Geocoding is the process of capturing an address and converting it to exact latitude and longitude coordinates. Starting with release 8.5.11.0, apps generated with Code On Time now support automatic geocoding of address fields with the proper tags, as well as a Geocode() method available in C# or Visual Basic business rules.
Please make sure to follow Google Maps APIs Terms Of Service. Of note is section 10.5.d, which restricts long-term storage of Content.
Both methods below require addition of a Maps API Identifier. The following examples will use a modified version of the Employees table from the Northwind sample project. Use the following script to add the required columns before creating the project.
ALTER TABLE Employees
ADD Latitude decimal(9, 6) NULL,
Longitude decimal(9, 6) NULL
If using an existing project, make sure to refresh the application after executing the script. Then, open the model for Employees and check the checkbox next to the three new fields to include them in the Employees controller.
Geocoding with Tags
The easiest way to geocode a set of address fields is to tag the source and destination data fields in the view. If the correct fields are tagged, the values will be geocoded when the user saves a new record or updates an existing record. When updating an existing record, the geocode request will only be sent if at least one of the source fields has been modified, in order to avoid extraneous API requests.
Let’s add the relevant tags to start geocoding employees.
Start the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, double-click on “Employees / container1 / view1 (Employees, grid1) / createForm1 / c1 – New Employees / Address” data field node.
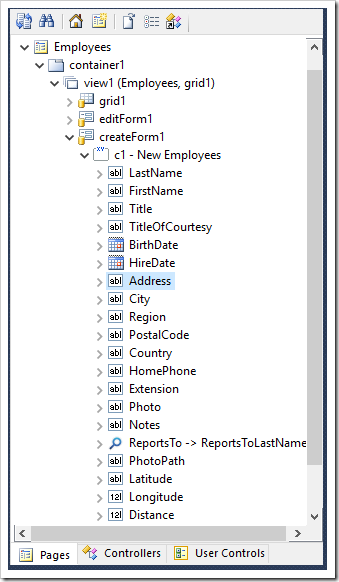
Make the following change:
| Property |
Value |
| Tags |
geocode-address |
Press OK to save the data field. Use the above procedure to make the changes below:
| Data Field |
Tag |
| City |
geocode-city |
| Region |
geocode-region |
| PostalCode |
geocode-zip |
| Country |
geocode-country |
| Latitude |
geocode-latitude |
| Longitude |
geocode-longitude |
On the toolbar, press Browse. When the application opens in the default browser, create a new employee.
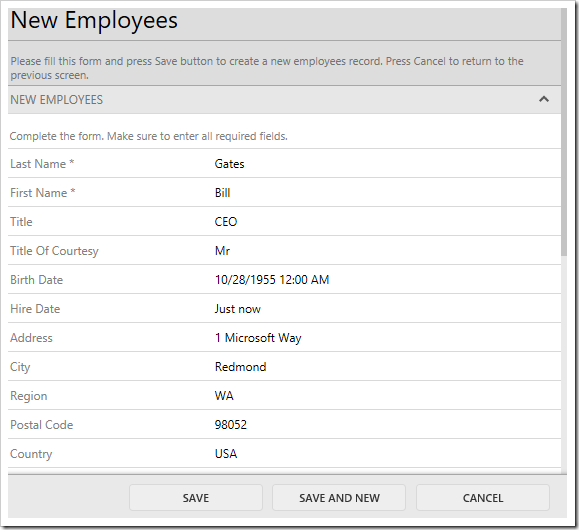
Upon pressing Save, the geocode request will be sent. If a result is returned, the new employee record will have updated Latitude and Longitude fields.
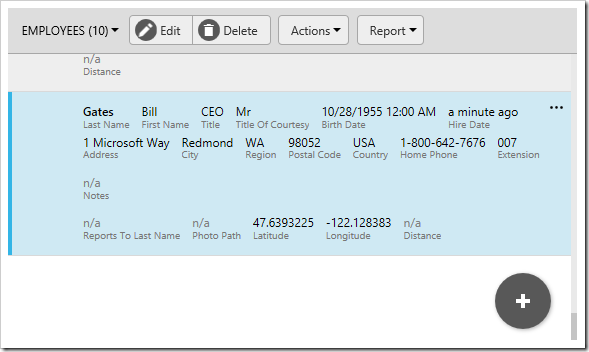
Geocoding in C#/Visual Basic Business Rules
The tag method explained in the previous section is convenient for automatic update of Latitude and Longitude fields. However, if the latitude and longitude need to be used in a calculation, the Geocode() business rule method can be used. Let’s add a business rule that utilizes this method to geocode the employee’s address and show an alert with the resulting latitude and longitude.
In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab. Right-click on “Employees / Actions / ag4 (ActionBar) – Edit/Delete” and press New Action.
