Multiple database services are common in the modern business environment. Code On Time generator has the capability to tie this data together in a single web application.
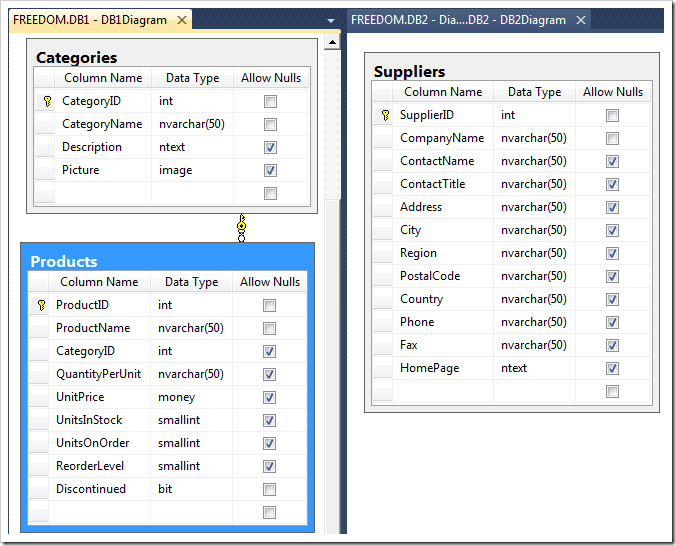
In this example, DB1 holds the Categories and Products tables of an web-based order management system. DB2 holds the Suppliers table used by the purchasing department. You can see the database schemas in the picture below.
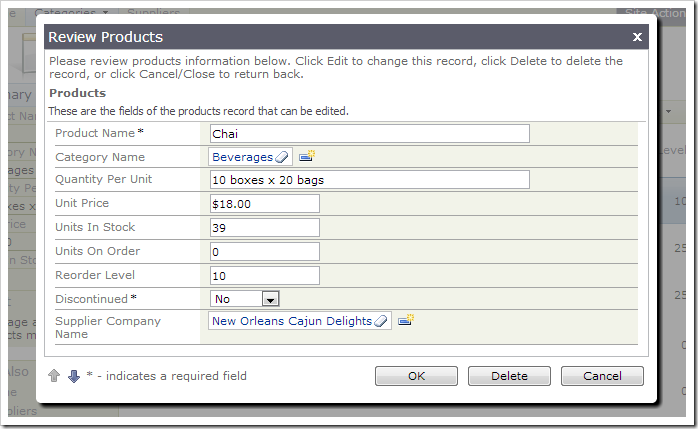
Suppose that business requirements demand displaying vendor information next to the product name. We would like to add fields in Products to capture information from the Supplier, as well as allow access to information about Suppliers, all in the same application.
How do we overcome the physical separation of DB1 and DB2?
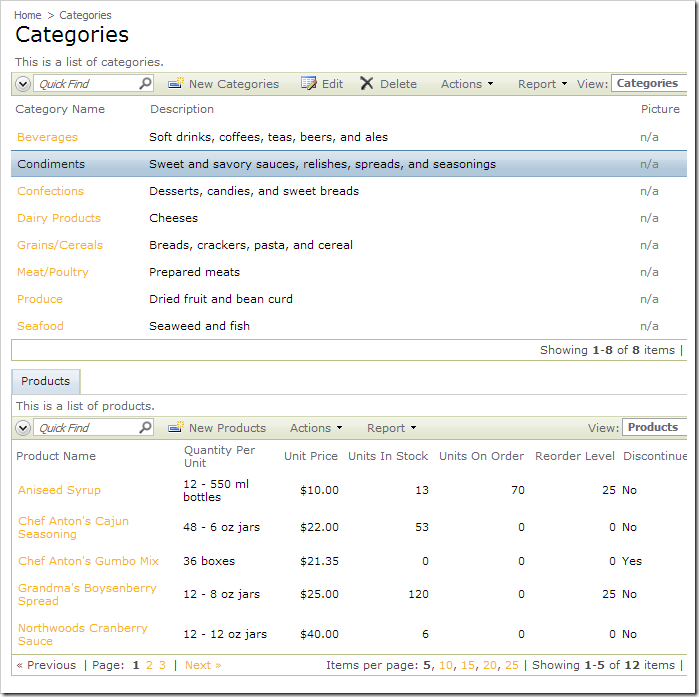
Take a look at the default web app generated from DB1 below. You will see that two pages have been created for Categories and Products, respectively. We will need to add Suppliers to this web app as well.
