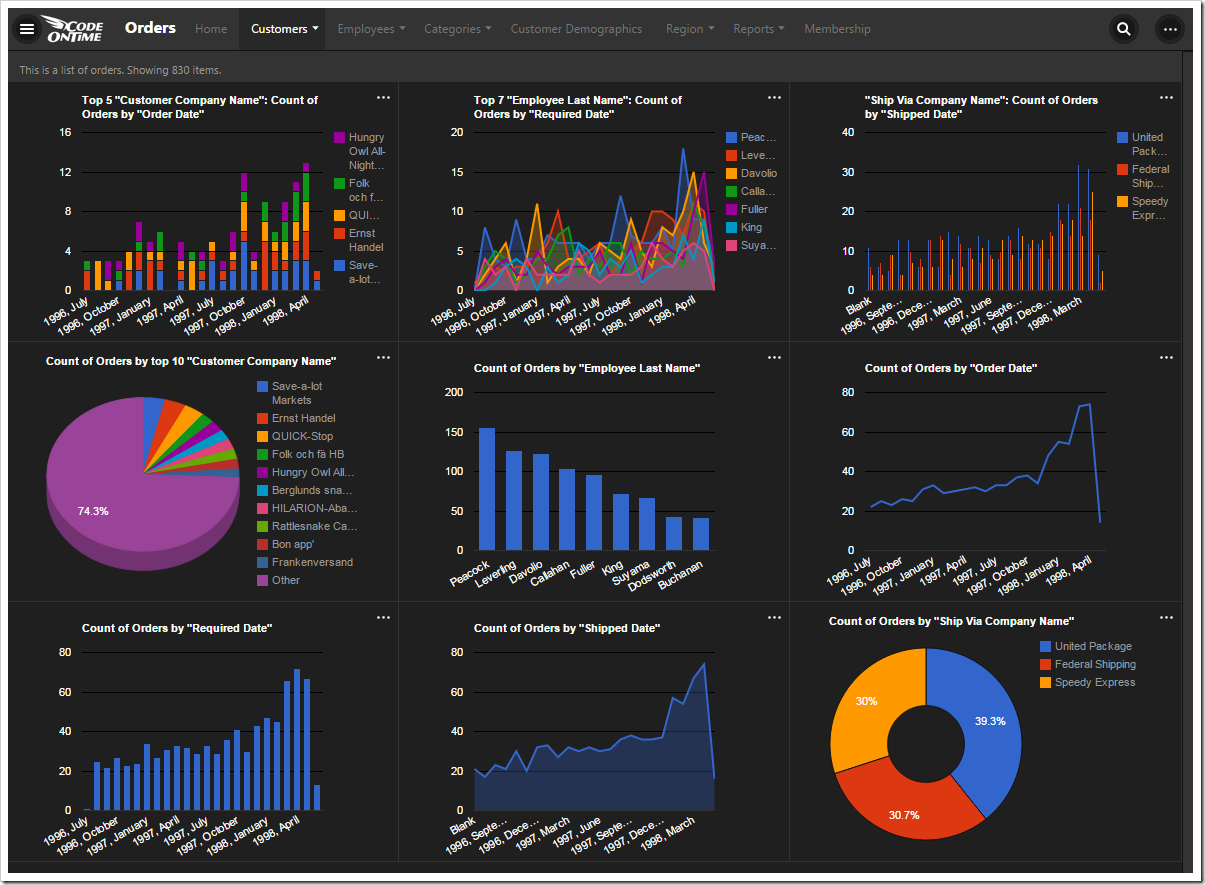
The automatically created definitions for all of the nine charts are shown below. Each chart is described with one or two tags that start with “pivot-“ keyword followed by properties. The elegant simplicity of the tag language makes possible sophisticated collections of charts defined both by developers and end users.
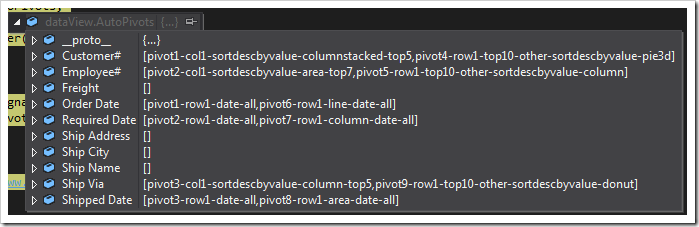
Application framework performs efficient server-side data pivots following the tag specification. Data pivots for all charts are performed on the server simultaneously. Data pivots take into account application-level and user-defined filters.
