Data integrity can be ensured on different tiers of a web application. Code On Time web apps take advantage of the business rules engine that allows creating JavaScript Business Rules (Client Tier), Code Business Rules (Application Tier), and SQL Business Rules (Data Tier).
About Business Rules
Business rules are abstracted from the presentation of data. Developers manipulate field values directly as if the field values are local variables. The client library and application framework pass collections of values to the business rules making unnecessary a complex task of inspecting user interface elements. A business rule can access “old” value, “new” value, and “current” value of any field. It is also known if a field is “read-only” or “modified”. Business rules are executed in response to actions that have “before”, “execute”, and “after” phase. Changes to the values of the fields may affect the data that ends up in the database. Calculated field values are presented to the user on the client device.
This approach to business rule implementation allows continues improvement to the user interface client library. It guarantees that business rules will remain unchanged even for the future supported client devices.
Selecting an Application Tier
The major challenge is to select an application tier for a business rule implementation.
The client tier is most commonly used to correct user spelling or for basic data integrity enforcement. For example, formatting of a phone number most definitely lends itself to a client side business rule. Client business rules allow avoiding a server-side round trip.
If a business rule requires a database lookup then the data tier works best in most situation. A script written in SQL dialect of the application database engine can select data from a table, call a stored procedure, and perform complex data manipulations.
Some business rules may require access to operating system resources, file system, or web services. Application tier business rules are written in C# or Visual Basic. The full power of Microsoft.NET is at disposal of a developer. “Code” business rules supersede SQL business rules at a cost of using special classes when a database access is required.
Hybrid Business Rules
If a server-side data is required for a client-side JavaScript business rule, then the business rule is a hybrid. This type of rules is difficult to implement.
The server-code implemented on the application or data tier cannot have a “conversation” with a user. Conditional execution with a user confirmation can be performed on the client only. The client business rule must have a way to request information from the server before confronting a user with requests for additional information.
RESTFul Application Server
Code On Time web applications may include application server components that enable interaction with clients supporting Representational State Transfer protocol know as REST. When enable, the application server components can respond to HTTP requests for information or commands to execute an action.
The responses to such HTTP request are encoded in XML or JSON. The latter is a great match to JavaScript Business Rules since a response is essentially a JavaScript object.
Example of a RESTful Business Rule
Consider entering of new products in the Northwind sample.
There is product with the name “Chai” with a different price. The existing product is supplied by another vendor.
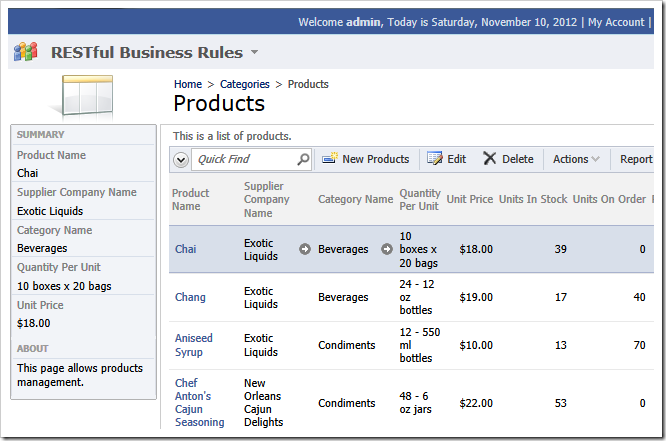
There may be a business requirement to warn a user about a potential duplicate.
A business rule written in JavaScript may contact the app to verify if a matching product exists. The URL of a web request may look as follow:
http://demo.codeontime.com/northwind/appservices/Products?ProductName=Chai
or
http://demo.codeontime.com/northwind/appservices/Products?ProductName_Filter_Equals=Chai
Here is the response encoded in XML.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Products totalRowCount="1" pageSize="100" pageIndex="0" rowCount="1">
<items>
<item ProductName="Chai" SupplierID="1" CategoryID="1" QuantityPerUnit="10 boxes x 20 bags"
UnitPrice="$18.00" UnitsInStock="39" UnitsOnOrder="0" ReorderLevel="10"
Discontinued="False" ProductID="1"
SupplierCompanyName="Exotic Liquids" CategoryCategoryName="Beverages" />
</items>
</Products>
The business rule can display a warning to a user about a potential duplicate. If a user does not confirm creation of a duplicate product, then a new record is not created.
First, may sure to enable REST requests to the data controller products. Select the data controller in Project Explorer and change it as follows.
| Property |
Value |
| Representational State Transfer (REST) Configuration |
Uri: .
Users: *
|
This will ensure that only authenticated users can send requests to application server components.
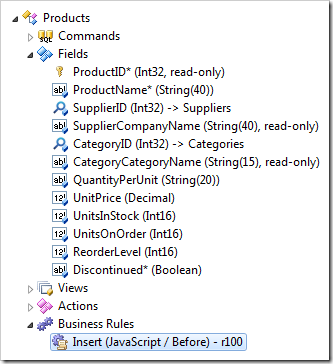
Enter a new JavaScript business rule in Products data controller configured as follows:
| Property |
Value |
| Type |
JavaScript |
| Command Name |
Insert |
| Phase |
Before |
Enter this code in the Script property of the rule and click OK button.
