Project requirements may dictate that conversion should be performed on field values.
For example, the Customer# field of the Customers table in the Northwind database may need to be converted to uppercase.
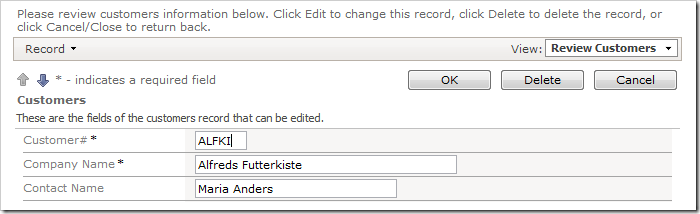
However, there is no mechanism preventing users from saving lowercase letters in the field.
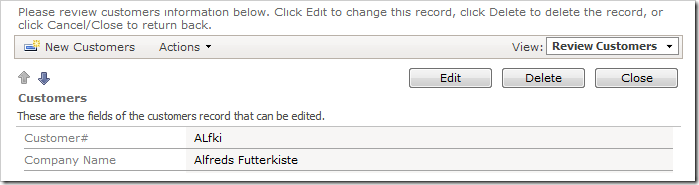
Let’s create an SQL Business Rule to perform field value conversion.
Validate on Insert or Update
Start the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab. Right-click on Customers / Business Rules node, and select New Business Rule.
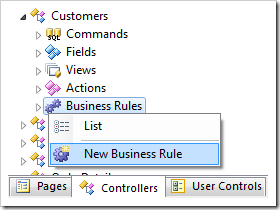
Use the following properties:
| Property | Value |
| Command Name | Insert|Update |
| Type | SQL |
| Phase | Before |
| Script | set @CustomerID = UPPER(@CustomerID)
|
Press OK to save the business rule. On the toolbar, press Browse.
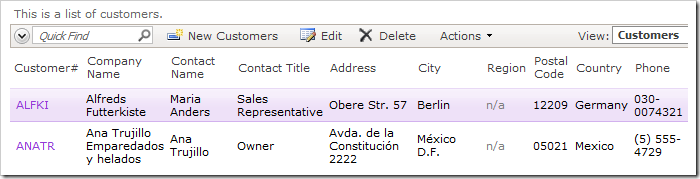
Navigate to the Customers page, and edit a record. Insert some mixed-case letters in the Customer# field.
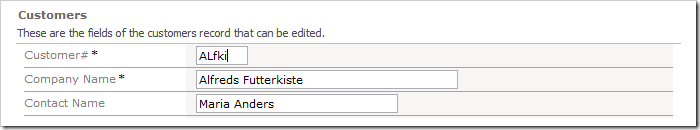
Save the record. The field value will be converted to uppercase.
Validate on Calculate
You can also perform just-in-time value conversion, when the user moves focus away from the field.
Switch back to the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, double-click on Customers / Business Rule / Insert|Update node.
Change the Command Name property:
| Property |
New Value |
| Command Name |
Calculate |
Press OK to save the business rule. In order for the calculation to be performed, the field needs to cause a server request.
In the Project Explorer, double-click on Customers / Fields / CustomerID field node.
Make the following changes:
| Property |
New Value |
| The value of this field is calculated by a business rule expression. |
True |
| Context Fields |
CustomerID |
Press OK to save the field. On the toolbar, press Browse.
On the Customers page, edit a record. Insert mixed-case characters into the Customer# field.
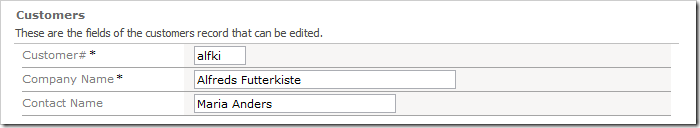
Press Tab on your keyboard or click on another field. The client library will convert the value in Customer# field into uppercase.
Expanding the Business Rule
The user may still click on the OK button and save the lowercase characters in the field. Therefore, you may need to combine both Insert|Update and Calculate command handling. The following Command Name will cover all possible methods of changing the field.
| Property |
New Value |
| Command Name |
Calculate|Insert|Update |
The same business logic can be implemented with the help of C#/Visual Basic Business Rules.