Let’s see how each chart works.
Chart 1 – Stacked Column + Dates
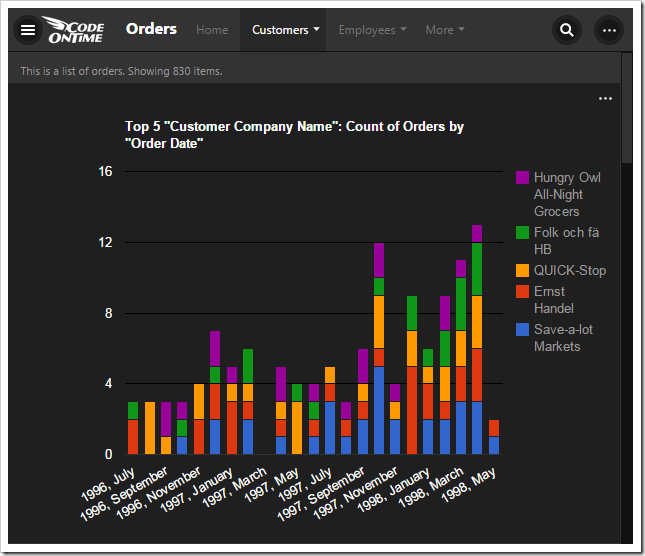
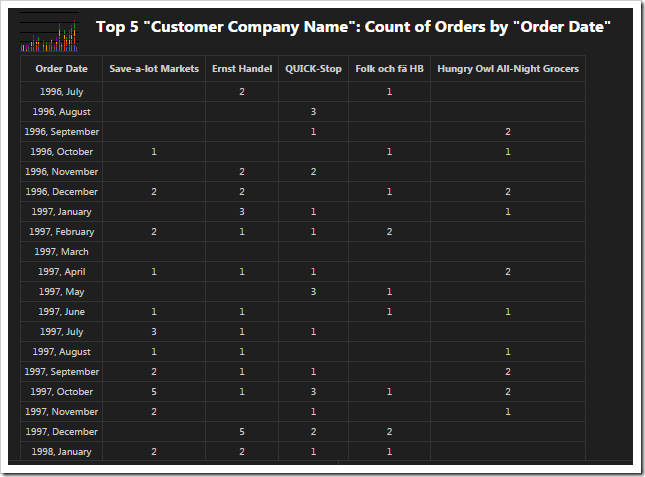
This chart uses the first date field, OrderDate, as the rows. The “pivot1” property assigns the field to the pivot with ID of “1”. The “row” property sets the field as a row in the pivot, and assigns it index “1”.
The property “date” instructs the application to try several date bucket groups and choose the best one available based on the number of rows in the output. Application framework tries not to have too many or too few “date” rows in a pivot. For the dataset in the picture, the framework has produced the pivoted data as if tags “pivot1-row1-year pivot1-row2-month” were specified.
The “all” property ensures that any empty gaps in the data will be included in the pivot dimension.
The first lookup field, CustomerID, is used for the columns. The columns are sorted in descending order by the value of each column. Then, only the top five customers are kept, and the rest of them are dropped from the output. The “columnstacked” property defines the type of chart.
When a value field is not defined for the chart, a count of the first available field is used.