Code On Time Generator does not support generation from multiple databases. Creating an application that handles different data sources will require a combined sample database that you can generate from. After the web app is created, you can change the connection strings to connect the remote data. In this example, it would be easiest to add the Suppliers table to DB1. Also, add SupplierID and SupplierCompanyName to the Products table. These fields, while not foreign keys in the database, will capture information from DB2 when we set them up as lookups.
Adding Suppliers Table to DB1
Start SQL Server Management Studio. In the Object Explorer, right-click on Databases / DB1 / Tables node, and press New Table.
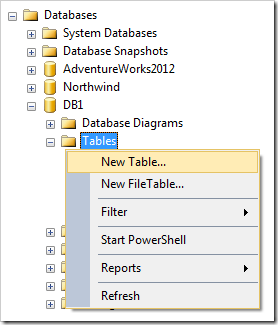
Assign the following values:
| Column Name | Data Type | Allow Nulls |
| SupplierID | int | no |
| CompanyName | nvarchar(50) | no |
| ContactName | nvarchar(50) | yes |
| ContactTitle | nvarchar(50) | yes |
| Address | nvarchar(50) | yes |
| City | nvarchar(50) | yes |
| Region | nvarchar(50) | yes |
| PostalCode | nvarchar(50) | yes |
| Country | nvarchar(50) | yes |
| Phone | nvarchar(50) | yes |
| Fax | nvarchar(50) | yes |
| HomePage | ntext | yes |
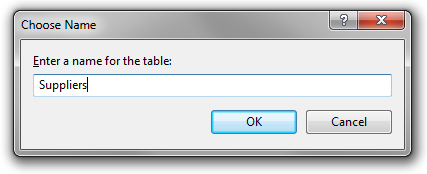
Press Ctrl+S to save the table. Assign the table a name of “Suppliers”.
In the Object Explorer, right-click on Databases / DB1 / Tables / dbo.Products table node, and press Design.
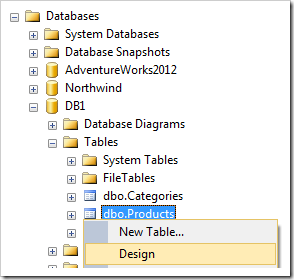
Add the following columns:
| Column Name | Data Type | Allow Nulls |
| SupplierID | int | yes |
| SupplierCompanyName | nvarchar(50) | yes |
Save the table. Switch back to the app generator, click on the project name, and press Refresh.
Check the boxes next to Products controller and dbo.Suppliers table, and click Refresh.
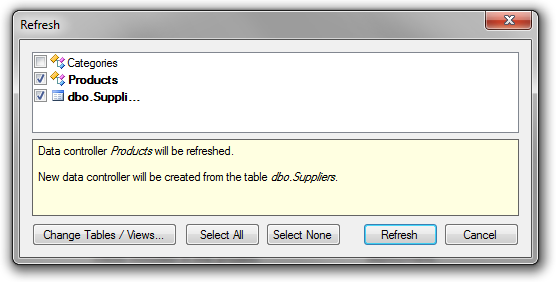
Proceed to regenerate the application.
When complete, notice that the Suppliers page has been added to the web app. However, there are no suppliers to be found. We will need to change the connection string for the Suppliers controller.
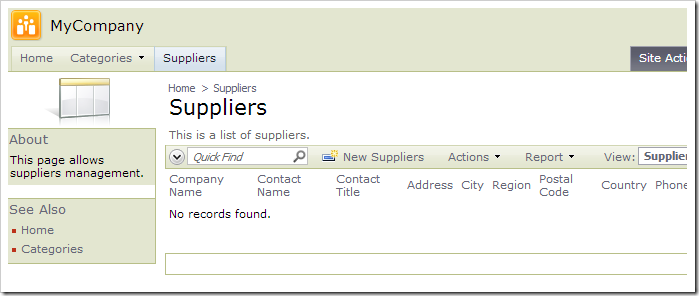
Adding a Second Connection String
Switch back to the app generator. Click on the project name, and press Settings. Click on Web Server Configuration.
