Data Aquarium Framework features automatic data binding and presentation that are performed by the client-side JavaScript library interpreting the content of server-side data controller definitions to produce interactive grids and forms.
Sometimes your project may require a custom functionality that is not supported by the user interface components of the framework. You can still take advantage of excellent support for filtering, sorting and paging of very large data sets via standard ObjectDataSource component available in .NET Framework or ControllerDataSource component that comes with the premium versions Data Aquarium Framework.
The examples described below are based on an application generated with Data Aquarium premium project from sample Northwind database with business objects enabled.
Overview of Business Objects
Business objects generated as a part of your project are needed if you plan to develop custom web forms with ObjectDataSource components or if you would like to have a programmatic API on top of your database tables.
Business objects are placed in MyCompany.Data.Objects namespace where MyCompany is the namespace of your project. Each object name is matched with the name of the database table and is accompanied by a Factory class.
The default naming of CRUD methods will yield the following methods for each business object: Select, SelectSingle, Insert, Update, and Delete. Here is a sample signature of Select method of Shippers business object.
C#:
public static List<Shippers> Select(
Nullable<int> shipperID,
string companyName,
string phone)
VB:
Public Overloads Shared Function [Select]( _
ByVal shipperID As Nullable(Of Integer), _
ByVal companyName As String, _
ByVal phone As String) As List(Of Shippers)
Here are a few examples that show how the business objects can be used to manipulate database information. Developers can create new records; retrieve records by primary key, by example, or by individual field values specified as parameters. Updating and deleting existing objects is a snap.
C#:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
using MyCompany.Data.Objects;
public partial class Demo : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// create a new shipper
Shippers s = new Shippers();
s.CompanyName = "Code OnTime";
s.Phone = "877-467-6340";
if (s.Insert() != 1)
throw new Exception("Failed to create a shipper");
// find a shipper by ID
Shippers s2 = Shippers.SelectSingle(s.ShipperID);
if (s2 == null)
throw new Exception("Shipper not found");
// find a list of matching shippers by example
Shippers query = new Shippers();
query.Phone = "877-467-6340";
List<Shippers> list = Shippers.Select(query);
if (list.Count == 0)
throw new Exception("Shippers not found");
// find a list of matching shippers by values
List<Shippers> list2 = Shippers.Select(null, "code", null);
if (list2.Count == 0)
throw new Exception("Shippers not found");
// update shipper
list[0].CompanyName = "My Company";
if (list[0].Update() != 1)
throw new Exception("Failed to update shipper");
// delete shipper
if (list2[0].Delete() != 1)
throw new Exception("Failed to delete shipper");
}
}
VB:
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports MyCompany.Data.Objects
Partial Class Demo
Inherits System.Web.UI.Page
Protected Sub Page_Load(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Me.Load
' create a new shipper
Dim s As Shippers = New Shippers()
s.CompanyName = "Code OnTime"
s.Phone = "877-467-6340"
If s.Insert() <> 1 Then
Throw New Exception("Failed to create a shipper")
End If
' find a shipper by ID
Dim s2 As Shippers = Shippers.SelectSingle(s.ShipperID)
If s2 Is Nothing Then
Throw New Exception("Shipper not found")
End If
' find a list of matching shippers by example
Dim query As Shippers = New Shippers()
query.Phone = "877-467-6340"
Dim list As List(Of Shippers) = Shippers.Select(query)
If list.Count = 0 Then
Throw New Exception("Shippers not found")
End If
' find a list of matching shippers by values
Dim list2 As List(Of Shippers) = _
Shippers.Select(Nothing, "code", Nothing)
If list2.Count = 0 Then
Throw New Exception("Shippers not found")
End If
' update shipper
list(0).CompanyName = "My Company"
If list(0).Update() <> 1 Then
Throw New Exception("Failed to update shipper")
End If
' delete shipper
If list2(0).Delete() <> 1 Then
Throw New Exception("Failed to delete shipper")
End If
End Sub
End Class
Business object is nothing more than a shell that provides placeholders to all fields of underlining data set. Data manipulation methods are simply passing the parameters to the corresponding methods of object factories.
