Requirements
A minimal membership provider requires a dedicated table to keep track of user names and passwords.
This is a sample “Users” table with “identity” primary key.
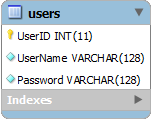
SQL:
create table Users (
UserID int not null AUTO_INCREMENT primary key,
UserName varchar(128) not null,
Password varchar(128) not null
);
Here is how the table may look if a “unique identifier” primary key is implemented. MySQL does not have built-in unique identifier capabilities, so the ID must be generated by a trigger.
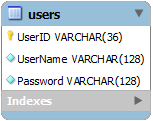
SQL:
create table Users (
UserID varchar(36) not null primary key default '',
UserName varchar(128) not null,
Password varchar(128) not null
);
delimiter $$
create trigger userinsert
before insert on Users
for each row
begin
set New.UserID = UUID();
end $$
User roles are hardcoded in the minimal Role Provider implementation.
Configuration
Create a table in your database using one of the scripts specified above.
Select the project name on the start page of the application generator and choose Settings.
Proceed to Authentication and Membership.
Select “Enable custom membership and role providers” option and enter the following configuration settings.
table Users=Users
column [int|uiid] UserID = UserId
column [text] UserName = UserName
column [text] Password = Password
role Administrators = admin
role Users = admin, user
role Everybody = *
The configuration maps logical table Users required for membership provider implementation to the physical database table Users. It also defines three user roles – Administrators, Users, and Everybody.
Generate the project.