| Field Name | Tag |
| OrderDate | pivot1-row1-date-all |
| CustomerID | pivot1-col1-sortdescbyvalue-columnstacked-top5 |
Chart 2 – Area + Dates
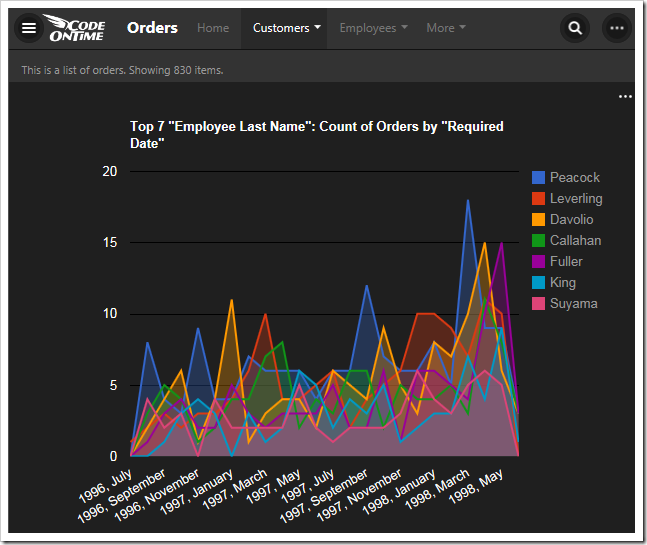
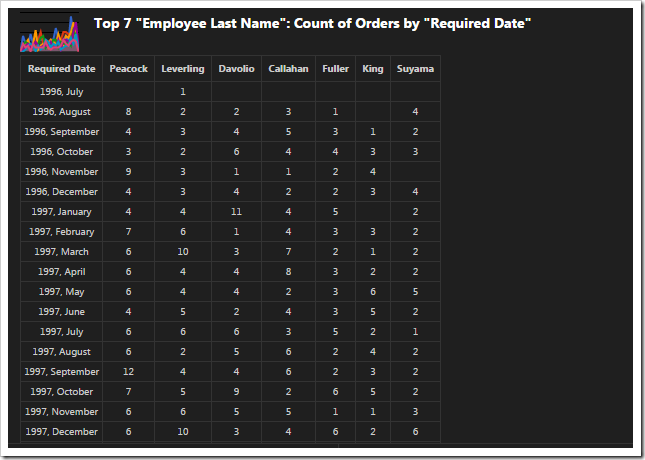
This chart uses the second date field, RequiredDate, as the rows.
The second lookup field, EmployeeID, is used for the columns, and the top seven employees sorted in descending order are used. The “area” property specifies the chart type.
| Field Name | Tag |
| RequiredDate | pivot2-row1-date-all |
| EmployeeID | pivot2-col1-sortdescbyvalue-area-top7 |
Chart 3 – Column + Dates
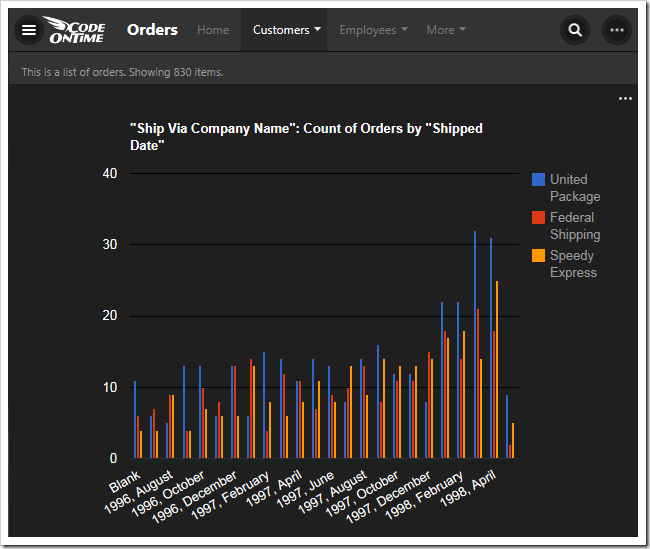
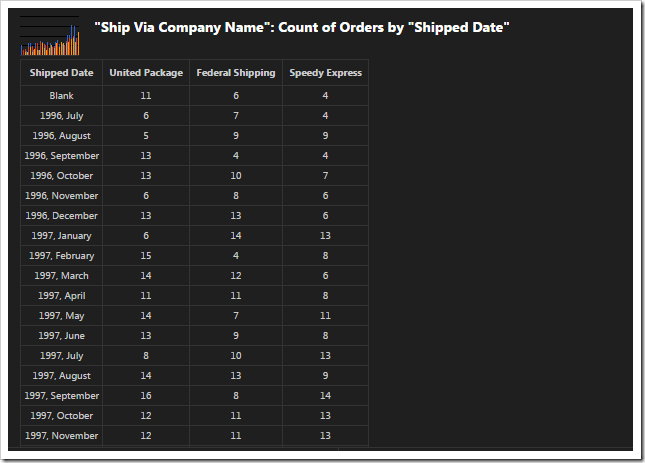
This chart uses the third date field, ShippedDate, as the rows of the output.