The purpose of factories is to interact with the Controller class of Data Aquarium Framework. This very class is executing all operations requested by AJAX scripts that constitute the other half of the framework. The implication of this is that the XML data controller descriptors are driving the behavior of business objects as well.
As a matter of fact, business objects are selecting data by imitating requests of JavaScript components of the framework. This allows complete reuse of business logic and rules that are linked to data controllers of your application.
JavaScript client components are always retrieving the exact number of data fields that are declared in the data controller views. Business objects are automatically configured to use the very first view of the corresponding controller. If your business object has a couple of dozen fields and you select data as described in this article then only the fields that are defined in the first view of the controller are retrieved. You can change that by creating a custom view that lists all fields that you do need and making this view first in the data controller definition. You can also add missing fields to the existing first view of the data controller and mark them as “hidden” if you don’t want these fields to be displayed in the user interface and only indent to manipulate the fields in your business logic.
This might seem as an overhead but is done to provide maximum efficiency and code reuse. Continue reading to learn how to benefit from the framework capabilities when building custom web forms.
Business Objects And Data Sources
If you don’t plan to write custom business rules then your only reason to generate business objects is to take advantage of ObjectDataSource data binding features of ASP.NET. Business object factories are constructed to fully support filtering, sorting, paging, and editing via ObjectDataSource.
You don’t need business objects if you take advantage of ControllerDataSource component that comes with Data Aquarium Framework. This component implements a generic factory and interacts with Controller of your application as custom business object factories do. It means that you are taking advantage of data controller descriptors and gain the same great features. You can filter, sort, page, and edit very large data sets without writing any code at all. You will still be required to list all fields that need to be retrieved by modifying view definitions in the corresponding data controller files.
Simple Data Binding
Let’s take a look at data binding with both data source components.
Here is the markup of a grid bound to ControllerDataSource.
<asp:GridView ID="GridView1" runat="server" DataSourceID="Cds1" />
<aquarium:ControllerDataSource ID="Cds1" runat="server"
DataController="Products" DataView="grid1" />
The following presentation will be rendered.
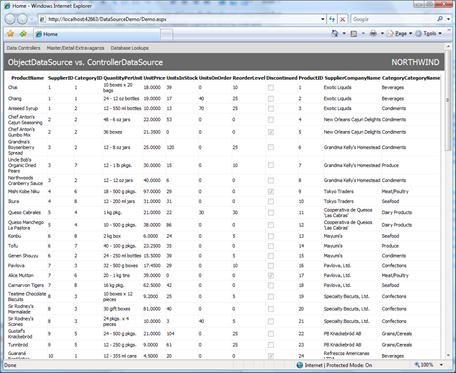
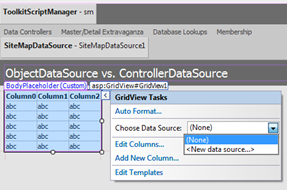
Here is how you can link an ObjectDataSource component to a grid view and take advantage of ProductsFactory class generated as a part of business object library of your application. Open a web form in design mode and select New data source option when choose source of data.
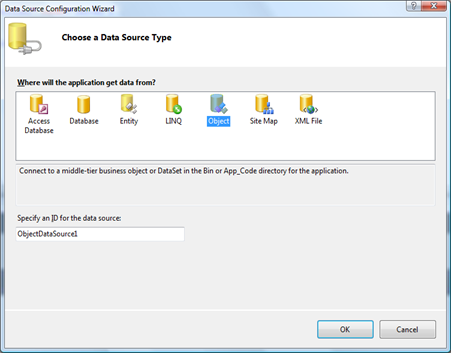
A wizard will show up. Select Object and click OK button.
Select MyCompany.Data.Objects.ProductsFactory as a business object.