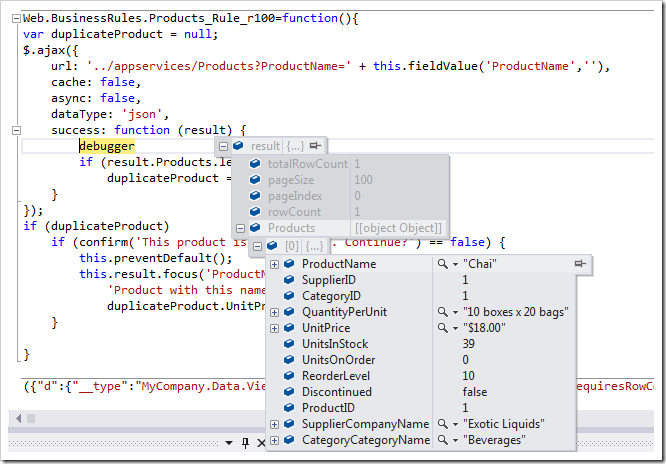
var duplicateProduct = null;
$.ajax({
url: '../appservices/Products?ProductName=' + [ProductName],
cache: false,
async: false,
dataType: 'json',
success: function (result) {
if (result.Products.length > 0)
duplicateProduct = result.Products[0];
}
});
if (duplicateProduct)
if (confirm('This product is a duplicate. Continue?') == false) {
this.preventDefault();
this.result.focus('ProductName',
'Product with this name and price of {0} is supplied by "{1}".',
duplicateProduct.UnitPrice, duplicateProduct.SupplierCompanyName);
}
This is how the rule will be displayed in Project Explorer.
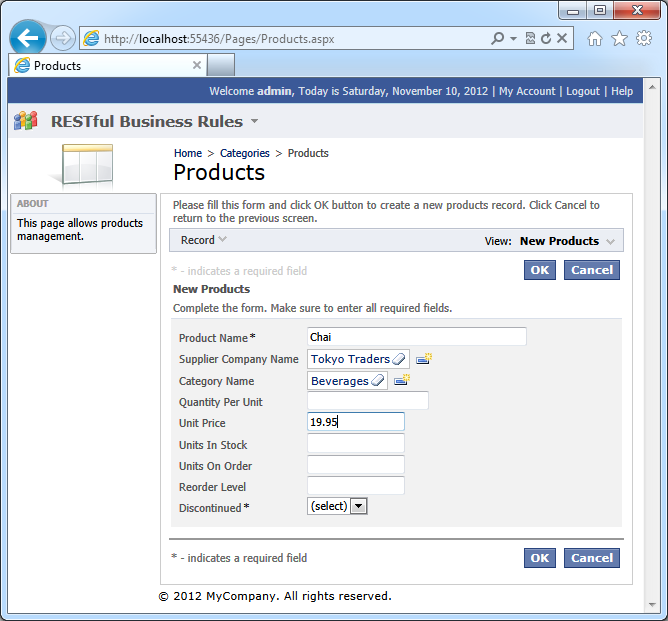
Click Browse and navigate to Products page. Enter a new product with the name “Chai” and click OK to save the new record.
A standard browser confirmation will be displayed.
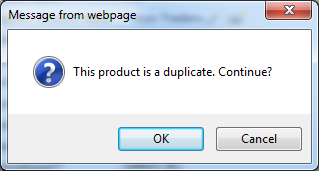
Click Cancel button to prevent creation of the product. The focus will be on Product Name field. The information about the duplicate product will be displayed next to the field.
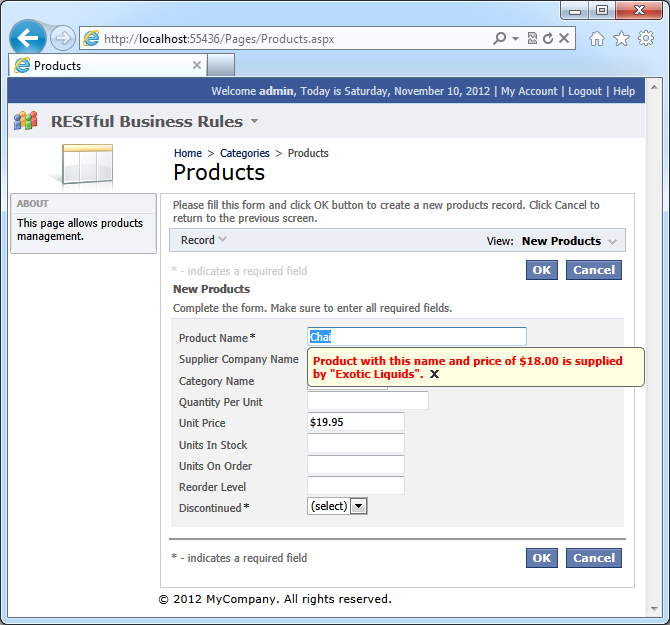
The script makes a web request to the application server to locate a potential duplicate product. The request is executed synchronously making both user and web browser wait for its completion.
The scripts analyzes the response and displays a confirmation if there is a duplicate product. The supplier name and unit price of the existing product are displayed next to the product name field. A call to the method preventDefault will not allow the Insert action to proceed.
The screenshot displays a JSON response to a request for a product by name as presented in Visual Studio 2012.