The ShipVia lookup field is used, and only the top five values are kept. The type of the chart is defined as “column”.
| Field Name | Tag |
| ShipVia | pivot3-col1-sortdescbyvalue-column-top5 |
| ShippedDate | pivot3-row1-date-all |
Chart 4 – 3d Pie
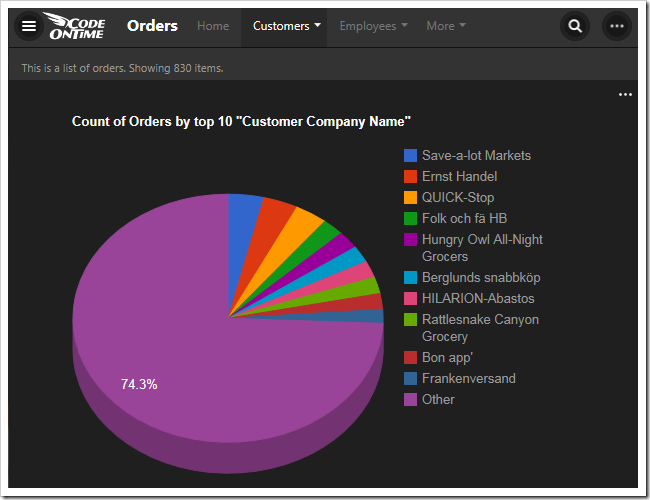
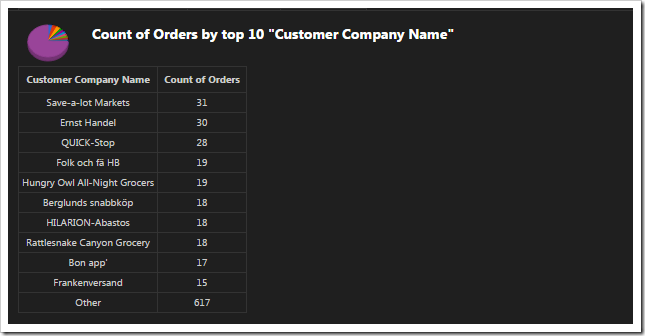
The fourth chart uses CustomerID as the row values. The top ten values are displayed. The “other” property commands the server to sum up the rest of the values in an “Other” row. The type of chart is “pie3d”.
When no column field is defined, there will be only one column to display the value.
| Field Name | Tag |
| CustomerID | pivot4-row1-top10-other-sortdescbyvalue-pie3d |
Chart 5 – Columns
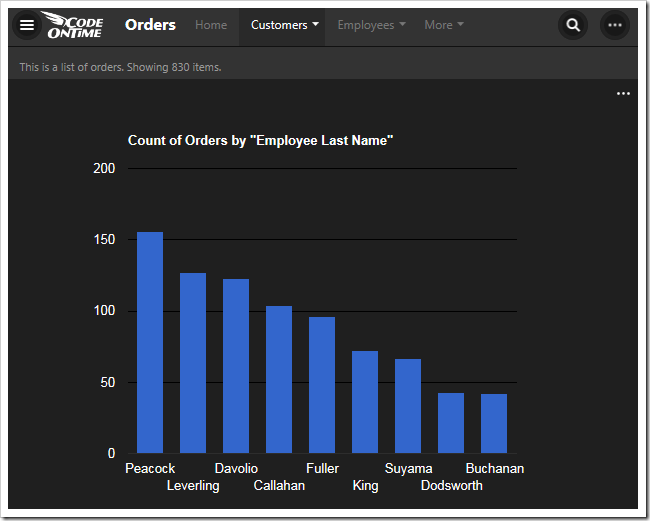

The fifth chart uses EmployeeID lookup field for the rows. The top ten values are displayed, and the rest are summed up into an “Other” row. The type of chart is “column”.