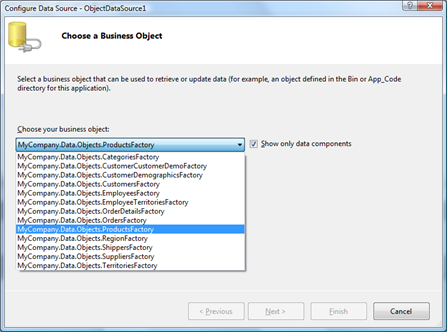
Wizard will automatically select appropriate Select, Update, Insert, and Delete methods thanks to the data attributes that are applied to the appropriate factory class methods.
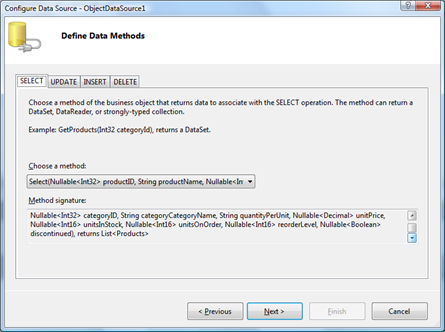
Finish the remaining wizard steps without making any further changes. This is the markup generated by wizard.
<asp:GridView ID="GridView1" runat="server" AutoGenerateColumns="False"
DataKeyNames="ProductID" DataSourceID="ObjectDataSource1" >
<Columns>
<asp:BoundField DataField="ProductID" HeaderText="ProductID"
InsertVisible="False" ReadOnly="True" SortExpression="ProductID" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="ProductName" HeaderText="ProductName"
SortExpression="ProductName" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="SupplierID" HeaderText="SupplierID"
SortExpression="SupplierID" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="SupplierCompanyName"
HeaderText="SupplierCompanyName" SortExpression="SupplierCompanyName" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="CategoryID" HeaderText="CategoryID"
SortExpression="CategoryID" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="CategoryCategoryName"
HeaderText="CategoryCategoryName" SortExpression="CategoryCategoryName" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="QuantityPerUnit" HeaderText="QuantityPerUnit"
SortExpression="QuantityPerUnit" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="UnitPrice" HeaderText="UnitPrice"
SortExpression="UnitPrice" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="UnitsInStock" HeaderText="UnitsInStock"
SortExpression="UnitsInStock" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="UnitsOnOrder" HeaderText="UnitsOnOrder"
SortExpression="UnitsOnOrder" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="ReorderLevel" HeaderText="ReorderLevel"
SortExpression="ReorderLevel" />
<asp:CheckBoxField DataField="Discontinued" HeaderText="Discontinued"
SortExpression="Discontinued" />
</Columns>
</asp:GridView>
<asp:ObjectDataSource ID="ObjectDataSource1" runat="server"
DataObjectTypeName="MyCompany.Data.Objects.Products" DeleteMethod="Delete"
InsertMethod="Insert" OldValuesParameterFormatString="original_{0}"
SelectMethod="Select" TypeName="MyCompany.Data.Objects.ProductsFactory"
UpdateMethod="Update">
<SelectParameters>
<asp:Parameter Name="productID" Type="Int32" />
<asp:Parameter Name="productName" Type="String" />
<asp:Parameter Name="supplierID" Type="Int32" />
<asp:Parameter Name="supplierCompanyName" Type="String" />
<asp:Parameter Name="categoryID" Type="Int32" />
<asp:Parameter Name="categoryCategoryName" Type="String" />
<asp:Parameter Name="quantityPerUnit" Type="String" />
<asp:Parameter Name="unitPrice" Type="Decimal" />
<asp:Parameter Name="unitsInStock" Type="Int16" />
<asp:Parameter Name="unitsOnOrder" Type="Int16" />
<asp:Parameter Name="reorderLevel" Type="Int16" />
<asp:Parameter Name="discontinued" Type="Boolean" />
</SelectParameters>
</asp:ObjectDataSource>
At first glance the markup of ObjectDataSource component seems to be more verbose but will be comparable in size if you define grid view fields for ControllerDataSource as well.
