Get started quickly with the tutorials we have prepared for you. Take a single Tasks table and develop a full-blown task management application with file upload, many-to-many fields, master-detail pages, and more.
Watch: Building a ToDo App 
Our product helps you turn your database schema into a modern application that works offline, online, and on-premises.
Here is a summary of what you will learn:
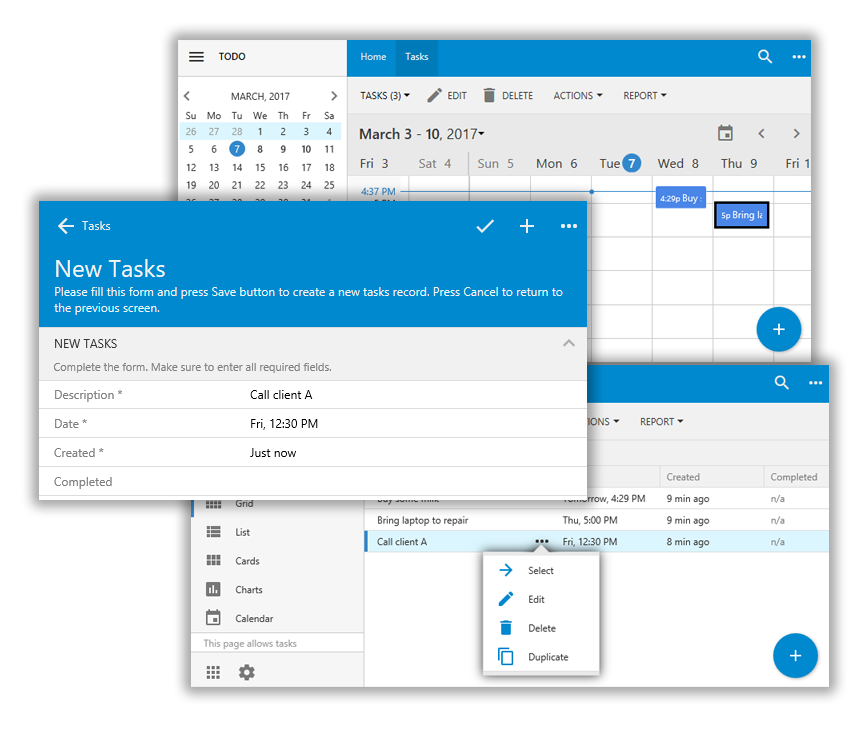
- We will begin by creating a database and add a "Tasks" table. We will then create the app and explore the features. Finally, we will add an icon to the Tasks forms using the Project Designer.
- To set up business rules, we will configure default values for the "Date" and "Created" fields. Then, we'll hide the "Created" field from the create form, and prevent the user from modifying the field for existing records. Finally, we will add a custom action that will mark tasks as completed. The "Completed" field will be hidden from the create form, and prevent editing in the edit form. Finally, we will create two views, "Active Tasks" and "All Tasks".
- To add a lookup, we will add the "Categories" table and add a foreign key to "Tasks" table, and update the Tasks model with the new foreign key. Then, we will explore the features of lookups in apps created with Code On Time.
- We will now add maps by creating a "Locations" table in the database and creating the model. A location lookup will be added to tasks. We will then add some locations, and assign these locations to tasks using the map.
- In order to add master-detail relationships, we will create the "Attachments" table, create a model, and add a data view field on the Tasks form. We will then upload several files to a task.
- Now we would like to restrict user access to data. The fields "Creator" and "Owner" will be added to the Tasks table. The corresponding model will be updated to include those fields. Users and Roles will be added to the app using ASP.NET Membership. The two fields will be marked as "User Name" lookups. Business rules will be added to set the current user as the creator and owner by default. Filters will be added to ensure that users can only see tasks created by or owned by them.
- We will need to add some calculated fields. First, we will add the Expenses table and link it to tasks. We will add "Total Price" calculated field. Expenses data view field will be added on the Tasks form. We will add business rules to calculate the Total Price field, and display some aggregates on the Tasks form.
- Then, we will need to add many-to-many fields. First, we will add "Tags" and "TaskTags" tables and models. Then, we will add a "Tags" field into the tasks form. This field will first be configured as a checkbox list. We will add several records in-line. Then, we will convert the field to a basket style drop down list. Finally, we will remove the now redundant Categories table.
- Adding a status bar will help the user. First, we will add a static lookup field "Status" to the "Tasks" table. Then, we will change the business rules to automatically modify the "Status" value. Finally, we will enter a status bar definition for each value of the Status field to visually communicate the state of tasks to the users.
- Customize forms to enhance the workflow of your users. Learn rapid development of responsive forms that work on any device with any screen size. Master the form design with field flow, tabs, multi-column categories, and custom layouts. Start by changing a flow of fields after a brief introduction of responsive forms. Group in categories, configure categories to display as tabs. Configure a modal popup. Try your hand with custom form layouts.
- Organize navigation between the single page apps of your universal business application with Quick Launch icons and menu. Drag and drop pages in the navigation hierarchy, set a few icons to populate the Quick Launch bar, and move the menu from the toolbar to the sidebar.
- Set up a cloud to deploy the app. Our app is ready for production. Learn how to set up Microsoft Azure Cloud for publishing from the app generator. This episode explains how to sign up for an account and provides step-by-step instruction for Azure Active Directory configuration.
- Add a database to your cloud. An application deployed to Microsoft Azure is typically configured as Web App. The deployment infrastructure of Web App includes an Internet-facing App Service and Database Server. In this episode we will set up a database server and transfer development database schema to the cloud database.
- Learn to deploy your app as an "app service" to service both web and mobile users. App Service is an Internet facing server that reads and writes data by making SQL queries to the database engine in the cloud. We will set up our app service in the "Standard" tier with SSL, multiple deployment slots, and on-demand performance with auto scaling.
- Learn the staging-production pipeline to enhance your productivity. Deploy changed app to Staging slot for a live preview. Instantly swap Staging and Production versions of application directly from the app generator.
- Learn to store binary data outside of the database. Large photos and documents can run up the database size quickly. Such objects known as BLOBs (Large Binary Objects) are frequently stored in the external file system or attached storage. We will show you how to set up external storage of attachments in the file system and Microsoft Azure.
Don't hesitate. Jump right in!