One quick way of getting your app deployed online is to set up a Windows Azure Virtual Machine (VM). These VMs offer the benefit of a full-fledged Windows Server machine without the hassle of dealing with electricity and cooling costs, storing a computer on-premise, or dealing with network configuration. They also offer the additional benefits of a very fast internet connection and easy scalability.
Getting a new Azure Virtual Machine
Let’s set up a new Azure VM for a Northwind web app created with Code On Time generator.
Navigate to http://azure.com and click on Portal in the top right corner of the screen. Enter your credentials and log in.
In the bottom left corner of the page, press New. Select Compute | Virtual Machine | Quick Create. Enter the DNS name and select the server image from the dropdown. Make sure to select the correct size as needed, as pricing is different for each one. Finally, enter the administrator credentials and select Create a Virtual Machine.
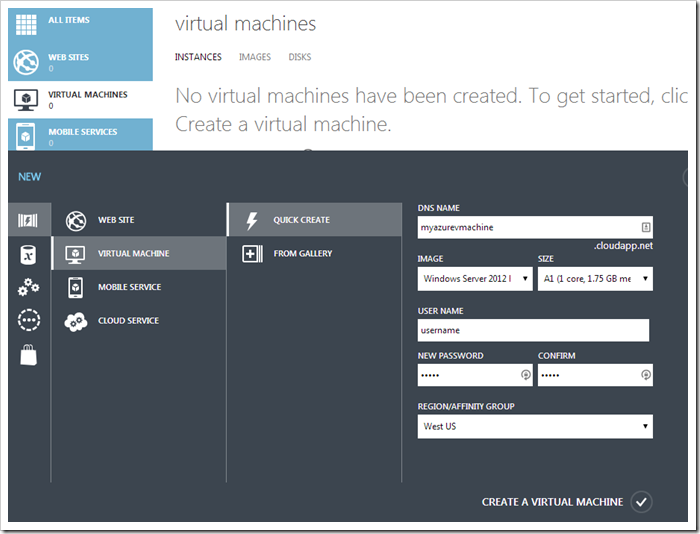
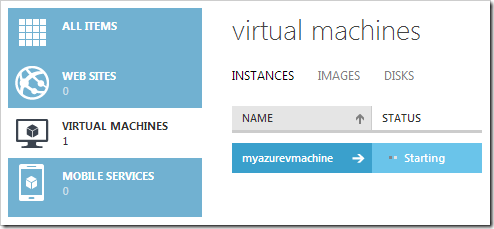
The virtual machine will be created in a few minutes. You can watch progress by clicking on the Virtual Machines section of the site.
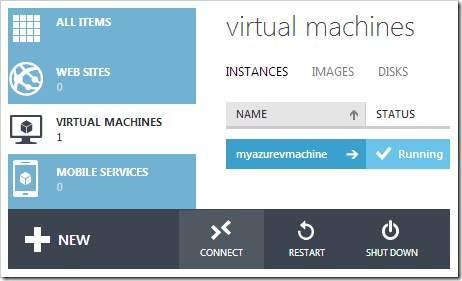
Once the virtual machine is online, click on the VM in the list, and select CONNECT on the bottom action bar.
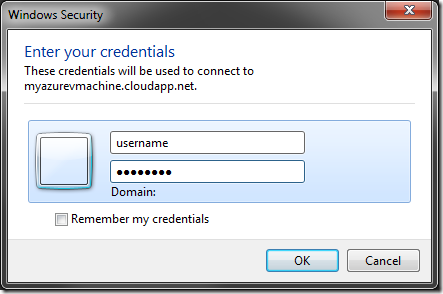
Confirm to save the downloaded *.rdp file, and open the file to start connecting to your VM using Remote Desktop Connection. Enter the previously specified username and password, and press OK.
Confirm that you want to connect to a computer without a certificate, and you will be connected.
Enabling HTTP Traffic to the Azure VM
In order for your application to be visible on the internet, you must enable HTTP traffic.
