Picklists are commonly used in web applications in order to allow a user to pick one item from a list of available options. These lists prevent duplication of similar values, such as alternate spellings. Picklists are physically different from database lookup fields since there is no foreign key relationship between the tables. The application generator automatically configures lookup fields. Developers can configure a picklist on any field in a web application.
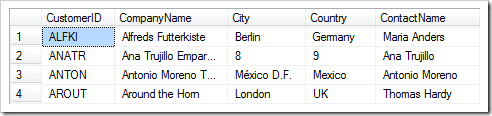
For example, let’s look at the City and Country fields in the Customers edit form. Both fields are simple text boxes – the user can type any value.
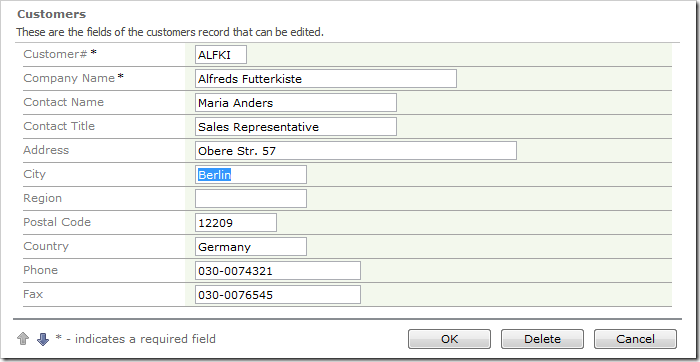
Let’s convert both fields to picklists.
Creating Cities and Countries Tables
Start SQL Server Management Studio. In the Object Explorer, right-click on Databases / Northwind / Tables node, and select New Table option.
Give this table the following columns:
| Column Name | Data Type | Allow Nulls |
| CountryID | int | No |
| CountryName | nvarchar(50) | No |
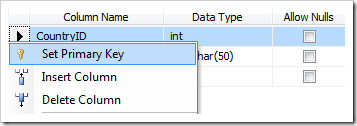
Right-click on the CountryID column, and select Make Primary ID.
Under Column Properties, change the following setting:
| Property | Value |
| (Is Identity) | Yes |
Press Ctrl+S to save the table. Give the table the name of “Countries”.
Create another table with the following columns:
| Column Name | Data Type | Allow Nulls |
| CityID | int | No |
| CityName | nvarchar(50) | No |
Right-click on the CityID column, and select Make Primary ID.
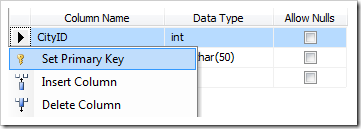
Under Column Properties, change the following setting:
| Property | Value |
| (Is Identity) | Yes |
Save the table, and give it the name of “Cities”.
Start Code On Time web application generator. Refresh, and add the two new tables to the web application.
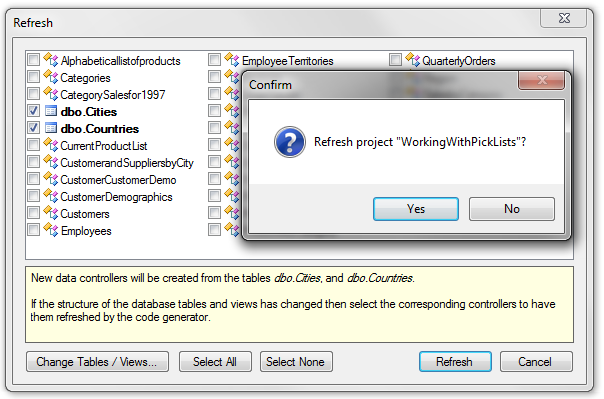
Finish generating the application.
Populate the Tables
Next, populate the Cities and Countries table using the values currently existing in the Customers table. A full list of values can be found by activating the dropdown on the column header and clicking the “Filter…” option.
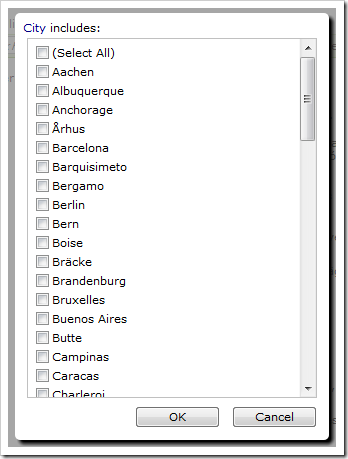
Insert all City values in the Cities table, and all Country values in the Countries table.
Converting Country and City fields into a Picklist
Start the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab. Double-click on Customers / Fields / City field node.
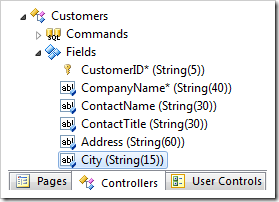
Change the following properties:
| Property | Value |
| Items Style | Lookup |
| Items Data Controller | Cities |
Press OK to save the field. Double-click on Customers / Fields / Country field node.
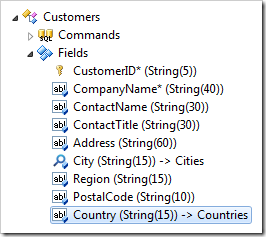
Make the following changes:
| Property | Value |
| Items Style | Lookup |
| Items Data Controller | Countries |
Press OK to save the field. On the toolbar, press Browse.
