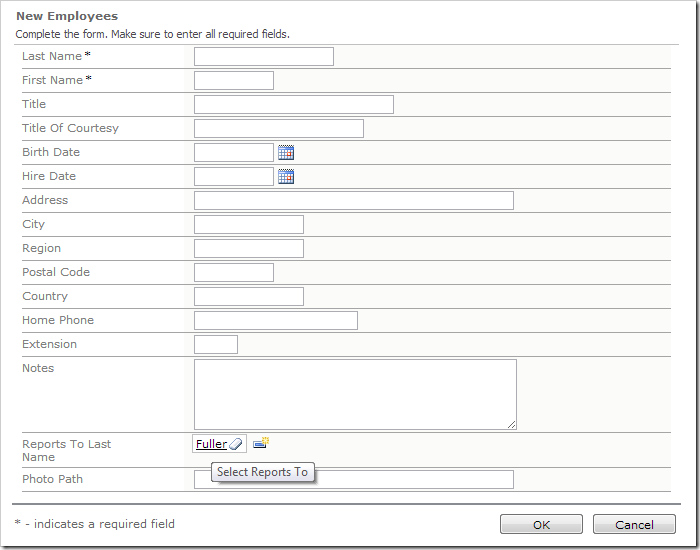
A common enhancement in line-of-business web applications is to provide default values when a new record is being created. Default values may be set using an SQL business rule. However, lookup fields require two fields to be populated – one value for the actual foreign key column in the table (typically a unique identifier or Guid) and another value for the alias field (typically the name of the lookup item).
For example, the ReportsTo column of the Employees table in the Northwind sample database contains the EmployeeID of the manager employee. A default web application created from this database creates an alias field ReportsToLastName. This virtual field is selected from the parent table and displayed as the value.
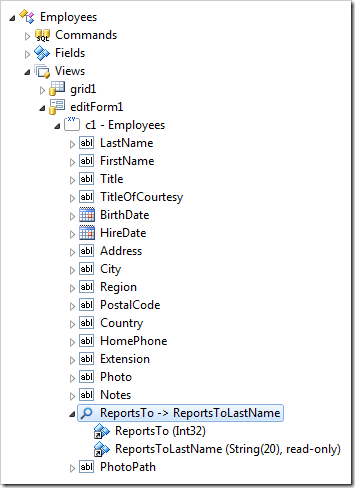
If a default value is set for the ReportsTo field, the display text will not be updated and will appear to be null. However, when the user saves the record, the ReportsToLastName field value will be calculated and displayed properly.
To ensure that the last name is displayed, let’s create an SQL business rule that will populate both ReportsTo and ReportsToLastName.
Start the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab. Right-click on Employees / Business Rules node, and press New Business Rule.
Select one of the following methods below.
SQL Business Rule
Assign the following values:
| Property | Value |
| Type | SQL |
| Command Name | New |
| Phase | Execute |
| Script | set @ReportsTo = 1
set @ReportsToLastName = 'Fuller'
|
Press OK to save the business rule.
JavaScript Business Rule
Assign the following values:
| Property |
Value |
| Type |
JavaScript |
| Command Name |
New |
| Phase |
After |
| Script |
set @ReportsTo = 1
set @ReportsToLastName = 'Fuller'
|
Press OK to save the business rule.
C# / Visual Basic Business Rule
Assign the following values:
| Property |
Value |
| Type |
C# / Visual Basic |
| Command Name |
New |
| Phase |
Execute |
Press OK to save. On the toolbar, press Browse to generate the business rule file.
When complete, right-click on Employees / Business Rules / New (Code / After) – r100 and press Edit Rule in Visual Studio.
The file will open in Visual Studio. Replace the code base with the following:
C#:
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Security;
using MyCompany.Data;
namespace MyCompany.Rules
{
public partial class EmployeesBusinessRules : MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
{
[Rule("r100")]
public void r100Implementation(
int? employeeID,
string lastName,
string firstName,
string title,
string titleOfCourtesy,
DateTime? birthDate,
DateTime? hireDate,
string address,
string city,
string region,
string postalCode,
string country,
string homePhone,
string extension,
string notes,
int? reportsTo,
string reportsToLastName,
string photoPath)
{
UpdateFieldValue("ReportsTo", 1);
UpdateFieldValue("ReportsToLastName", "Fuller");
}
}
}
Visual Basic:
Imports MyCompany.Data
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.Data
Imports System.Linq
Imports System.Text.RegularExpressions
Imports System.Web
Imports System.Web.Security
Namespace MyCompany.Rules
Partial Public Class EmployeesBusinessRules
Inherits MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
<Rule("r100")> _
Public Sub r100Implementation( _
ByVal employeeID As Nullable(Of Integer), _
ByVal lastName As String, _
ByVal firstName As String, _
ByVal title As String, _
ByVal titleOfCourtesy As String, _
ByVal birthDate As Nullable(Of DateTime), _
ByVal hireDate As Nullable(Of DateTime), _
ByVal address As String, _
ByVal city As String, _
ByVal region As String, _
ByVal postalCode As String, _
ByVal country As String, _
ByVal homePhone As String, _
ByVal extension As String, _
ByVal notes As String, _
ByVal reportsTo As Nullable(Of Integer), _
ByVal reportsToLastName As String, _
ByVal photoPath As String)
UpdateFieldValue("ReportsTo", 1)
UpdateFieldValue("ReportsToLastName", "Fuller")
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Viewing the Results
On the toolbar, press Browse.
Navigate to the Employees page. On the action bar, press New Employees. Note that the default value for Reports To field is correctly displayed.