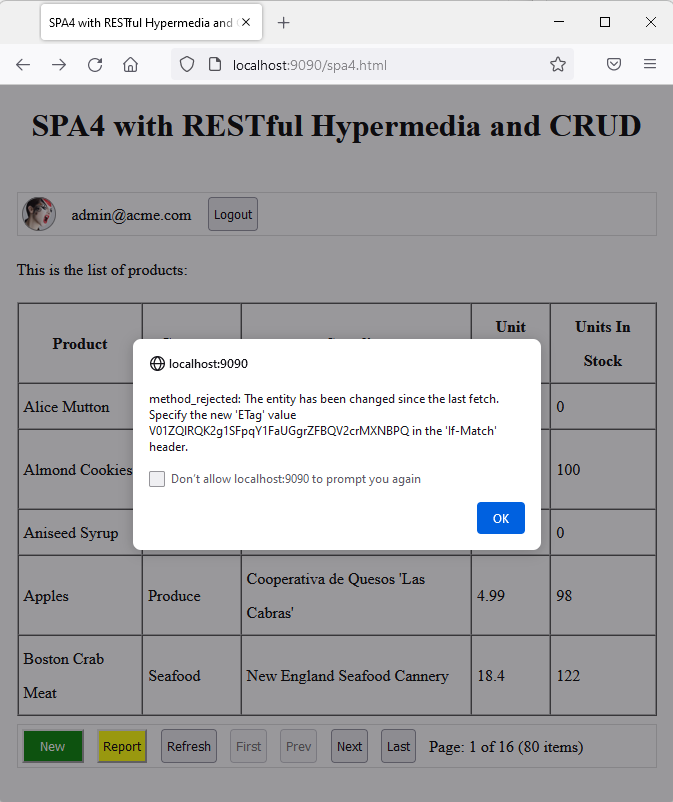
RESTful API Engine responses are provided with the ETag header. Browsers automatically submit ETag with the subsequent requests to fetch the same resource. The engine responds with the HTTP status 304 and empty body if the ETag of the resource has not changed. Apps can also submit ETag with CRUD requests for conflict detection.
Detect the data editing conflicts and build high performance applications by taking advantage of the HTTP protocol.
The ETag of the resource specified in the If-Match header of the PATCH request allows detecting the data editing conflicts.
The items of the Supplier Company Name and CategoryName lookups are fetched from the RESTful Application with GET requests. The physical data transfer happens one time only for each lookup for each subsequent opening of the Edit Product form.
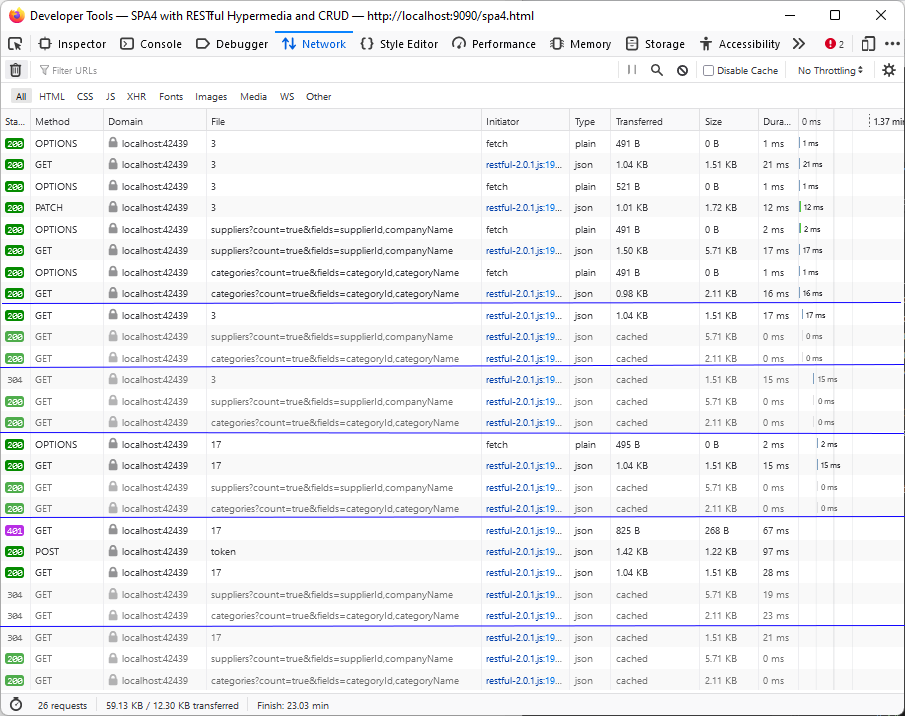
The RESTful Application responds to the lookup requests with the HTTP status code 304. It tells the client that the ETag of the corresponding resource is unchanged and the previously fetched copy of the response can be used instead.
This tutorial is part of the RESTful Workshop designed to empower individual developers and teams to create amazing enterprise-quality backends for mobile and web applications. Zero experience and no code is required to provide your data with the REST API conforming to the Level 3 of Richardson Maturity Model with the built-in OAuth 2.0 and Open ID Connect.