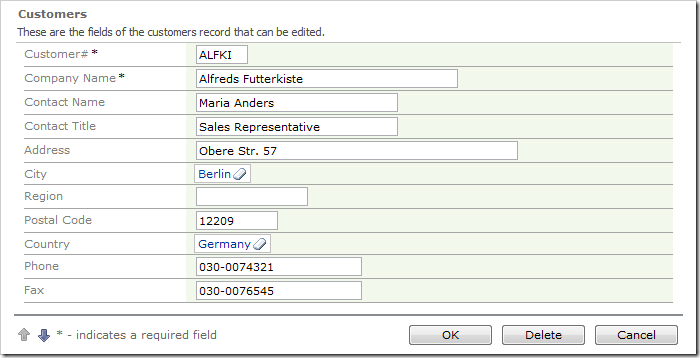
Navigate to the Customers page, and edit a record. The City and Country fields will be rendered as lookup links.
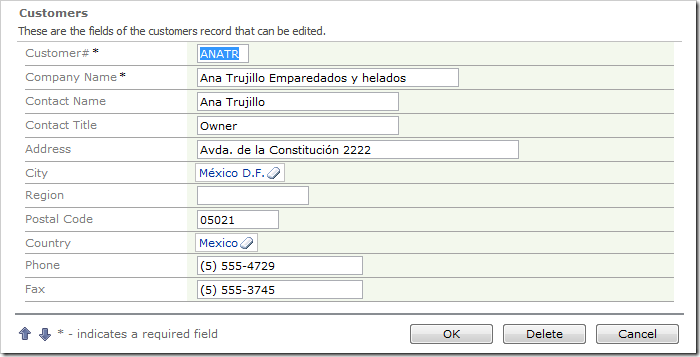
Click on the link for City field, and a lookup modal window will display a list of cities.
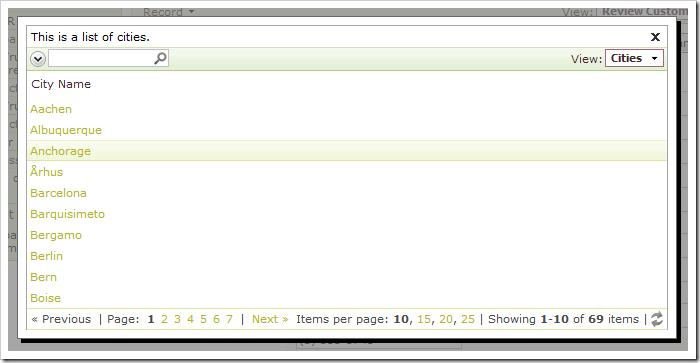
Select a lookup item from the list. Save the record, and select the record again. Instead of CityName being inserted into the field, the CityID was inserted.
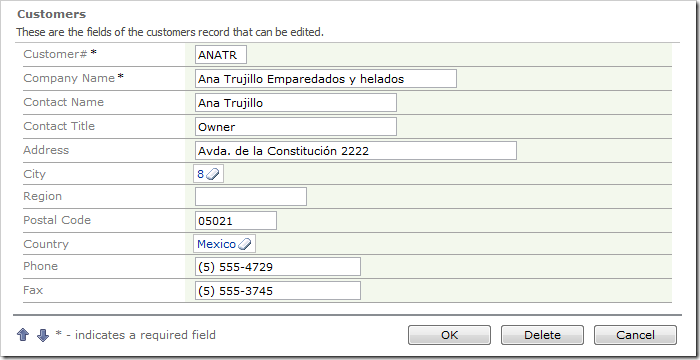
The same behavior occurs for Country lookup field.
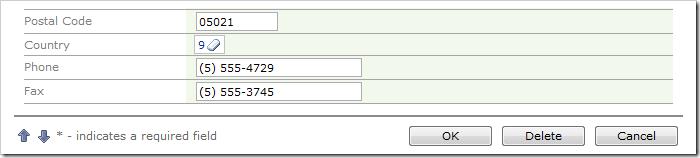
This is happening because the primary key of the lookup is automatically used as the value of the selected record.
You can address this in two different ways.
Changing the Primary Key of the Lookup Controller
Switch back to the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, right-click on Countries / Fields node, and select List option.
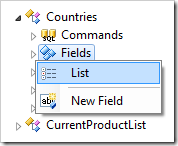
Change the field properties:
| Name | Is Primary Key |
| CountryID | No |
| CountryName | Yes |
You can repeat this procedure for Cities controller, or configure the lookup properties of the City field as explained next.
Specifying the Data Value Field and Data Text Field
In the Project Explorer, double-click on Customers / Fields / City field node.
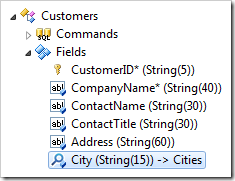
Make the following changes:
| Property | Value |
| Data Value Field | CityName |
| Data Text Field | CityName |
Press OK to save the field.
The client library always uses Data Value Field and Data Text Field to determine which lookup field represents the key of the selected item, and which field represents the text. When the Data Value Field is not specified, then the value of the primary key field of the selected lookup item will become a lookup value. When the Data Text Field is not specified, the text will be derived from the first visible column.
Trying it Out
On the toolbar, press Browse. Navigate to Customers page and edit a record. Change the City and Country fields, save, and select the record again. The names of City and Country will be the values inserted into the respective fields.
This can be confirmed by checking the record in SQL Server Management Studio.