Data Aquarium Framework offers a unique approach to creating reusable business rules and logic for ASP.NET applications. Today we will explore filtering with business rules.
All code samples are built for a Data Aquarium application generated from Northwind database.
Task 1
You want to enhance the customer lookup capability of Northwind application to display only USA customers when users are editing orders in a grid view and have a UK customer list when users are editing orders in form view. This should not affect any other views that are presenting customers.
Solution
Create new class Class1 and add property Country as shown in example below.
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using MyCompany.Data;
public class Class1 : BusinessRules
{
public Class1()
{
}
[RowFilter("Customers", "grid1", "Country")]
public string Country
{
get
{
RowFilter.Canceled = String.IsNullOrEmpty(
RowFilter.LookupContextController);
if (RowFilter.LookupContextController == "Orders" &&
RowFilter.LookupContextView == "editForm1")
return "UK";
else
return "USA";
}
}
}
VB
Imports Microsoft.VisualBasic
Imports MyCompany.Data
Public Class Class1
Inherits BusinessRules
<RowFilter("Customers", "grid1", "Country")> _
Protected ReadOnly Property Country() As String
Get
RowFilter.Canceled = _
String.IsNullOrEmpty(RowFilter.LookupContextController)
If RowFilter.LookupContextController = "Orders" AndAlso _
RowFilter.LookupContextView = "editForm1" Then
Return "UK"
Else
Return "USA"
End If
End Get
End Property
End Class
This class is inherited from MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules base.
Property Country is adorned with RowFilter attribute. This attribute will force the framework to evaluate the property whenever grid1 view of data controller Customers is expected to present data. The value of the property will be applied as a server-side filter.
The filtering property Country is notifying the framework that its value shall be ignored when property LookupContextController of RowFilter is null. This can be accomplished by assigning boolean value False to RowFilter.Canceled.
Row filter is constructed only once for each data page request received from the client. The framework will reset the cancellation flag of row filter prior to evaluating each business rules property matched to the requesting data controller view. If evaluation of the property has resulted in cancellation then property value is ignored. Otherwise the value is inserted as a parameterized SQL expression in the WHERE clause of SELECT statement constructed by the framework.
The third argument of RowFilter attribute applied to Country property specifies the name of the field that must be filtered. This is useful if the property of the business rule is named differently than the actual field defined in the data controller view. It is redundant in our example.
Class BusinessRules features RowFilter property that gives you access to Controller, View, LookupContextController, LookupContextView, and LookupContextFieldName that are useful to determine if and how the filter shall be applied. Lookup context properties are informing you if the data has been requested by the lookup field. You can examine lookup context field name to apply a server-side filter to the data that might be helpful if the same database lookup data is used to provide lookup values to more than one table in your database. If the data is requested by a standalone data view then you will find that all of the lookup context properties are equal to null.
Multiple RowFilter attributes can be applied to the same property.
Now you have to link the new business rules to Customers data controller defined in ~/Controllers/Customers.xml. This is done by adding attribute handler as shown here.
<dataController name="Customers"
conflictDetection="overwriteChanges"
label="Customers" xmlns="urn:schemas-codeontime-com:data-aquarium"
handler="Class1">
......
Run your application or navigate to the online demo at http://dev.codeontime.com/demo/filteringrules/?controller=Orders.
Start editing any order in the grid view of orders.
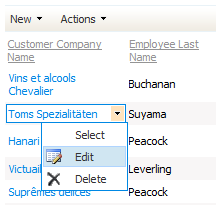
Click on the link with the customer name.
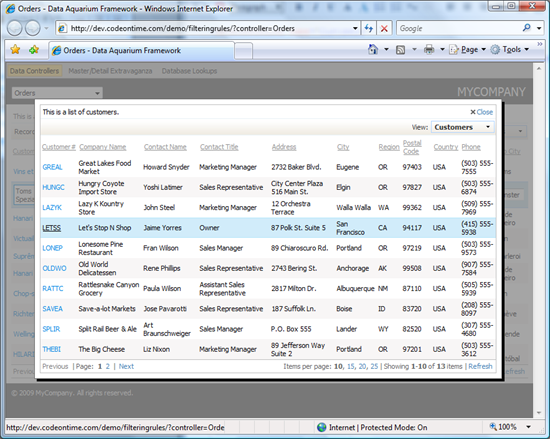
Customer lookup window will display 13 records of customers from USA.
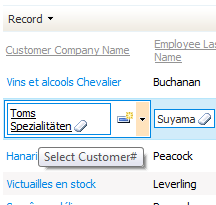
Press Escape key and click on any other link in Customer Company Name column. Click Edit button to start editing record in the form view editForm1.