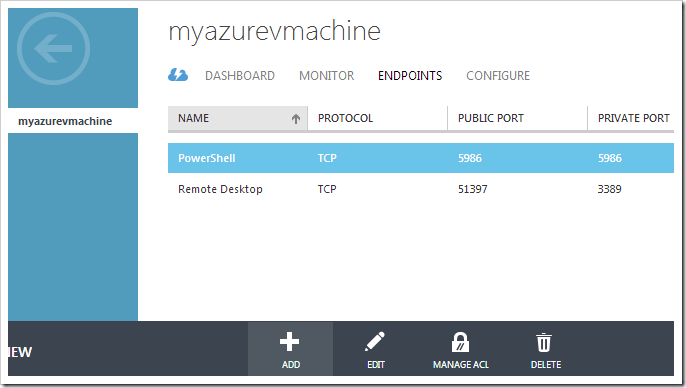
Switch back to the Microsoft Azure Portal. Click on the name of the virtual machine to access the properties. At the top of the page, click on ENDPOINTS tab. On the bottom action bar, press ADD.
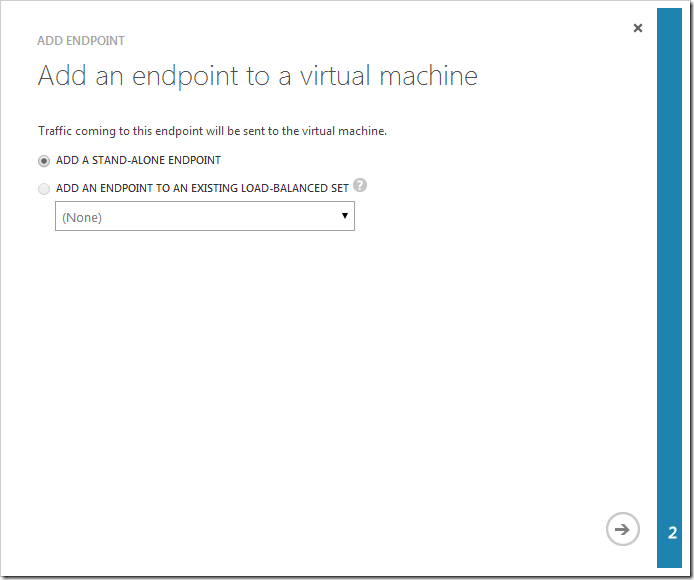
Select “ADD A STAND-ALONE ENDPOINT” and press the right arrow.
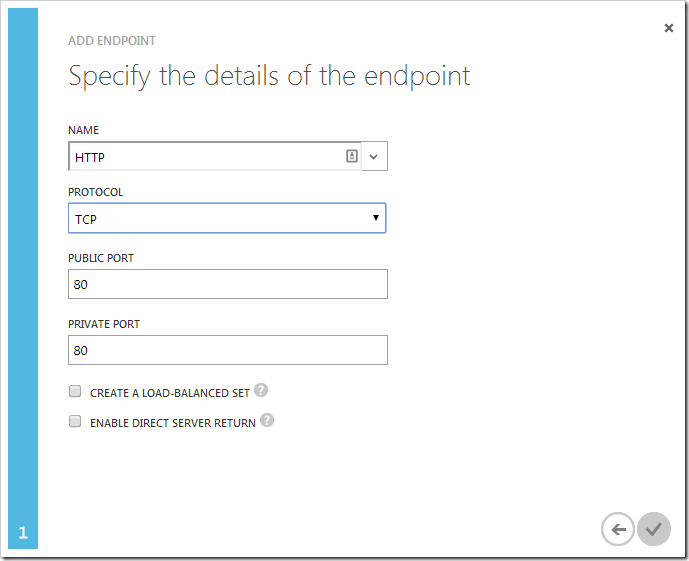
Click on the dropdown in the NAME field and select “HTTP”. Then, press the checkmark to save the endpoint.
You can now deploy your web app to this server.