The web form will render virtually identically in a web browser with the exception of the field order.
Sorting and Paging
All available product records are being retrieved by both data source configurations.
Let’s enable sorting and paging. We will start with ControllerDataSource.
Select the grid view and enable sorting and paging.
Here is the changed markup.
<asp:GridView ID="GridView1" runat="server" DataSourceID="Cds1"
AllowPaging="True" AllowSorting="True" />
<aquarium:ControllerDataSource ID="Cds1" runat="server"
DataController="Products" DataView="grid1" />
Save and open the page in a web browser.
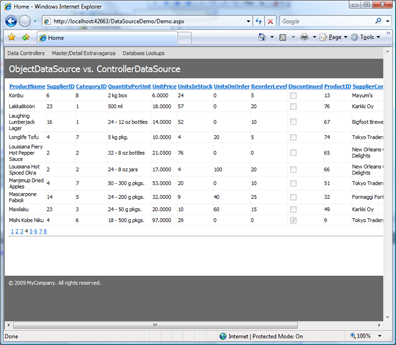
Paging and sorting is instantly available.
Note that the exact number of visible rows is now retrieved from the database every time you sort or page through the records. This allows you to sort and page through very large data sets. The default page size of GridView component is ten. ControllerDataSource will never retrieve more than 10 records as configured. Standard SqlDataSource component is not able to deliver such performance.
Paging in the ObjectDataSource example is configured in a similar fashion. The markup changes are exactly the same. Sorting option is not available though and the entire set of records is automatically retrieved from the database instead of just the records that are rendered on the page.
ObjectDataSource component requires additional instructions to support sorting and perform efficient data retrieval operations.
Select ObjectDataSource component and bring up the data source configuration wizard.
Choose the second Select method on the second step of the wizard and complete the remaining steps
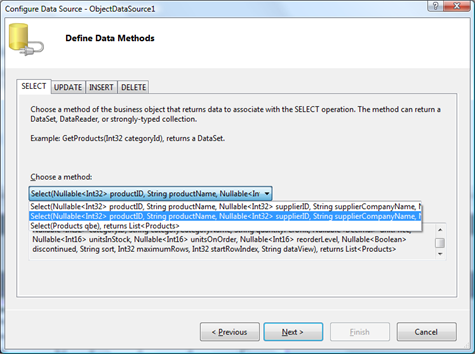
The second method is similar to the first one but features additional parameters sort, maximumRows, startRowIndex and dataView. The three of these parameters are needed to support sorting and efficient record retrieval as dictated by ObjectDataSource requirements for high performance business objects. The last parameter allows you to choose the data controller view of Data Aquarium Framework application that must be used as a source of data.
Continue making change to the ObjectDataSource. Use Properties Window of Visual Studio to change SortParameterName, EnablePaging, and SelectCountMethod of the component. Change them to sort, True, and SelectCount accordingly.
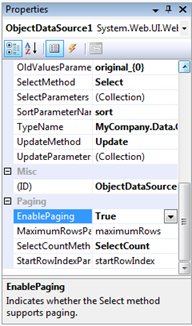
The sort parameter has been added to the data source markup by wizard. Paging is supported by the extended Select method of ProductsFactory via maximumRows and startRowIndex parameters. Method SelectCount is available in ProductsFactory.
Select the grid and enable sorting.
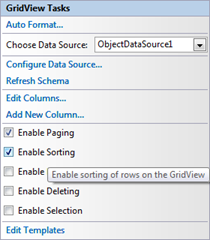
Now paging and sorting in the grid linked to ObjectDataSource are efficient and will never read more records from the database than are needed for presentation.
Filtering
Data filtering is an important element of any application. From the developer’s prospective filtering must translate into SQL statements with WHERE clause to be considered efficient. Filtering supported in the standard SqlDataSource is performed only by retrieving all records from the database, which does not match this criterion of efficiency.
