Upsert is an insert operation with detection of duplicates. The application will update the existing record when a duplicate is detected instead of creating a new record instance. Modern database engines support a dedicated SQL command Merge that performs this function. Applications created with Code On Time offer an elegant mechanism of SQL Business Rules that allows creating flexible and configurable Merge operations.
Let’s implement upsert for the Products table of the Northwind sample. The picture below shows two duplicate records of the product “Chai”.
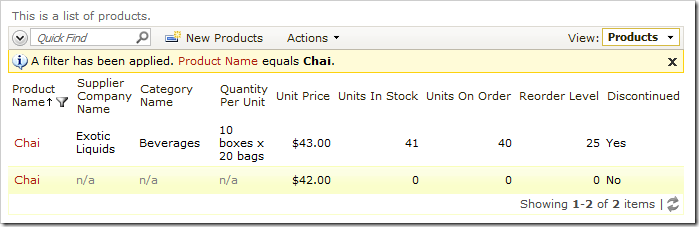
The upsert implementation will detect an attempt to insert a duplicated product, and will update the values of the existing one.
Delete the duplicate “Chai” record from the list of Products, and paste the following query into SQL Server Management Studio:
-- debug
declare @ProductID int
declare @ProductName nvarchar(40) = 'Chai'
declare @SupplierID int
declare @CategoryID int
declare @QuantityPerUnit nvarchar(20)
declare @UnitPrice money = 42
declare @UnitsInStock smallint
declare @UnitsOnOrder smallint
declare @ReorderLevel smallint
declare @Discontinued bit
declare @BusinessRules_PreventDefault int
-- end debug
select @ProductID = ProductID
from Products
where ProductName = @ProductName
if @ProductID is not null
begin
set @BusinessRules_PreventDefault = 1
update Products
set
SupplierID = IsNull(@SupplierID,SupplierID),
CategoryID = IsNull(@CategoryID,CategoryID),
QuantityPerUnit = IsNull(@QuantityPerUnit,QuantityPerUnit),
UnitPrice = IsNull(@UnitPrice,UnitPrice),
UnitsInStock = IsNull(@UnitsInStock,UnitsInStock),
UnitsOnOrder = IsNull(@UnitsOnOrder,UnitsOnOrder),
ReorderLevel = IsNull(@ReorderLevel,ReorderLevel),
Discontinued = IsNull(@Discontinued,Discontinued)
where ProductID = @ProductID
end
The sample debug parameters represent values of a new product where Product Name is “Chai”, and Unit Price is “42”. The script will try to find an existing product that matches the Product Name. If a match is found, then the application framework is instructed to prevent executing the default Insert command. This is accomplished by setting the value of @BusinessRules_PreventDefault parameter to true. Then the new record values will be used to update the existing product. If a new column value is null, then the current column value is preserved with the help of IsNull function.
Execute the query. A message will state that 1 row was affected. Go back to the application and refresh the view, and you will see that the query has only updated the existing “Chai” record.
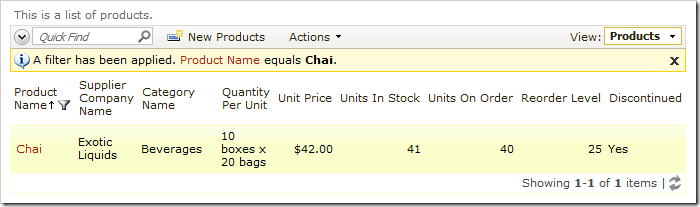
Let’s integrate this script in a new business rule of Products controller.
Start the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab. Right-click on Products / Business Rules node, and select New Business Rule option.
Use the following properties.
| Property |
Value |
| Command Name |
Insert |
| Type |
SQL |
| Phase |
Before |
| Script |
Copy and paste the script from above.
|
This business rule will execute before every Insert command.
The application framework will ignore the debug section. You can keep the debug section in the script or take it out – it will not make any difference.
Press OK to save the new business rule. On the toolbar, click Browse option.
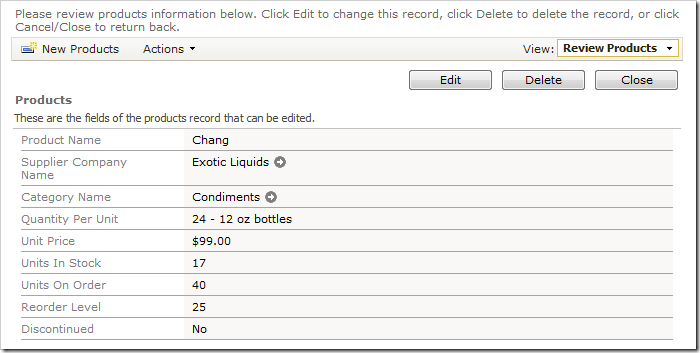
Navigate to the Products page. Create a new product with the following field values:
| Field |
Value |
| Product Name |
Chang |
| Category Name |
Condiments |
| Unit Price |
99 |
Instead of creating the new record, the application updated the existing product. It is automatically selected in the user interface.
This business rule will also work with the Import action. Create a spreadsheet, and paste in the following table:
| Product Name |
Supplier Company Name |
Unit Price |
| Alice Mutton |
|
120 |
| Aniseed Syrup |
Tokyo Traders |
44 |
| ABCDE |
|
42 |
Save the spreadsheet as a CSV (Comma delimited) file type.
On the action bar of the web application, select Actions | Import from File option.
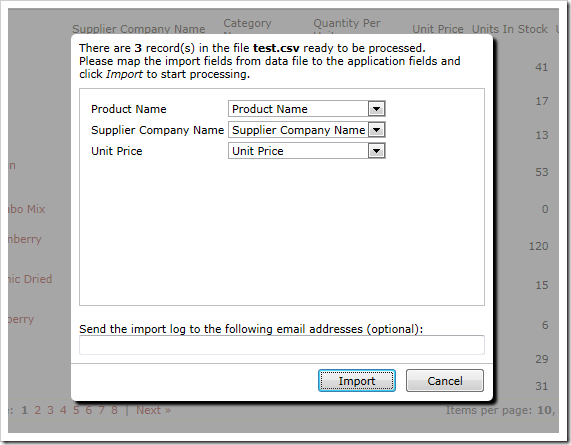
Make sure that the columns are matching, and press Import.
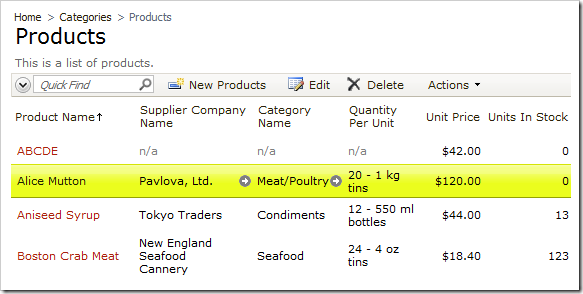
Confirm the operation. Sort by the Product Name field by clicking on the header text. Two of the records already existed, and Unit Price and Supplier Company Name for these records has been updated. The “ABCDE” Product Name was unique, so the row was added.
There are advantages of using SQL Business Rules over the standard Merge operation. If additional processing is required or duplicate records have to be staged in a separate table, then business rules provide more flexibility over the insert/update combination offered by Merge.