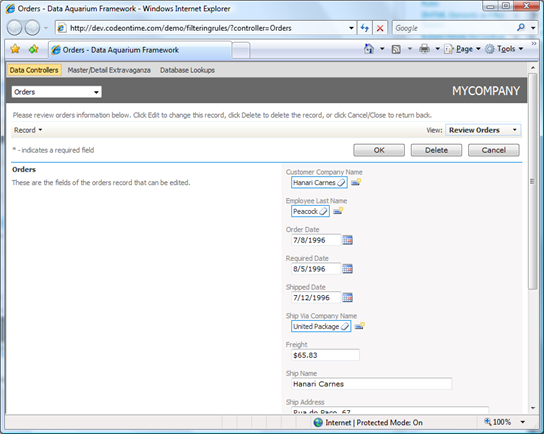
Click on the lookup link in Customer Company Name field. Notice that only UK customers are presented.
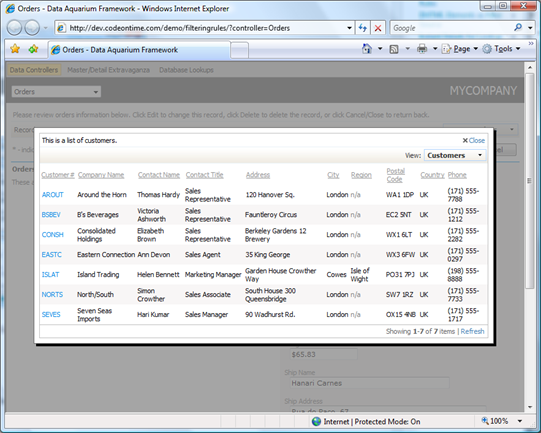
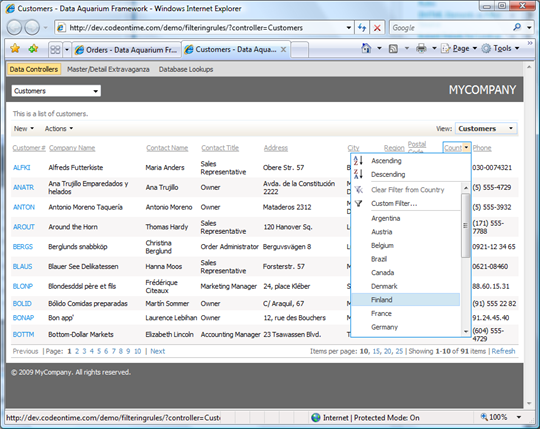
Let’s see if our business rules have affected the global list of customers. Navigate to http://dev.codeontime.com/demo/filteringrules?controller=Customers. About ninety customer records shall be displayed. We have used RowFilter.Canceled property to prevent filtering when the data is no requested in the context of the lookup field.
Task 2
You want to limit the list of employees to those born between 1/1/1950 and 11/1/1960.
Solution
Continue modifying our class and add BirthDate and BirthDate2 properties.
C#
[RowFilter("Employees", "grid1", "BirthDate",
RowFilterOperation.GreaterThanOrEqual)]
public DateTime BirthDate
{
get
{
return new DateTime(1950, 1, 1);
}
}
[RowFilter("Employees", "grid1", "BirthDate",
RowFilterOperation.LessThanOrEqual)]
public DateTime BirthDate2
{
get
{
return new DateTime(1960, 1, 1);
}
}
VB
<RowFilter("Employees", "grid1", "BirthDate", _
RowFilterOperation.GreaterThanOrEqual)> _
Protected ReadOnly Property BirthDate() As DateTime
Get
Return New DateTime(1950, 1, 1)
End Get
End Property
<RowFilter("Employees", "grid1", "BirthDate", _
RowFilterOperation.LessThanOrEqual)> _
Protected ReadOnly Property BirthDate2() As DateTime
Get
Return New DateTime(1960, 1, 1)
End Get
End Property
Link Class1 to ~/Controllers/Employees.xml data controller in the same fashion as we did for Customers data controller. Properties BirthDate and BirthDate2 are creating a range filter for employee field BirthDate.
You can see filtering by BirthDate in action at http://dev.codeontime.com/demo/filteringrules/?controller=Employees.
This filter is consistently applied whenever employee information is presented in data views.
Task 3
You want to filter data based on ASP.NET session variable.
Solution
Business rules have property Context that provide access to standard Request, Response, Session, Cache, and Application objects available in ASP.NET web forms. If you have a value stored in the session variable then you can easily apply its value as a filter.
<RowFilter("Customers", "grid1", "Country")> _
Protected ReadOnly Property CountryFilter() As String
Get
Return Context.Session("Country")
End Get
End Property
Task 4
You want to filter data for a certain user roles.
Solution
The following code will inspect user role if a current user is not a member of Admin role then only customers from Finland are presented. Administrator’s view is not limited by a filter, which is accomplishing by cancelling filtering caused by CountryFilter property.
<RowFilter("Customers", "grid1", "Country")> _
Protected ReadOnly Property CountryFilter() As String
Get
If Context.User.IsInRole("Admin") Then
RowFilter.Canceled = True
Return String.Empty
Else
Return "Finland"
End If
End Get
End Property
Remember that if multiple filter properties are applicable to a give data page request then each filtering property must cancel row filter on its own.
Conclusion
Business rules in Data Aquarium Framework web applications allow efficient data filtering logic that is reused throughout your application. Subscribe to premium projects and start being productive today.