Both, ControllerDataSource and ObjectDataSource filtering implementations in Data Aquarium Framework applications are efficient.
Change the markup of ControllerDataSource sample web form as shown below.
<%@ Page Title="" Language="C#" MasterPageFile="~/MasterPage.master"
AutoEventWireup="true" CodeFile="Demo.aspx.cs" Inherits="Demo" %>
<asp:Content ID="Content1" ContentPlaceHolderID="head" runat="Server">
</asp:Content>
<asp:Content ID="Content2" ContentPlaceHolderID="Header1Placeholder"
runat="Server">
ObjectDataSource vs. ControllerDataSource
</asp:Content>
<asp:Content ID="Content3" ContentPlaceHolderID="Header2Placeholder"
runat="Server">
Northwind
</asp:Content>
<asp:Content ID="Content4" ContentPlaceHolderID="BodyPlaceholder" runat="Server">
<table>
<tr>
<td>
Product:<br />
<asp:TextBox ID="ProductName" runat="server" />
</td>
<td>
Supplier:<br />
<aquarium:DataViewLookup ID="SupplierLookup" runat="server"
DataController="Suppliers" />
</td>
<td>
<br />
<asp:Button ID="Button1" runat="server" Text="Go" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<asp:GridView ID="GridView1" runat="server" DataSourceID="Cds1" AllowPaging="True"
AllowSorting="True" AutoGenerateColumns="False" DataKeyNames="ProductID">
<Columns>
<asp:BoundField DataField="ProductName" HeaderText="Product Name"
SortExpression="ProductName" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="SupplierCompanyName"
HeaderText="Supplier Company Name"
ReadOnly="True" SortExpression="SupplierCompanyName" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="CategoryCategoryName"
HeaderText="Category Category Name"
ReadOnly="True" SortExpression="CategoryCategoryName" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="QuantityPerUnit" HeaderText="Quantity Per Unit"
SortExpression="QuantityPerUnit" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="UnitPrice" HeaderText="Unit Price"
SortExpression="UnitPrice" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="UnitsInStock" HeaderText="Units In Stock"
SortExpression="UnitsInStock" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="UnitsOnOrder" HeaderText="Units On Order"
SortExpression="UnitsOnOrder" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="ReorderLevel" HeaderText="Reorder Level"
SortExpression="ReorderLevel" />
<asp:CheckBoxField DataField="Discontinued" HeaderText="Discontinued"
SortExpression="Discontinued" />
</Columns>
</asp:GridView>
<aquarium:ControllerDataSource ID="Cds1" runat="server" DataController="Products"
DataView="grid1">
<FilterParameters>
<asp:ControlParameter Name="ProductName" ControlID="ProductName" />
<asp:ControlParameter ControlID="SupplierLookup" Name="SupplierID"
PropertyName="SelectedValue" />
</FilterParameters>
</aquarium:ControllerDataSource>
</asp:Content>
You can modify filter parameters visually in Properties Window of Visual Studio if you select the ControllerDataSource component and edit FilterParameters properties.
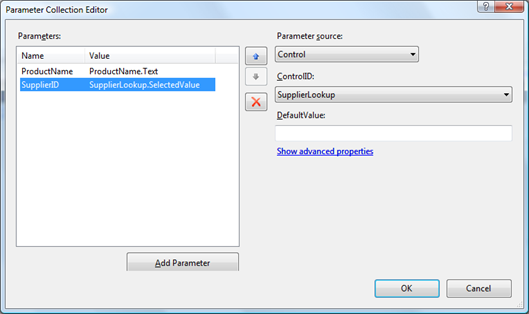
Run application and try data filtering in actions.