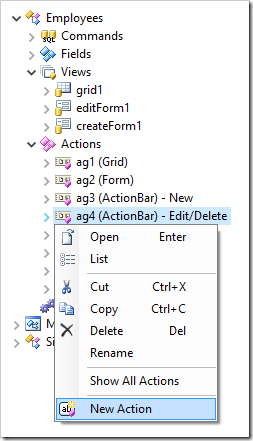
Specify the following properties and press OK to save the new action.
| Property |
Value |
| Command Name |
Custom |
| Command Argument |
ShowLatLong |
| Header Text |
Show Lat/Long |
| When Key Selected |
Yes |
Next, right-click on “Employees / Business Rules” node, and press New Business Rule.
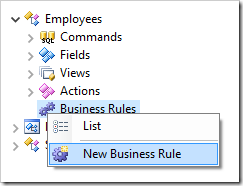
Configure the rule as following:
| Property |
Value |
| Type |
C# / Visual Basic |
| Command Name |
Custom |
| Command Argument |
ShowLatLong |
| Phase |
Execute |
Press OK to save the new business rule. Then, press Browse on the toolbar to generate the application, as well as create the relevant business rule file.
When complete, press “Edit Rule” on the action bar to open the file in Visual Studio.
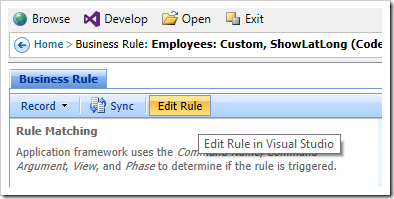
Replace the contents of the file with the following:
C#:
using MyCompany.Data;
using MyCompany.Models;
namespace MyCompany.Rules
{
public partial class EmployeesBusinessRules : MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
{
/// <summary>
/// This method will execute in any view for an action
/// with a command name that matches "Custom" and argument that matches "ShowLatLong".
/// </summary>
[Rule("r100")]
public void r100Implementation(EmployeesModel instance)
{
decimal latitude;
decimal longitude;
// join address parts with "," separator
string address = string.Join(",", instance.Address, instance.City,
instance.Region, instance.PostalCode, instance.Country);
if (Geocode(address, out latitude, out longitude))
{
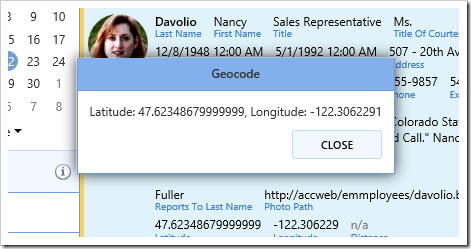
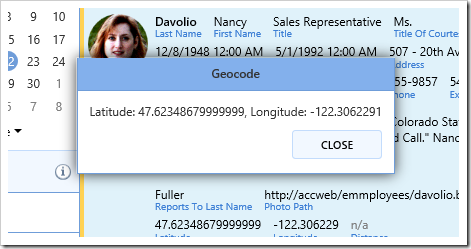
Result.ShowAlert("Latitude: " + latitude + ", Longitude: " + longitude);
}
else
{
Result.ShowAlert("Geocode failed to resolve address.");
}
}
}
}
Visual Basic:
Imports MyCompany.Data
Imports MyCompany.Models
Namespace MyCompany.Rules
Partial Public Class EmployeesBusinessRules
Inherits MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
''' <summary>
''' This method will execute in any view for an action
''' with a command name that matches "Custom" and argument that matches "ShowLatLong".
''' </summary>
<Rule("r100")> _
Public Sub r100Implementation(ByVal instance As EmployeesModel)
Dim latitude As Decimal
Dim longitude As Decimal
' join address parts with "," separator
Dim address = String.Join(",", instance.Address, instance.City,
instance.Region, instance.PostalCode, instance.Country)
If (Geocode(address, latitude, longitude)) Then
Result.ShowAlert("Latitude: " & latitude & ", Longitude: " & longitude)
Else
Result.ShowAlert("Geocode failed to resolve address.")
End If
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Switch back to the application running in your default browser, and navigate to the Employees page. Ctrl+click on a row to highlight the row. On the toolbar, press “Show Lat/Long”.
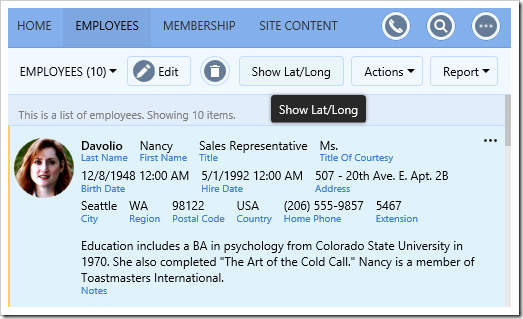
A message box will be displayed with the employee’s latitude and longitude.