| Field Name | Tag |
| EmployeeID | pivot5-row1-top10-other-sortdescbyvalue-column |
Chart 6 – Line
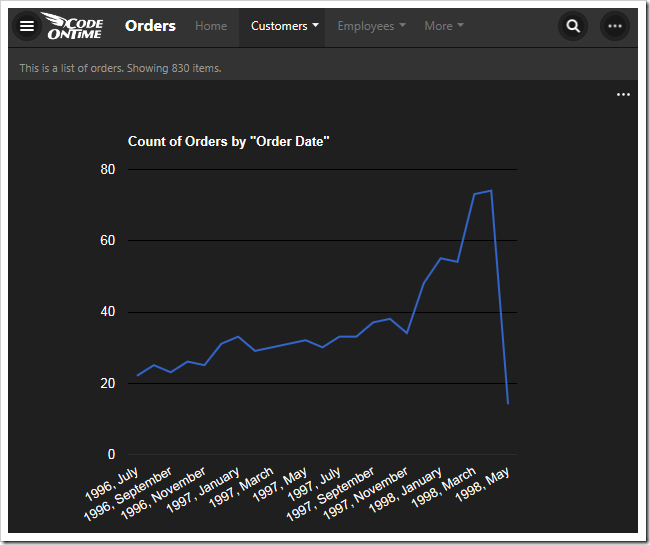
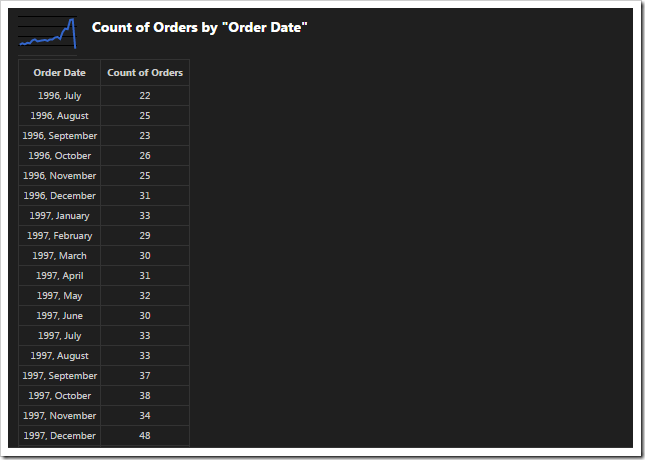
The next chart uses the OrderDate field as the rows. The “date” property will generate multiple sets of data, differentiated by bucket size, and use the best result for the chart. The property “all” will ensure that there are no missing values in the date range. The type of chart is “line”.
| Field Name | Tag |
| OrderDate | pivot6-row1-line-date-all |
Chart 7 – Columns
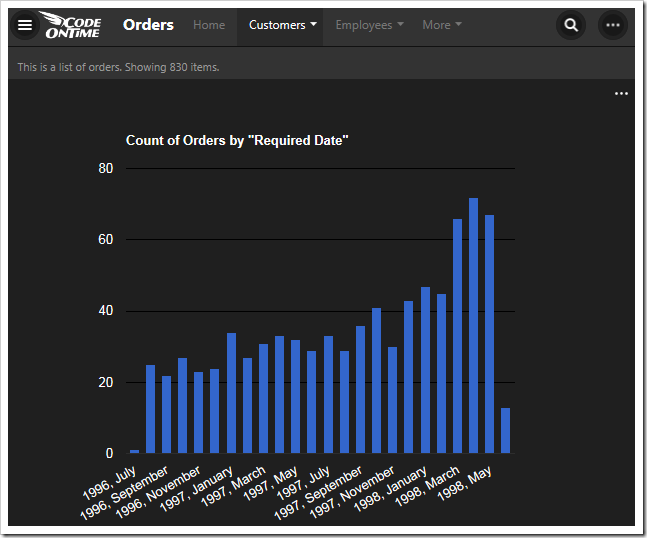
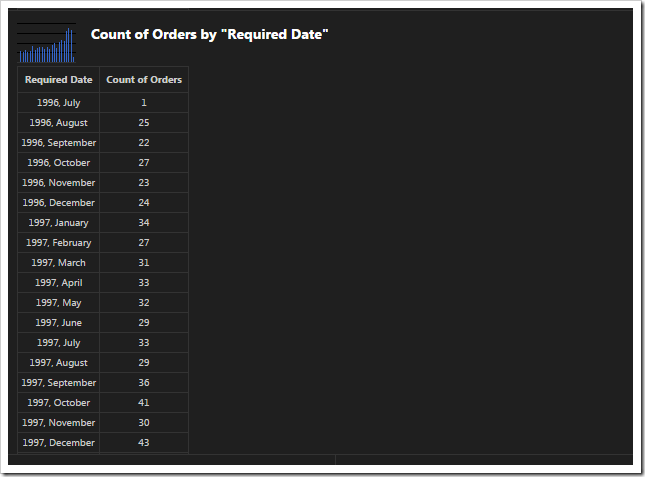
This chart uses the RequiredDate field for the row values. The type of chart is “column”. The server will compose multiple results and pick the best one that fits in the graph when “date” is used. The chart will not miss any gaps in dates with the “all” keyword.