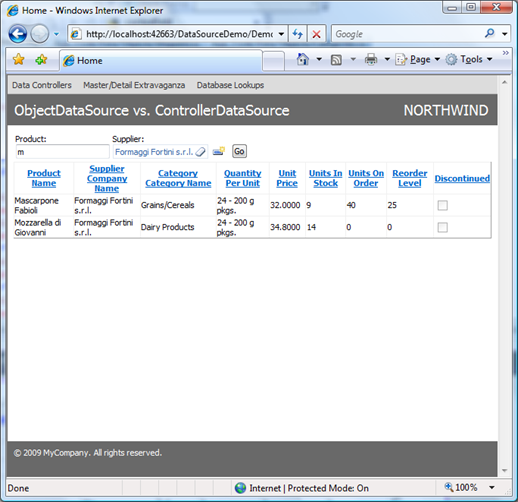
You can bind filter parameters to any ASP.NET components available to you. This sample is using standard TextBox and DataViewLookup component found in Data Aquarium Framework.
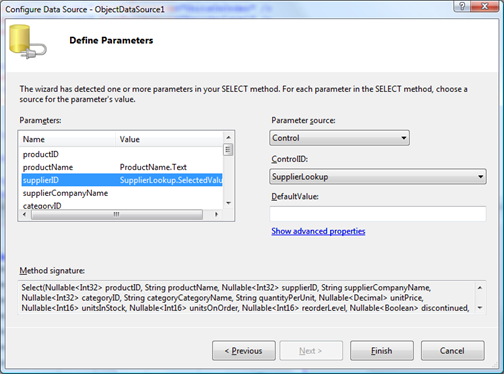
If you copy the markup for the table of filtering parameters to the ObjectDataSource sample and set parameter binding in the object data source configuration wizard then you will achieve exactly the same capability. There is a slight difference in configuring parameters. All available parameters of ProductsFactory.Select method are listed in parameter configuration step of the wizard.
Update, Insert, Delete
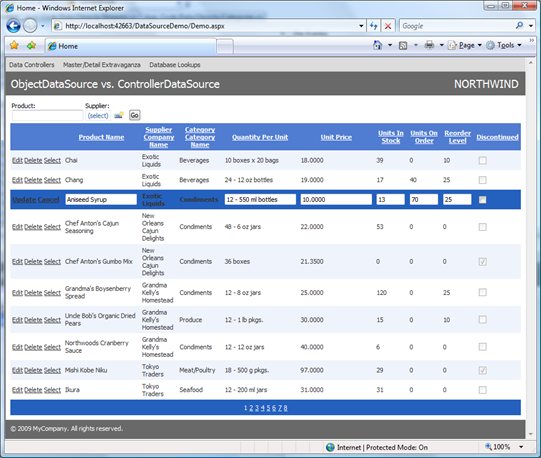
Update and Delete operations are automatically enabled for both data source components if you enable support for these features in the grid view. Here is the ControllerDataSource sample application with Classic auto-formatting applied to it.
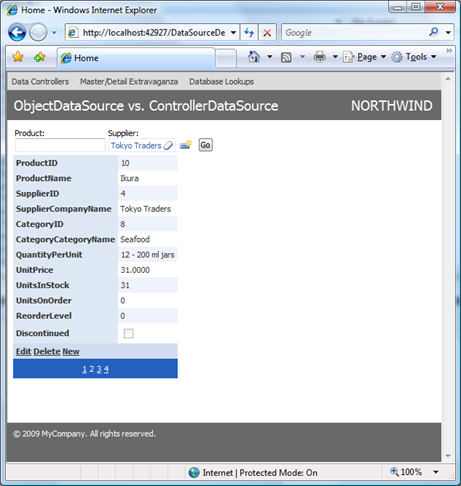
Use standard DetailsView component if you want to be able to insert new records. Here is the ObjectDataSource sample with DetailsView component that has Classic auto-formatting applied to it.
Conclusion
Data Aquarium Framework does not stop with AJAX-enabled user interfaces. Any ASP.NET components supporting the data source architecture of Microsoft.NET will benefit from paging, sorting, and filtering of data sets of any size available in Data Aquarium application.
Business objects generated as a part of application are not mandatory and can be replaced with any external data access engine or library available to you.