Requirements
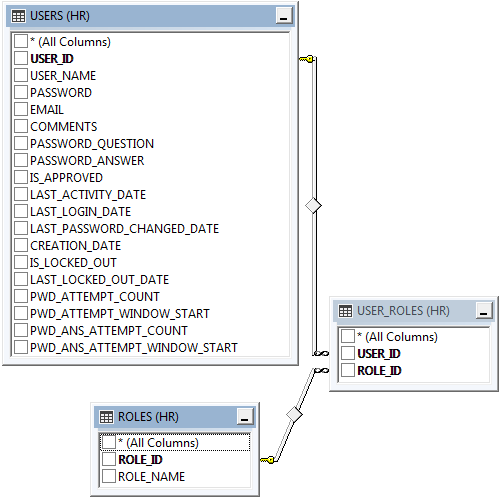
An advanced membership and role provider requires three tables.
One table keeps track of user information. This information includes the user_name, email, and comments. Additional columns allow for implementation of a password question and answer in order to recover a forgotten password. When users are created, they can not be approved by default. Additional information is captured about the most recent login, activity, and change of password. When a user inputs an incorrect password past the limit, the user will become locked out. The number of failed attempts and most recent failed attempt will be stored.
Two tables are required to keep track of roles and associations of users with roles.
These are the advanced membership and role provider tables with “identity” primary keys.
SQL:
create sequence users_seq;
create table users
(
user_id int not null primary key,
user_name varchar2(128) not null,
password varchar2(128) not null,
email varchar2(128),
comments nclob,
password_question varchar2(256),
password_answer varchar2(128),
is_approved number(1,0) check (is_approved in (1,0)) not null,
last_activity_date date not null,
last_login_date date not null,
last_password_changed_date date not null,
creation_date date not null,
is_locked_out number(1,0) check(is_locked_out in (1,0)) not null,
last_locked_out_date date not null,
pwd_attempt_count int not null,
pwd_attempt_window_start date not null,
pwd_ans_attempt_count int not null,
pwd_ans_attempt_window_start date not null
);
create or replace trigger users_trigger
before insert
on users
for each row
declare
u_id users.user_id%type;
begin
select users_id_seq.nextval into u_id from dual;
:new.user_id := u_id;
end users_trigger;
/
create sequence roles_seq;
create table roles
(
role_id int not null primary key,
role_name varchar2(50)
);
create or replace trigger roles_trigger
before insert
on roles
for each row
declare
r_id roles.role_id%type;
begin
select roles_seq.nextval into r_id from dual;
:new.role_id := r_id;
end roles_trigger;
/
create table user_roles
(
user_id int not null,
role_id int not null,
constraint pk_user_roles primary key(user_id, role_id),
constraint fk_users foreign key(user_id) references users(user_id),
constraint fk_roles foreign key(role_id) references roles(role_id)
);
These are the advanced membership and role provider tables with “unique identifier” primary keys.
SQL:
create table users(
user_id raw(16) default sys_guid() not null primary key,
user_name varchar2(128) not null,
password varchar2(128) not null,
email varchar2(128),
comments nclob,
password_question varchar2(256),
password_answer varchar2(128),
is_approved number(1,0) default 1 check (is_approved in (1,0)) not null,
last_activity_date timestamp not null,
last_login_date timestamp not null,
last_password_changed_date timestamp not null,
creation_date timestamp not null,
is_locked_out number(1,0) default 1 check(is_locked_out in (1,0)) not null,
last_locked_out_date timestamp not null,
pwd_attempt_count int not null,
pwd_attempt_window_start timestamp not null,
pwd_ans_attempt_count int not null,
pwd_ans_attempt_window_start timestamp not null
);
create table roles
(
role_id raw(16) default sys_guid() not null primary key,
role_name varchar2(50)
);
create table user_roles
(
user_id raw(16) not null,
role_id raw(16) not null,
constraint pk_user_roles primary key(user_id, role_id),
constraint fk_users foreign key(user_id) references users(user_id),
constraint fk_roles foreign key(role_id) references roles(role_id)
);
Configuration
Use one of the scripts above to create the membership and role provider tables in your database.
Start Code On Time web application generator, select the project name on the start page, and choose Settings. Select Authentication and Membership.
Select “Enable custom membership and role providers” option and enter the following configuration settings.
table Users = users
column [int|uiid] UserID = user_id
column [text] UserName = user_name
column [text] Password = password
column [text] Email = email
column [text] Comment = comments
column [text] PasswordQuestion = password_question
column [text] PasswordAnswer = password_answer
column [bool] IsApproved = is_approved
column [date] LastActivityDate = last_activity_date
column [date] LastLoginDate = last_login_date
column [date] LastPasswordChangedDate = last_password_changed_date
column [date] CreationDate = creation_date
column [bool] IsLockedOut = is_locked_out
column [date] LastLockedOutDate = last_locked_out_date
column [int] FailedPasswordAttemptCount = pwd_attempt_count
column [date] FailedPasswordAttemptWindowStart = pwd_attempt_window_start
column [int] FailedPasswordAnswerAttemptCount = pwd_ans_attempt_count
column [date] FailedPasswordAnswerAttemptWindowStart = pwd_ans_attempt_window_start
table Roles = roles
column [int|uiid] RoleID = role_id
column [text] RoleName = role_name
table UserRoles = user_roles
column [int|uiid] UserID = user_id
column [int|uiid] RoleID = role_id
The configuration will guide the code generator in mapping the logical tables Users, Roles, and UserRoles to the physical tables in the database.
Generate the project to create the custom membership and role provider.