| Field Name | Tag |
| RequiredDate | pivot7-row1-column-date-all |
Chart 8 - Area
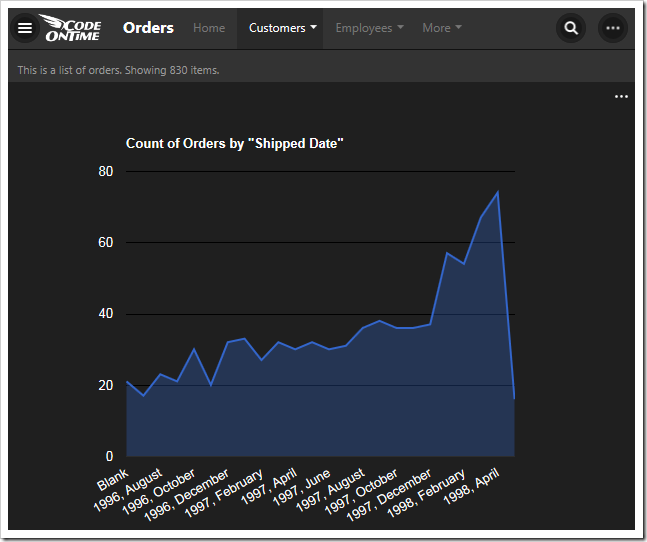
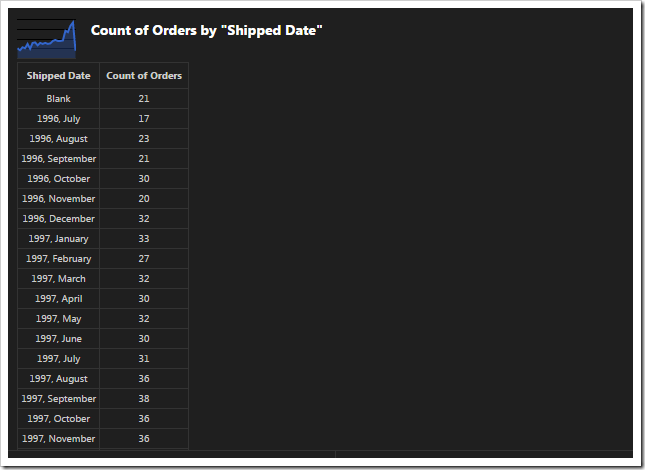
This chart shows values grouped into rows by the ShippedDate field.
| Field Name | Tag |
| ShippedDate | pivot8-row1-area-date-all |
Chart 9- Donut
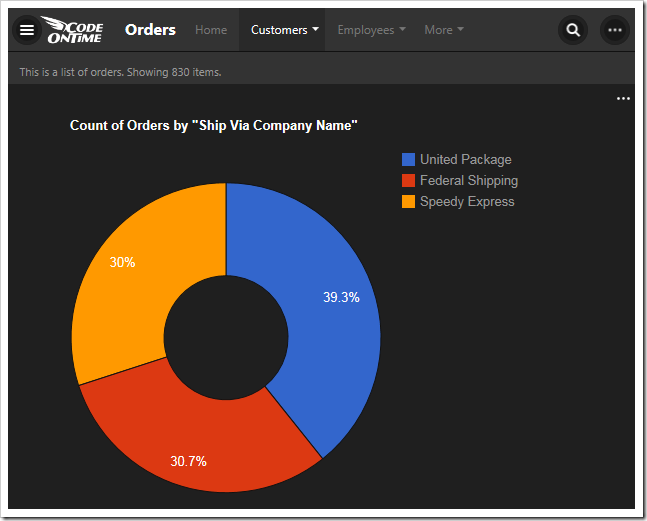
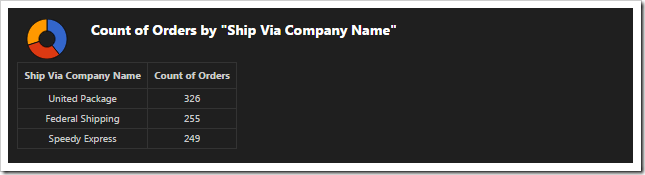
This chart uses the ShipVia lookup field for the rows of the result. The “top10” tag is disregarded as there are less than ten values in the result.
| Field Name | Tag |
| ShipVia | pivot9-row1-top10-other-sortdescbyvalue-donut |