In the Web.Config modification instructions textbox, add the following:
| AppendChild: /configuration/connectionStrings
<add name="DB2" connectionString="Data Source=.;Initial Catalog=DB2;Integrated Security=True;" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" /> |
Press Finish to skip to the Summary page. Click Design to activate the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab and double-click on Suppliers controller node.
Change the Connection String Name property:
| Property | Value |
| Connection String Name | DB2 |
Press OK to save.
Configuring Cross-Database Lookups
Double-click on Products / Fields / SupplierID node.
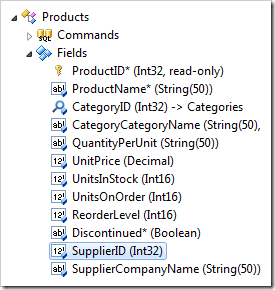
Make the following changes:
| Property | Value |
| Items Style | Lookup |
| Items Data Controller | Suppliers |
| Data Value Field | SupplierID |
| Data Text Field | CompanyName |
| New Data View | createForm1 |
| Copy | SupplierCompanyName=CompanyName |
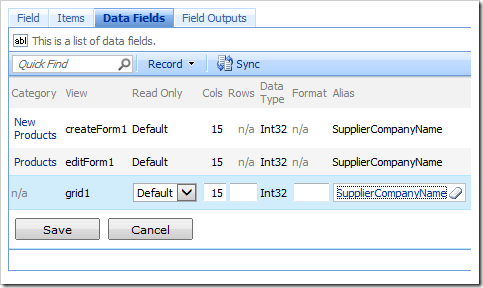
Press OK to save. At the top of the Project Browser window, switch to the Data Fields tab. Assign an Alias of “SupplierCompanyName” to all SupplierID data fields.
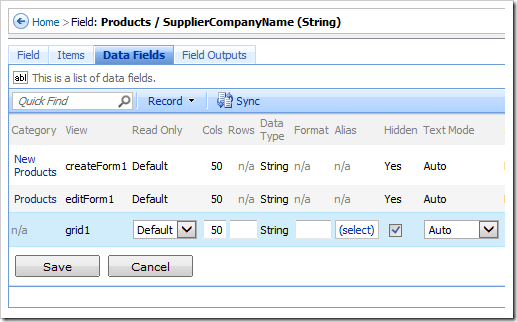
In the Project Explorer, double-click on Products / Fields / SupplierCompanyName (String(50)) node.
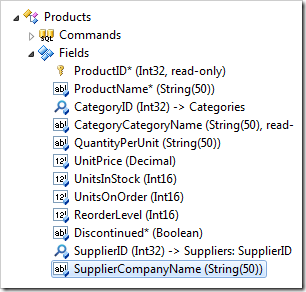
Switch to the Data Fields tab. Mark all data fields as hidden.
Viewing the Results
On the toolbar, press Browse. Navigate to the Products page, and start editing a record. Click on the SupplierCompanyName lookup – a list of suppliers will be displayed.
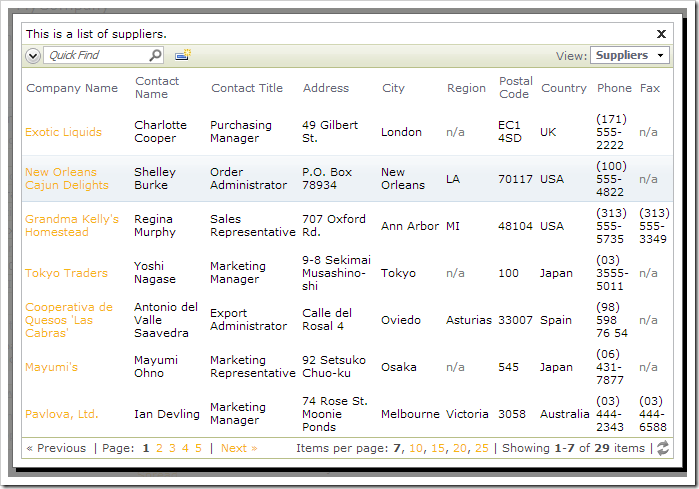
Select a supplier. The ID will be inserted into the field, but the name will be displayed.